Final ID: 4392875
Systemic Delivery of Angiopoietin-1 Derived Q-peptide Modulates the Fibroinflammatory Response to Improve Cardiac Function in a Rat Myocardial Infarction Model
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Ischemic cardiomyopathy secondary to myocardial infarction (MI) results in pathological remodeling that leads to end-stage heart failure (HF). Targeted anti-fibrotic and immunomodulatory therapies are a promising development, but many agents have non-specific effects and require intramyocardial delivery via surgical/interventional approaches. We examine the role of systemically delivered Q-peptide (QHREDGS), a chemically modified angiopoietin-1 derivative with known regenerative properties and long-term stability, in a small animal HF model.
Methods: 6-week-old male and female Sprague-Dawley rats (n=6/group) underwent MI via left coronary artery ligation and concurrent implantation of Alzet osmotic minipumps with 25 nmol/kg/day (low dose) or 50 nmol/kg/day (high dose) of soluble Q-peptide, or a corresponding dose of scrambled peptide (DGQESHR) delivered over 4 weeks. Echocardiography was performed prior to MI and at 2, 4, and 6 weeks post-MI to assess cardiac function. Cardiac MRI was used to acquire both cine functional images and delayed-enhancement infarct images following intravenous delivery of 1.2 mmol/kg gadolinium DTPA 4 weeks post-MI. Images were analyzed using Circle Cardiovascular Imaging software. Animals were sacrificed 6 weeks post-MI for histological/immunohistochemical analysis.
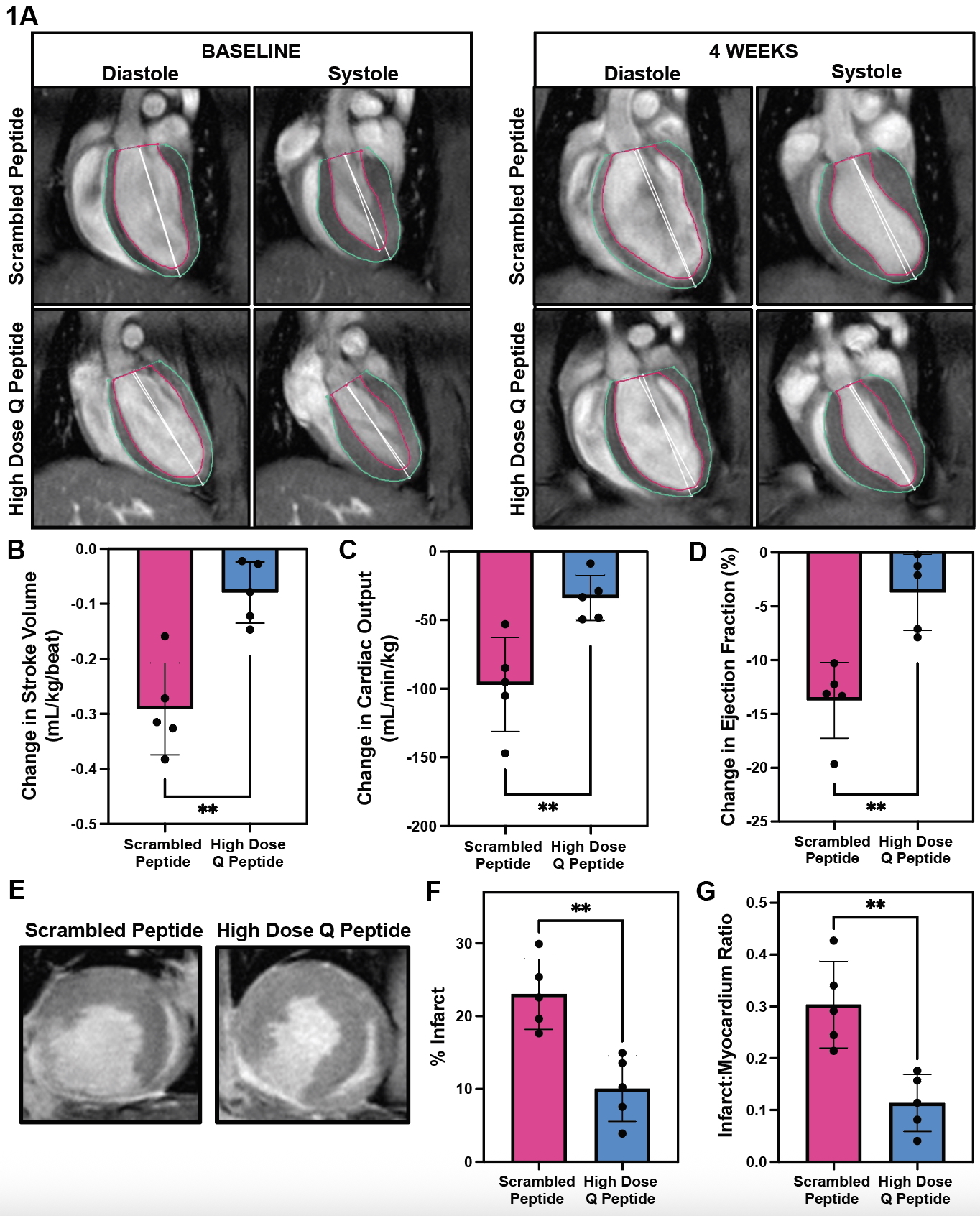
Results: Histological examination revealed no hepatic or renal toxicity from systemic Q-peptide therapy. Rats receiving high dose Q-peptide had significantly lower reductions in fractional shortening, ejection fraction (EF), and fractional area change on echo 4 weeks post-MI; this effect was maintained at 6 weeks. Animals showed significantly lower collagen deposition, improved cardiomyocyte (CM) retention, fewer aSMA+ myofibroblasts and CD68+ macrophages, and more CD31+ vessels in the infarct area 6 weeks post-MI. High dose Q-peptide rats demonstrated significantly improved stroke volume, cardiac output, and EF on cardiac MRI functional images compared to scrambled controls, and smaller infarct areas as quantified by late gadolinium enhancement (Figure 1).
Conclusions: Systemic delivery of Q-peptide over 4 weeks following MI attenuates the fibroinflammatory response and promotes angiogenesis to improve CM survival and reduce infarct size in a rodent HF model without off-target toxicity. This results in significant cardiac functional and morphological improvements, offering a novel approach that avoids invasive intramyocardial peptide delivery.
Methods: 6-week-old male and female Sprague-Dawley rats (n=6/group) underwent MI via left coronary artery ligation and concurrent implantation of Alzet osmotic minipumps with 25 nmol/kg/day (low dose) or 50 nmol/kg/day (high dose) of soluble Q-peptide, or a corresponding dose of scrambled peptide (DGQESHR) delivered over 4 weeks. Echocardiography was performed prior to MI and at 2, 4, and 6 weeks post-MI to assess cardiac function. Cardiac MRI was used to acquire both cine functional images and delayed-enhancement infarct images following intravenous delivery of 1.2 mmol/kg gadolinium DTPA 4 weeks post-MI. Images were analyzed using Circle Cardiovascular Imaging software. Animals were sacrificed 6 weeks post-MI for histological/immunohistochemical analysis.
Results: Histological examination revealed no hepatic or renal toxicity from systemic Q-peptide therapy. Rats receiving high dose Q-peptide had significantly lower reductions in fractional shortening, ejection fraction (EF), and fractional area change on echo 4 weeks post-MI; this effect was maintained at 6 weeks. Animals showed significantly lower collagen deposition, improved cardiomyocyte (CM) retention, fewer aSMA+ myofibroblasts and CD68+ macrophages, and more CD31+ vessels in the infarct area 6 weeks post-MI. High dose Q-peptide rats demonstrated significantly improved stroke volume, cardiac output, and EF on cardiac MRI functional images compared to scrambled controls, and smaller infarct areas as quantified by late gadolinium enhancement (Figure 1).
Conclusions: Systemic delivery of Q-peptide over 4 weeks following MI attenuates the fibroinflammatory response and promotes angiogenesis to improve CM survival and reduce infarct size in a rodent HF model without off-target toxicity. This results in significant cardiac functional and morphological improvements, offering a novel approach that avoids invasive intramyocardial peptide delivery.
More abstracts on this topic:
4D Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Identifies Differences in Regional Strain Patterns Among Pediatric Heart Transplant Patients with Acute Rejection or Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy
Henderson Christopher, Starnes Joseph, Samyn Margaret, Damon Bruce, Hernandez Lazaro, Goergen Craig, Soslow Jonathan, Prado Marco Aurélio, Earl Conner, Georgedurrett Kristen, Lee Simon, Nandi Deipanjan, Chan Kak-chen, Shugh Svetlana, Kikano Sandra
6-Nitrodopamine potentiates the positive chronotopic and inotropic effect induced by noradrenaline in the rat isolated heartLima Antonio, Sobanski Joao Fernando, Antunes Edson, De Nucci Gilberto