Final ID: MDP358
Ectopic Fat Distribution and Adverse Muscle Composition in South Asians: Findings from the UK Biobank
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: South Asians (SAs) have higher risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease compared with other ethnicities; however, detailed analyses of their body composition profile (BCP), including ectopic fat, muscle mass and muscle quality are lacking. Such data may help explain the higher rate of type 2 diabetes (T2D) in SAs, as muscle mass and quality are increasingly recognized as being linked to long-term health outcomes.
Aims: This study utilizes imaging data from the UK Biobank cohort to compare body composition between SAs and white Europeans (EUR) to better understand ethnic differences in fat distribution and muscle composition.
Hypothesis: We predict that SAs will have higher levels of ectopic fat (visceral-, liver-, and muscle fat) than matched EUR, which may explain their higher rates of T2D.
Methods: Using UK Biobank imaging data captured by MRI, we compared body composition data in SAs (n=323) without T2D relative to age, sex, height and weight-matched EUR (matched 5:1 to SA group). We also compared BCP in 66 SAs with T2D versus matched EUR (matched 3:1 to SA group).
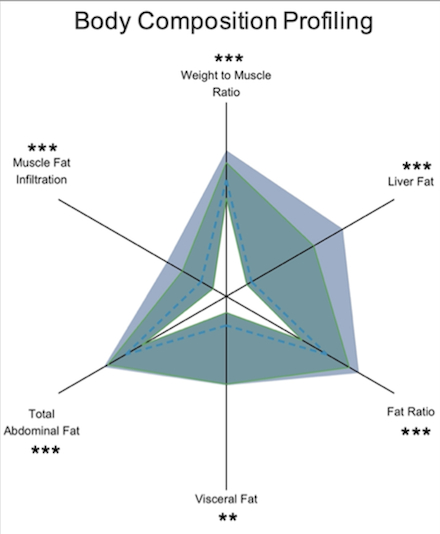
Results: SAs without T2D had higher overall levels of body fat compared to EUR (mean difference in: visceral adipose tissue 0.20 L; abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue 0.93 L; liver fat 0.92 percentage points (pp); muscle fat infiltration (MFI) 0.59 pp, all p75th percentile and muscle volume <25th percentile) was more prevalent in SAs (19.9% vs 7.9%, p<0.001). Differences remained significant after further adjustment for prevalent disease, lifestyle and socioeconomic factors. SAs with T2D had similar BCP compared with matched EUR with T2D.
Conclusions: SAs without T2D have greater visceral, liver, and muscle fat accumulation, and lower muscle volume compared to EUR. These findings may underlie their greater risk for T2D and atherothrombotic outcomes, especially as BCP was similar when comparing SAs with T2D to matched EUR with T2D. Lifestyle modification to increase physical activity and reduce weight gain may offset cardiometabolic risks in SAs through favorable changes in body composition.
Aims: This study utilizes imaging data from the UK Biobank cohort to compare body composition between SAs and white Europeans (EUR) to better understand ethnic differences in fat distribution and muscle composition.
Hypothesis: We predict that SAs will have higher levels of ectopic fat (visceral-, liver-, and muscle fat) than matched EUR, which may explain their higher rates of T2D.
Methods: Using UK Biobank imaging data captured by MRI, we compared body composition data in SAs (n=323) without T2D relative to age, sex, height and weight-matched EUR (matched 5:1 to SA group). We also compared BCP in 66 SAs with T2D versus matched EUR (matched 3:1 to SA group).
Results: SAs without T2D had higher overall levels of body fat compared to EUR (mean difference in: visceral adipose tissue 0.20 L; abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue 0.93 L; liver fat 0.92 percentage points (pp); muscle fat infiltration (MFI) 0.59 pp, all p75th percentile and muscle volume <25th percentile) was more prevalent in SAs (19.9% vs 7.9%, p<0.001). Differences remained significant after further adjustment for prevalent disease, lifestyle and socioeconomic factors. SAs with T2D had similar BCP compared with matched EUR with T2D.
Conclusions: SAs without T2D have greater visceral, liver, and muscle fat accumulation, and lower muscle volume compared to EUR. These findings may underlie their greater risk for T2D and atherothrombotic outcomes, especially as BCP was similar when comparing SAs with T2D to matched EUR with T2D. Lifestyle modification to increase physical activity and reduce weight gain may offset cardiometabolic risks in SAs through favorable changes in body composition.
More abstracts on this topic:
A cerebrovascular longitudinal atlas: different rates of morphological change in aneurysm patients associated with hypertension and diabetes
Chien Aichi, Salamon Noriko, Vinuela Fernando, Szeder Viktor, Colby Geoffrey, Jahan Reza, Boyle Noel, Villablanca Juan, Duckwiler Gary
Adiposomal microRNAs Mediate Vascular Dysfunction in Obesity-Associated Type 2 DiabetesMirza Imaduddin, Morsy Mohammed, Levitan Irena, Raj Usha, Mahmoud Abeer