Final ID: Tu106
Cardiomyocyte knockout of Ceramide Synthase 5 protects against metabolic cardiomyopathy and obesity in mice
Abstract Body: Introduction: The prevalence of metabolic cardiomyopathy in the absence of hypertension is on the rise. Ceramide Synthase 5 (CerS5) has been implicated in the pathophysiology of this cardiomyopathy.
Hypothesis: Depletion of cardiomyocyte CerS5 protects against metabolic cardiomyopathy.
Methods: Inducible cardiomyocyte-specific CerS5 knockout (CerS5 cKO) mice were generated and placed on a milk-fat diet (HFD) or control diet (CD) for 18 weeks along with control (Myh6-MCM) mice (n=6-11/group). Diet-induced metabolic syndrome was monitored through weekly weight measurements, glucose and insulin tolerance tests, and blood plasma collection for Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR). Echocardiography and systemic blood pressure were analyzed at baseline and end of diet. Hearts were assessed for hypertrophy, targeted lipidomics, untargeted metabolomics, and markers associated with cardiometabolic pathophysiology.
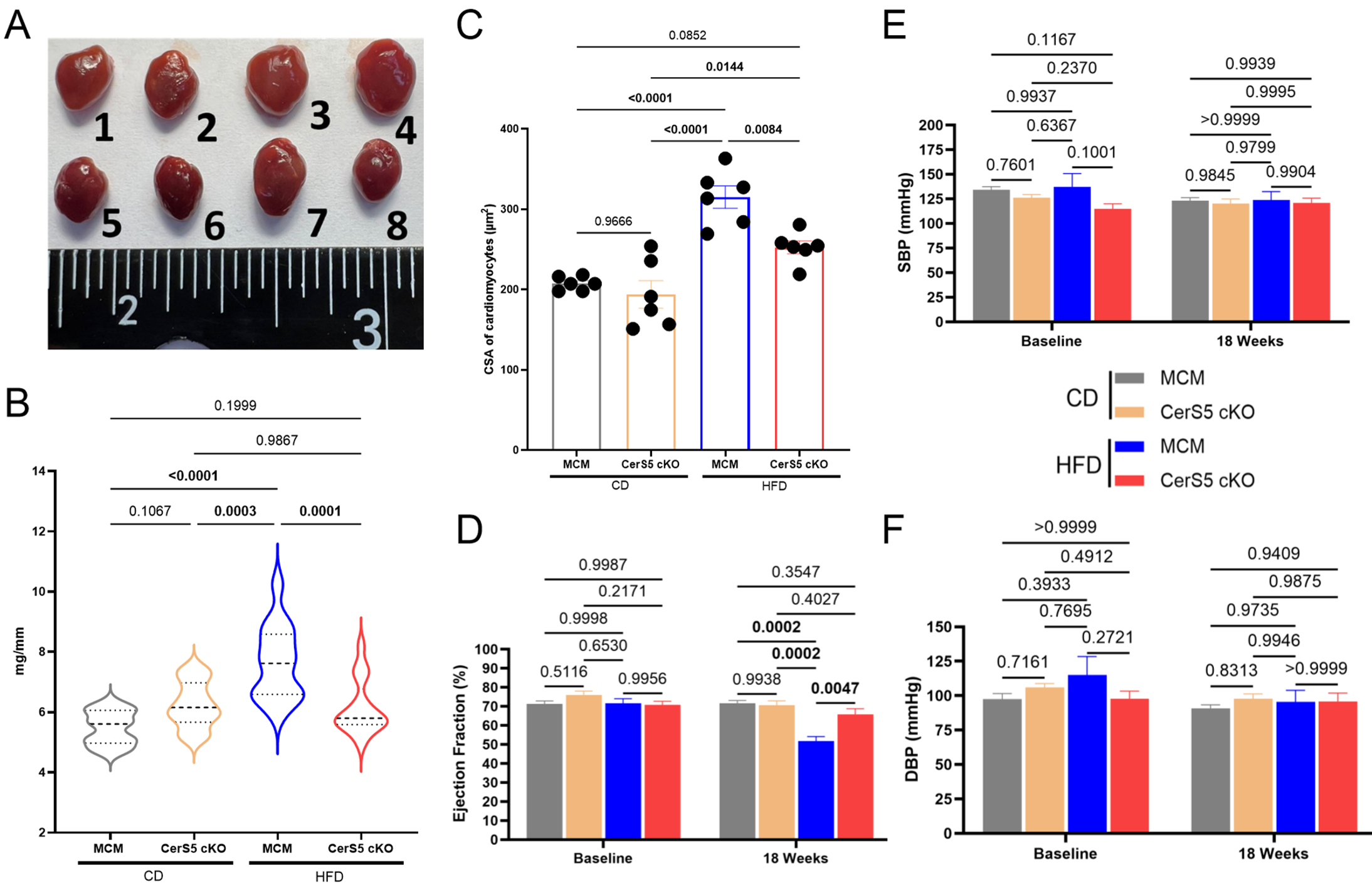
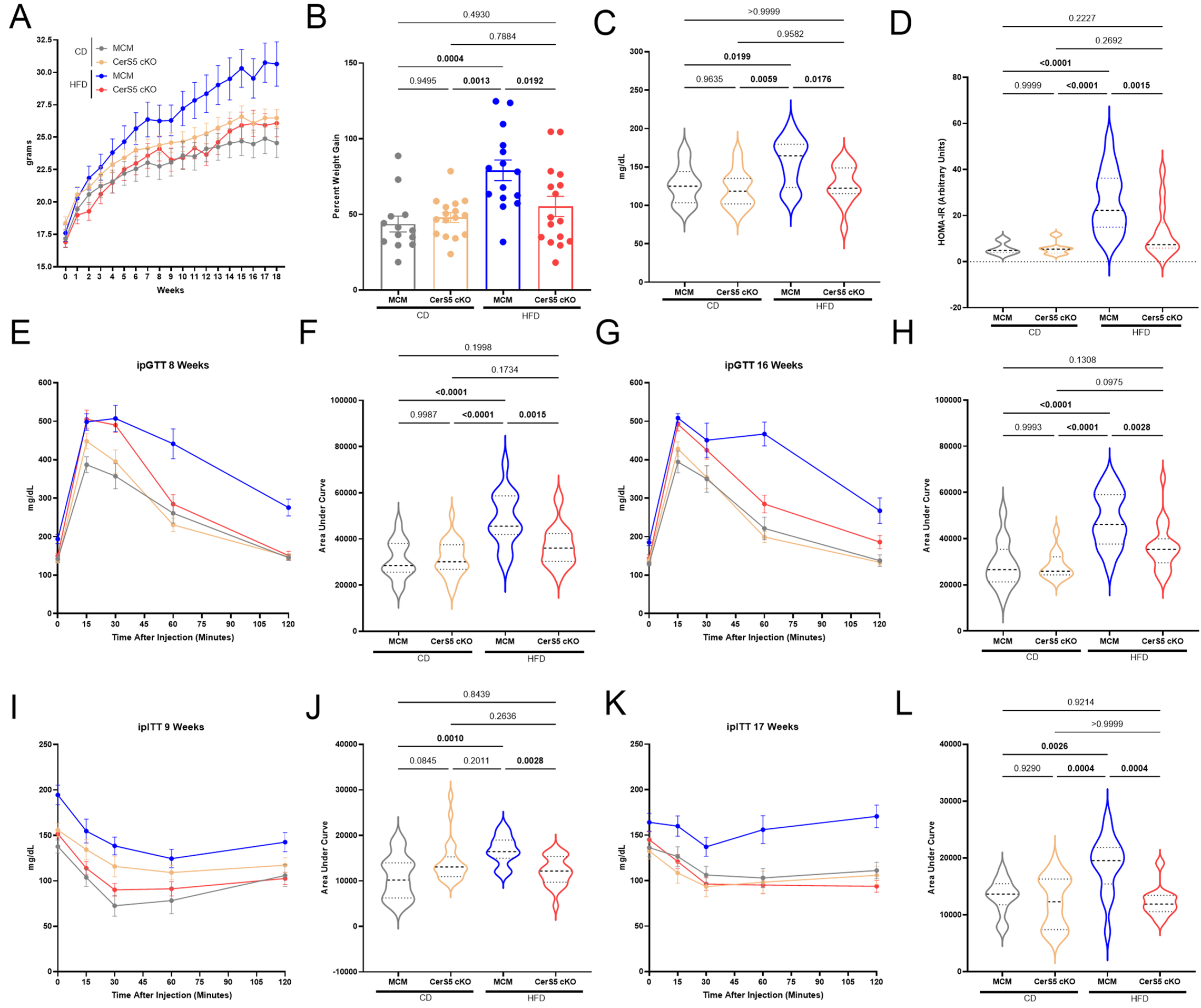
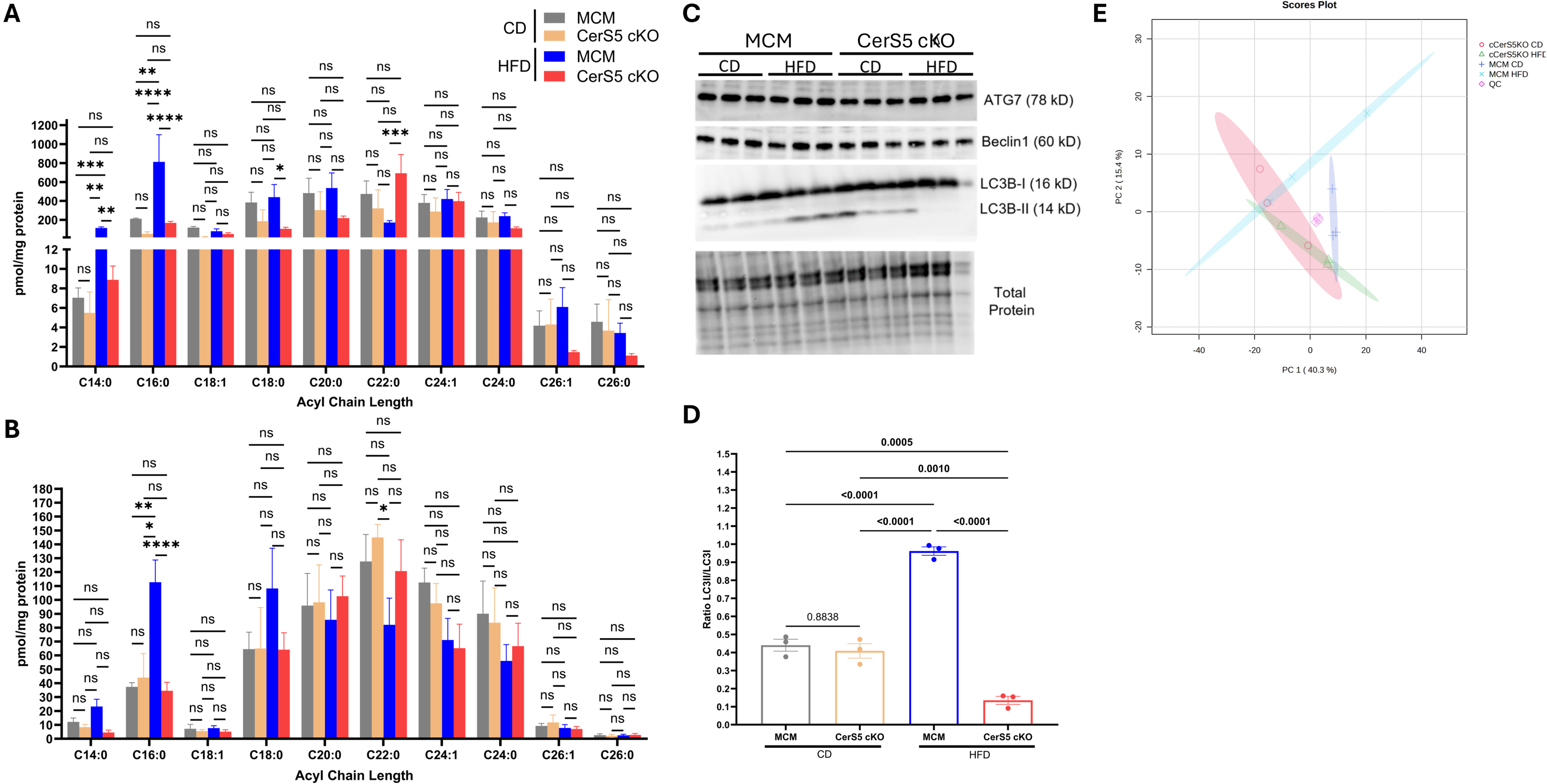
Results: CerS5 cKO mice on HFD exhibited protection from increased heart mass (Fig. 1A-B, KO:6.1±0.2 vs. control:7.6±0.3 mg/mm, P=0.0001), cardiomyocyte hypertrophy (Fig. 1C, KO:252.6±8.1 vs. control:315.2±14.0 µm2, P=0.0084), and reduced ejection fraction (Fig. 1D, KO:65.8±3.0 vs. control:51.7±2.4 %, P=0.0047) compared to controls on HFD. Systemic systolic (SBP) and diastolic (DBP) blood pressures at 18 weeks on diet did not vary between groups (Fig. 1E-F). KO mice on HFD also showed protection from metabolic comorbidities, including obesity (Fig. 2A-B, KO:26.1±1.1 vs. control:30.7±1.7 g, P=0.0192), increased HOMA-IR (Fig. 2C-D, KO:12.6±3.0 vs. control:26.0±3.4, P=0.0015), reduced glucose and insulin insensitivity (Fig. 2E-L) compared to control on HFD. This phenotype was associated with reduced CerS5-derived sphingomyelin C14 (Fig. 3A, KO:8.9±1.4 vs. control:164.5±13.5 pmol/mg protein, P=0.0082), C16 (Fig. 3A, KO:168.0±16.8 vs. control:812.4±287.6 pmol/mg protein, P<0.0001) and ceramide C16 (Fig. 3B, KO:34.6±6.2 vs. control:112.7±16.1 pmol/mg protein, P<0.0001), in the heart. Excessive autophagy (Fig. 3C-D) was observed in the hearts of control mice on HFD, but not in the KO mice on HFD. The heart metabolome of CerS5 cKO mice on HFD was more similar to control mice on CD than control mice on HFD (Fig. 3E).
Conclusions: Cardiomyocyte CerS5 depletion is crucial in maintaining cardiac and systemic metabolic homeostasis in mice with cardiometabolic pathophysiology. Excessive autophagy is a novel mechanism through which this may occur.
Hypothesis: Depletion of cardiomyocyte CerS5 protects against metabolic cardiomyopathy.
Methods: Inducible cardiomyocyte-specific CerS5 knockout (CerS5 cKO) mice were generated and placed on a milk-fat diet (HFD) or control diet (CD) for 18 weeks along with control (Myh6-MCM) mice (n=6-11/group). Diet-induced metabolic syndrome was monitored through weekly weight measurements, glucose and insulin tolerance tests, and blood plasma collection for Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR). Echocardiography and systemic blood pressure were analyzed at baseline and end of diet. Hearts were assessed for hypertrophy, targeted lipidomics, untargeted metabolomics, and markers associated with cardiometabolic pathophysiology.
Results: CerS5 cKO mice on HFD exhibited protection from increased heart mass (Fig. 1A-B, KO:6.1±0.2 vs. control:7.6±0.3 mg/mm, P=0.0001), cardiomyocyte hypertrophy (Fig. 1C, KO:252.6±8.1 vs. control:315.2±14.0 µm2, P=0.0084), and reduced ejection fraction (Fig. 1D, KO:65.8±3.0 vs. control:51.7±2.4 %, P=0.0047) compared to controls on HFD. Systemic systolic (SBP) and diastolic (DBP) blood pressures at 18 weeks on diet did not vary between groups (Fig. 1E-F). KO mice on HFD also showed protection from metabolic comorbidities, including obesity (Fig. 2A-B, KO:26.1±1.1 vs. control:30.7±1.7 g, P=0.0192), increased HOMA-IR (Fig. 2C-D, KO:12.6±3.0 vs. control:26.0±3.4, P=0.0015), reduced glucose and insulin insensitivity (Fig. 2E-L) compared to control on HFD. This phenotype was associated with reduced CerS5-derived sphingomyelin C14 (Fig. 3A, KO:8.9±1.4 vs. control:164.5±13.5 pmol/mg protein, P=0.0082), C16 (Fig. 3A, KO:168.0±16.8 vs. control:812.4±287.6 pmol/mg protein, P<0.0001) and ceramide C16 (Fig. 3B, KO:34.6±6.2 vs. control:112.7±16.1 pmol/mg protein, P<0.0001), in the heart. Excessive autophagy (Fig. 3C-D) was observed in the hearts of control mice on HFD, but not in the KO mice on HFD. The heart metabolome of CerS5 cKO mice on HFD was more similar to control mice on CD than control mice on HFD (Fig. 3E).
Conclusions: Cardiomyocyte CerS5 depletion is crucial in maintaining cardiac and systemic metabolic homeostasis in mice with cardiometabolic pathophysiology. Excessive autophagy is a novel mechanism through which this may occur.
More abstracts on this topic:
A drug target Mendelian randomization study of triglyceride lowering therapies for aortic stenosis
Ciofani Jonathan, Han Daniel, Gill Dipender, Rao Karan, Allahwala Usaid, Bhindi Ravinay
A human cardiomyocyte model of CD36 haploinsufficiency uncovers fatty acid oxidation deficits driving dilated cardiomyopathyAl Sayed Zeina, Klattenhoff Carla, Aragam Krishna, Ellinor Patrick, Willcox Jon, Zheng Alice, Koledova Vera, Srivastava Salil, Yin Xiaofei, Chaffin Mark, Rigaud Vagner, Kovacs-bogdan Erika