Final ID: 039
Circulating Metabolomic Biomarkers of 5-Year Unintentional Weight Loss in a Biracial Community-Dwelling Older Cohort
Abstract Body: Objective Unintentional weight loss in older populations is linked to greater mortality and morbidity risks than weight stability and intentional weight loss. We aimed to understand the metabolic mechanisms of unintentional weight loss and their relationship with body composition changes in older adults.
Methods We investigated plasma metabolite associations with weight and body composition changes over 5 years in 1335 participants from the Health, Aging and Body Composition (Health ABC) study. Using multinomial logistic regressions, we assessed the associations of 442 LC-MS measured metabolites with unintentional weight loss >5%, intentional weight loss >5%, weight gain >5%, and fluctuating weight (weight change <5% and coefficient of variation >3%) relative to weight stability. Percent attenuation by DXA and CT body composition changes was examined in metabolite-unintentional weight loss associations.
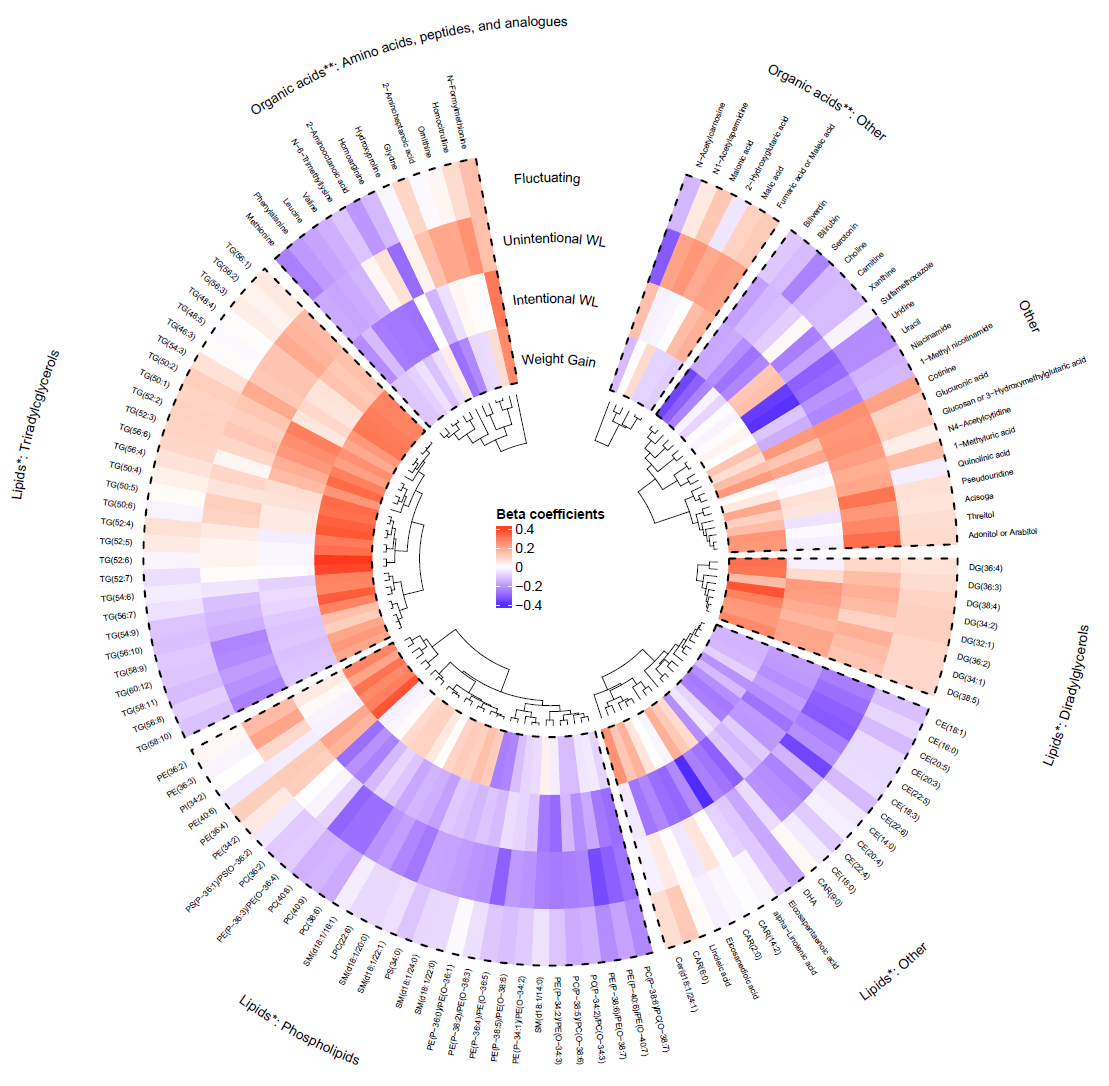
Results Among 1,335 older adults (mean age 73.4 years, 51% women, 33% Black), 12% experienced unintentional weight loss. Metabolite associations with unintentional weight loss differed from other weight change patterns. Lower levels of essential amino acids, phospholipids, long-chain polyunsaturated triglycerides, cholesterol esters, and uridine were associated with higher odds of unintentional, but not intentional, weight loss after adjusting for age, sex, race, and BMI (Fig 1). Fat mass and muscle mass changes each attenuated the associations between many metabolites, mainly phospholipids and essential amino acids, and unintentional weight loss by >20%. Fat changes further attenuated 9 muscle change-adjusted metabolite associations by >50%.
Conclusion Lipids and amino acids related to energy and protein balance were associated with unintentional weight loss in older adults. Fat and muscle mass changes partially attenuated these associations, suggesting connections of these metabolic pathways with muscle, and particularly adiposity dynamics.
Methods We investigated plasma metabolite associations with weight and body composition changes over 5 years in 1335 participants from the Health, Aging and Body Composition (Health ABC) study. Using multinomial logistic regressions, we assessed the associations of 442 LC-MS measured metabolites with unintentional weight loss >5%, intentional weight loss >5%, weight gain >5%, and fluctuating weight (weight change <5% and coefficient of variation >3%) relative to weight stability. Percent attenuation by DXA and CT body composition changes was examined in metabolite-unintentional weight loss associations.
Results Among 1,335 older adults (mean age 73.4 years, 51% women, 33% Black), 12% experienced unintentional weight loss. Metabolite associations with unintentional weight loss differed from other weight change patterns. Lower levels of essential amino acids, phospholipids, long-chain polyunsaturated triglycerides, cholesterol esters, and uridine were associated with higher odds of unintentional, but not intentional, weight loss after adjusting for age, sex, race, and BMI (Fig 1). Fat mass and muscle mass changes each attenuated the associations between many metabolites, mainly phospholipids and essential amino acids, and unintentional weight loss by >20%. Fat changes further attenuated 9 muscle change-adjusted metabolite associations by >50%.
Conclusion Lipids and amino acids related to energy and protein balance were associated with unintentional weight loss in older adults. Fat and muscle mass changes partially attenuated these associations, suggesting connections of these metabolic pathways with muscle, and particularly adiposity dynamics.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Cellular Mechanism Mediating Lipomatous Metaplasia In the Infarcted Heart.
Tuleta Izabela, Frangogiannis Nikolaos, Venugopal Harikrishnan, Huang Shuaibo, Humeres Claudio, Hernandez Velasco Silvia, Hanna Anis, Kubota Akihiko, O'leary Kevin, Zheng Deyou
A functional survey of postnatal heart maturation with in vivo Perturb-seq in spatial and temporal resolutionWang Haofei, Liu Jiandong, Dong Yanhan, Shi Huitong, Colon Marazzano, Liu Xingyan, Farber Gregory, Qian Yunzhe, Anthony Nicholas, Qian Li