Final ID: Tu059
Single-Nucleus Transcriptomics Demonstrates Endothelial Cell Expansion in Failing Human Right Ventricles
Abstract Body: Background: Right ventricular failure (RVF) is most commonly observed as a sequela of left ventricular failure (LVF)—for which it more than doubles the risk of mortality. Moreover, isolated RVF is the most common cause of death in pulmonary hypertension and is a leading cause of major adverse events in systemic right ventricle congenital heart diseases. Therapies which effectively treat LVF show poor efficacy for RVF. For example, beta blockade, a cornerstone of LVF therapy, has no efficacy in RVF. Therefore, there is a need for broader exploratory research to identify pathways which are dysregulated in RVF and which could serve as targets for future therapies.
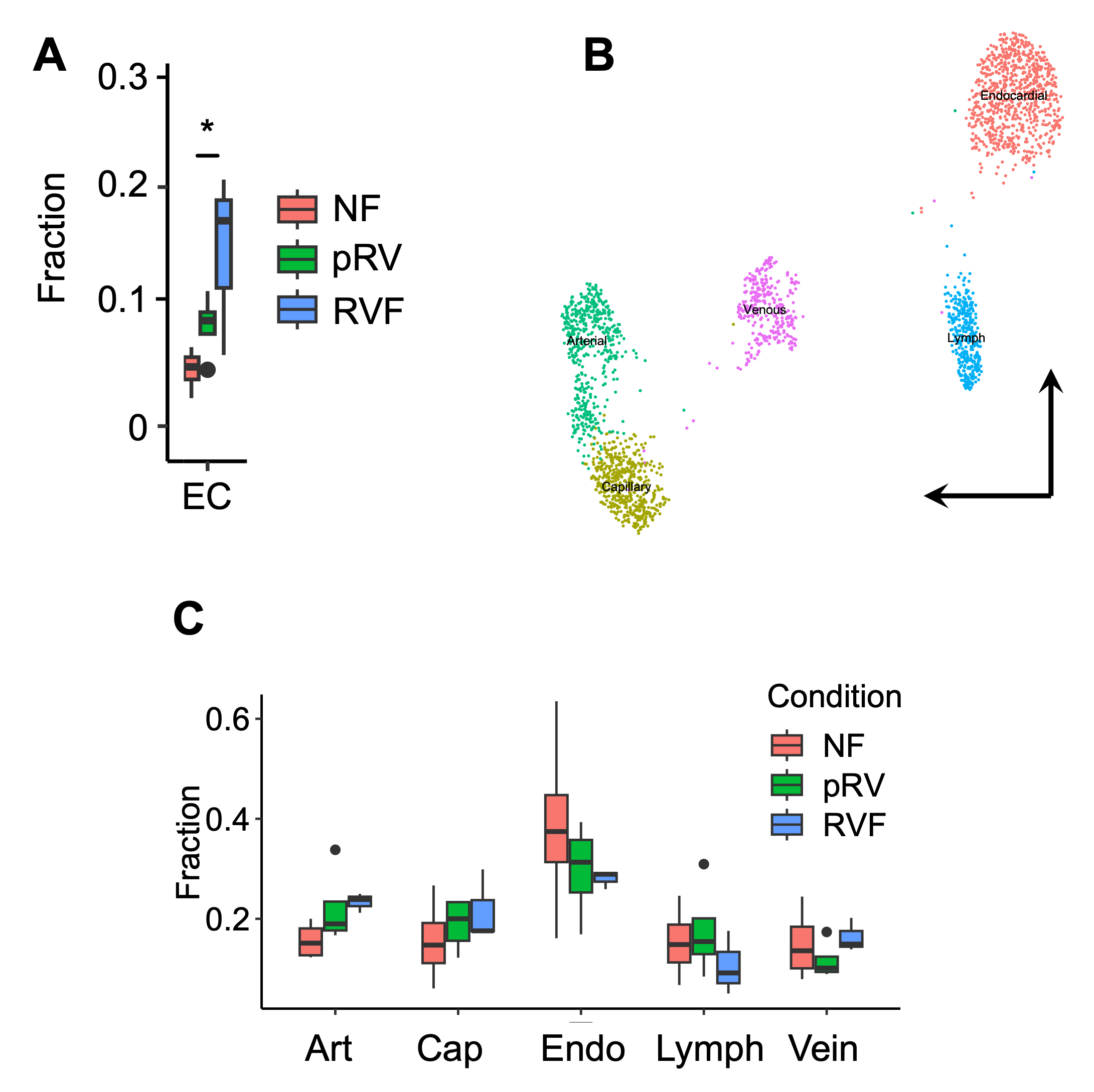
Methods/Results: To this end, we performed single-nucleus RNA sequencing (N=11) on RV myocardium from nonfailing or dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) hearts subgrouped by preserved systolic and diastolic RV function (pRV) or RVF. After cell-type assignment and differential expression analysis, we find a progressive upregulation of pro-angiogenic signaling in vascular endothelial cells (ECs) from nonfailing to pRV and RVF. There is a concomitant expansion of the EC pool from nonfailing to pRV and RVF (EC percentage 5%, 9%,15% for NF, pRV, and RVF; p < 0.05 for one-way ANOVA). We find increased HIF-mediated and VEGF-mediated signaling in these ECs, which may be mediating this expansion. Surprisingly, there is also increased expression of genes regulated by type 1 interferon signaling, which is thought to be anti-angiogenic.
Discussion: In summary, we have conducted a single-nuclei transcriptomic study of human RVF and found evidence for increased angiogenic signaling and EC expansion. These findings are significant, as the balance of pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors in RVF is still unclear, with studies in animal models showing conflicting results in terms of changes in macro/microvasculature in RVF. Here, we provide evidence that in human RVF the balance tends to lead toward a pro-angiogenic phenotype, even in dysfunctional RVs. Orthogonal studies to validate the causal nature of these observed changes in pathogenesis of RVF are currently ongoing.
Methods/Results: To this end, we performed single-nucleus RNA sequencing (N=11) on RV myocardium from nonfailing or dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) hearts subgrouped by preserved systolic and diastolic RV function (pRV) or RVF. After cell-type assignment and differential expression analysis, we find a progressive upregulation of pro-angiogenic signaling in vascular endothelial cells (ECs) from nonfailing to pRV and RVF. There is a concomitant expansion of the EC pool from nonfailing to pRV and RVF (EC percentage 5%, 9%,15% for NF, pRV, and RVF; p < 0.05 for one-way ANOVA). We find increased HIF-mediated and VEGF-mediated signaling in these ECs, which may be mediating this expansion. Surprisingly, there is also increased expression of genes regulated by type 1 interferon signaling, which is thought to be anti-angiogenic.
Discussion: In summary, we have conducted a single-nuclei transcriptomic study of human RVF and found evidence for increased angiogenic signaling and EC expansion. These findings are significant, as the balance of pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors in RVF is still unclear, with studies in animal models showing conflicting results in terms of changes in macro/microvasculature in RVF. Here, we provide evidence that in human RVF the balance tends to lead toward a pro-angiogenic phenotype, even in dysfunctional RVs. Orthogonal studies to validate the causal nature of these observed changes in pathogenesis of RVF are currently ongoing.
More abstracts on this topic:
A DHX38 Spliceosomal Mutation Impairs MYC Signaling, Cardiac Transcriptome Splicing, and Leads to Diastolic Dysfunction
Iwanski Jessika, Sarvagalla Sailu, Methawasin Mei, Van Den Berg Marloes, Churko Jared
Aggressive Lipid Lowering Differentially Impacts the Vascular Endothelium in Diabetic vs Healthy Individuals. Findings from the American Heart Association Cardiometabolic Health Strategically Focused Research NetworkGarshick Michael, Drenkova Kamelia, Schlamp Maria Florencia, Giannarelli Chiara, Fisher Edward, Goldberg Ira, Berger Jeffrey, Boothman Isabelle, Barrett Tessa, Jindal Manila, Newman Jonathan, Fadzan Maja, Bredefeld Cindy, Levy Natalie, Akinlonu Adedoyin