Final ID: Tu031
Immunosuppression Drug Modulation of Endothelial Cell Function
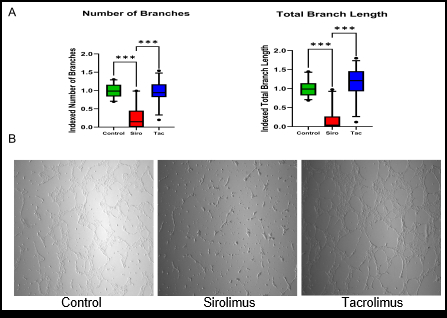
Abstract Body: Heart transplantation is a life-saving therapy for patients with end-stage heart failure with over 4,000 transplants occurring per year. The use of immunosuppression drugs is necessary in post transplantation to prevent graft rejection. Proliferation signal inhibitors have previously been shown to effectively reduce the incidence of cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) compared to calcineurin inhibitors but the differential mechanisms that drive this benefit and differences in vascular profile of immunosuppression drugs remain incompletely understood. In this study, we examined the direct effect of immunosuppressive agents on endothelial function to define cellular mechanisms that may contribute to differential vascular phenotypes. We used endothelial cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and treated them with calcineurin inhibitor (tacrolimus), mTOR inhibitor (sirolimus), or vehicle for 5 days with daily media changes. We examined endothelial function using scratch wound assay, tube formation assay, and LDL uptake. We also examined metabolic changes using Seahorse assay owing to metabolic changes induced by immunosuppression drugs in other organs. Our results indicate mTOR inhibitor (sirolimus) resulted in a reduction in endothelial cell proliferation and migration using the scratch wound assay and tube formation assay compared to vehicle or calcineurin inhibitor (tacrolimus)-treated cells. Sirolimus also reduced LDL uptake in iPSC-derived endothelial cells compared to vehicle or tacrolimus-treated cells. Tacrolimus was associated with a trend towards altered endothelial energetics. Tacrolimus and sirolimus exert differential endothelial cell functional profiles that do not fully explain the clinical outcomes observed suggesting a need to explore the drug endothelial profiles in the context of vascular injury and inflammation.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Right Coronary Artery Chronic Total Occlusion in a Transplanted Heart: To Stent or Not to Stent?
Krayem Hussein, Cooke Richard, Abouzaki Nayef, Kutkut Issa
A Heart Transplant Patient’s Mysterious Illness: A Diagnostic OdysseyAlkalbani Mutaz, Nayer Hassan, Cochrane Adam, Saeed Ibrahim, Psotka Mitchell, Rollins Allman, Kennedy Jamie, Blumer Vanessa