Final ID: Mo125
Translating ECG responses to drugs across sexes: model development and validation in the clinic
Abstract Body: Background: Sex-based differences in cardiac electrophysiology and their potential to impact susceptibility to cardiac arrhythmia and response to treatment are widely recognized. For example, female sex is an independent risk factor for drug-induced Long QT syndrome, Torsade de Pointes, and sudden cardiac death. However, arrhythmia studies have been predominantly performed in males, thus limiting our understanding of sex-specific arrhythmia mechanisms and the development of sex-specific metrics for arrhythmia risk. Computational tools are a powerful approach for integrating sex differences across scales and studying such multi-level phenomena, accelerating challenging and costly human and animal experiments.
Aim: To develop a quantitative tool that predicts drug-induced responses in female electrocardiogram (ECG) features based on ECG data collected in males (and vice versa).
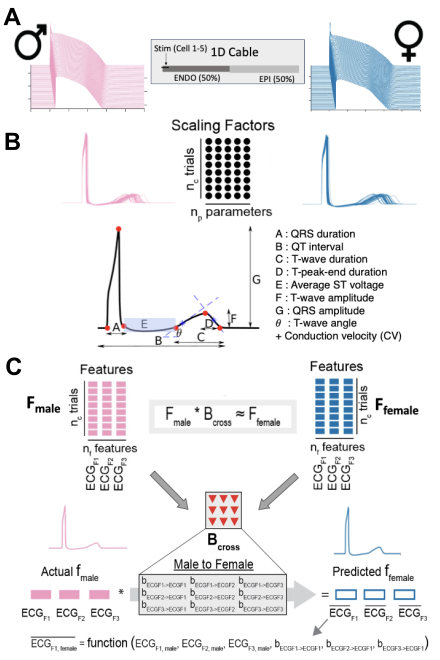
Methods: Male and female 1D cable models of ventricular cardiomyocytes were constructed by incorporating transmural heterogeneity and sex-specific parameterizations. We constructed populations of male and female models by randomly perturbing baseline parameters, and derived pseudo-ECGs from computed extracellular potentials. We then utilized lasso regression to map ECG features (QRS duration, QT interval, T-peak-end duration, and T-wave amplitude) extracted from the male pseudo-ECG onto the female ECG features (and vice versa) (Fig 1).
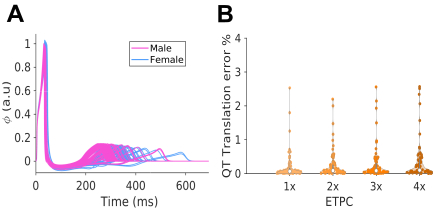
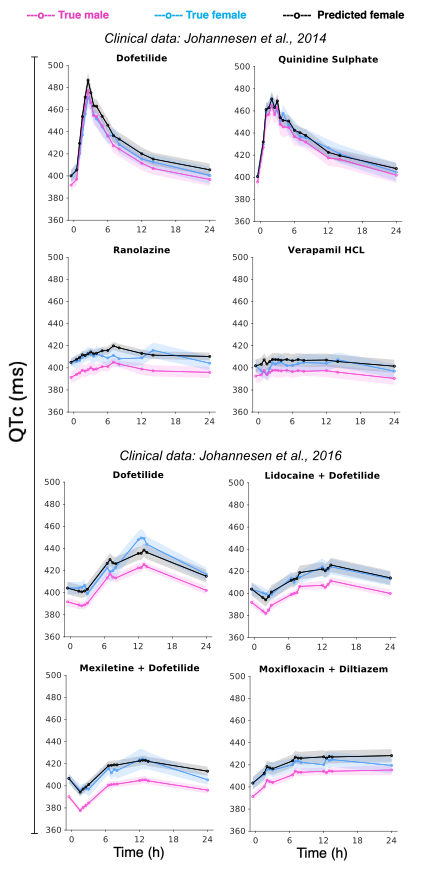
Results: Our simulated data-driven translator accurately predicted female pseudo-ECG features from male data in an independent simulated test set (R2 >0.95). This predictive capability was further assessed in an independent dataset simulating the effects of 95 drugs at different concentrations (Fig 2A), exhibiting an average translation error <1% for the QT interval (Fig 2B). Proof-of-concept application to ECG data sourced from publicly available FDA-approved datasets, in patients of both sexes under various anti-arrhythmic drugs and drug combinations, demonstrates high accuracy (Fig 3) and validates the translator's applicability to the clinic.
Conclusions: Our findings underscore the translator's potential in conducting sex-specific cardiac safety and efficacy assessments, enhancing the precision of evaluations in females. We plan to expand our translator capability to predict sex-specific effects of perturbations, including physiological and pathophysiological stressors.
Aim: To develop a quantitative tool that predicts drug-induced responses in female electrocardiogram (ECG) features based on ECG data collected in males (and vice versa).
Methods: Male and female 1D cable models of ventricular cardiomyocytes were constructed by incorporating transmural heterogeneity and sex-specific parameterizations. We constructed populations of male and female models by randomly perturbing baseline parameters, and derived pseudo-ECGs from computed extracellular potentials. We then utilized lasso regression to map ECG features (QRS duration, QT interval, T-peak-end duration, and T-wave amplitude) extracted from the male pseudo-ECG onto the female ECG features (and vice versa) (Fig 1).
Results: Our simulated data-driven translator accurately predicted female pseudo-ECG features from male data in an independent simulated test set (R2 >0.95). This predictive capability was further assessed in an independent dataset simulating the effects of 95 drugs at different concentrations (Fig 2A), exhibiting an average translation error <1% for the QT interval (Fig 2B). Proof-of-concept application to ECG data sourced from publicly available FDA-approved datasets, in patients of both sexes under various anti-arrhythmic drugs and drug combinations, demonstrates high accuracy (Fig 3) and validates the translator's applicability to the clinic.
Conclusions: Our findings underscore the translator's potential in conducting sex-specific cardiac safety and efficacy assessments, enhancing the precision of evaluations in females. We plan to expand our translator capability to predict sex-specific effects of perturbations, including physiological and pathophysiological stressors.
More abstracts on this topic:
Artificial Intelligence-enhanced Electrocardiography Sex-Discordance is Associated with Cardiovascular Events and Risk Factors in Women: from the ELSA-Brasil study
Camelo Lidyane, Zeidaabadi Boroumand, Pinto Filho Marcelo, Ribeiro Antonio Luiz, Ng Fu, Brant Luisa, Sau Arunashis, Barreto Sandhi, Giatti Luana, Oliveira Clara, Paixao Gabriela, Barker Joseph, Pastika Libor, Patlatzoglou Konstantinos
Ambulatory Atrial Fibrillation Ablation is Underutilized Among Women and Racial/Ethnic Minority GroupsMakmal Noam, Koplan Bruce