Final ID:
Primary Results from the Post Approval Study of a Next Generation Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillator System: the ACE-PAS Trial
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Wearable cardioverter defibrillators (WCD) have established safety and efficacy, yet contemporary data are limited evaluating performance in patients with ischemic and non-ischemic heart disease at risk for sudden cardiac death (SCD).
Objectives: To assess safety and efficacy of a next generation WCD system in a large, prospective study.
Methods: The ASSURE Clinical Evaluation–Post Approval Study (ACE-PAS) is an active surveillance registry conducted in accordance with FDA post-approval study guidelines enrolling consecutive patients prescribed the ASSURE WCD [Kestra Medical Technologies] from 2021 to 2025. The primary efficacy endpoint is overall shock conversion rate and the primary safety endpoint is inappropriate shock rate. Additional analyses include false shock alarm rate, total burden of detected ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias and wear compliance. All shock events were adjudicated by a panel of experts. Baseline clinical characteristics were collected. Descriptive statistics are reported using mean±SD or median (IQR).
Results: 21,628 patients were included in the analysis. Mean age was 64.0±14.0 years; 33.4% were female and body mass index 30±7. Median daily wear was 23.2 hours/day (IQR 16.2–23.9) over 40 days (IQR 11-85).
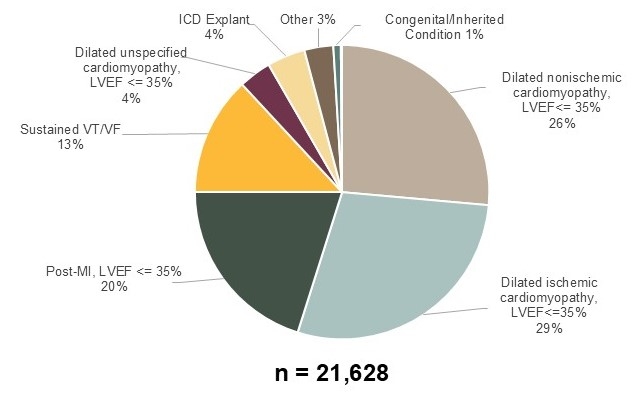
WCD indication was predominately for dilated cardiomyopathy (58%) with EF 23±7%. The next most common indication was post-myocardial infarction (MI) (20%) with EF 25±6%, followed by patients with prior sustained ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation (VT/VF) (13%), implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) explant (4%), and other indications (5%) (Figure).
Primary safety and efficacy endpoints will be presented. We found a clinically important occurrence of life-threatening VT/VF with the highest risk in the first month of wear. Atrial fibrillation was common, and often the first documented episode. Severe bradyarrhythmia, while infrequent, represent a critically important finding. False shock alarm rates are the lowest reported in the literature and wear compliance high.
Conclusions: In this largest prospective WCD series to date, we define VT/VF rates early after acute MI, and in vulnerable heart failure (HF) populations. These data provide contemporary insights into identifying patients at high risk for SCD who are not currently eligible for an ICD, such as in the post MI period and following a new HF diagnosis. WCDs can provide life-saving therapy and identify actionable new clinical arrhythmias.
Objectives: To assess safety and efficacy of a next generation WCD system in a large, prospective study.
Methods: The ASSURE Clinical Evaluation–Post Approval Study (ACE-PAS) is an active surveillance registry conducted in accordance with FDA post-approval study guidelines enrolling consecutive patients prescribed the ASSURE WCD [Kestra Medical Technologies] from 2021 to 2025. The primary efficacy endpoint is overall shock conversion rate and the primary safety endpoint is inappropriate shock rate. Additional analyses include false shock alarm rate, total burden of detected ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias and wear compliance. All shock events were adjudicated by a panel of experts. Baseline clinical characteristics were collected. Descriptive statistics are reported using mean±SD or median (IQR).
Results: 21,628 patients were included in the analysis. Mean age was 64.0±14.0 years; 33.4% were female and body mass index 30±7. Median daily wear was 23.2 hours/day (IQR 16.2–23.9) over 40 days (IQR 11-85).
WCD indication was predominately for dilated cardiomyopathy (58%) with EF 23±7%. The next most common indication was post-myocardial infarction (MI) (20%) with EF 25±6%, followed by patients with prior sustained ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation (VT/VF) (13%), implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) explant (4%), and other indications (5%) (Figure).
Primary safety and efficacy endpoints will be presented. We found a clinically important occurrence of life-threatening VT/VF with the highest risk in the first month of wear. Atrial fibrillation was common, and often the first documented episode. Severe bradyarrhythmia, while infrequent, represent a critically important finding. False shock alarm rates are the lowest reported in the literature and wear compliance high.
Conclusions: In this largest prospective WCD series to date, we define VT/VF rates early after acute MI, and in vulnerable heart failure (HF) populations. These data provide contemporary insights into identifying patients at high risk for SCD who are not currently eligible for an ICD, such as in the post MI period and following a new HF diagnosis. WCDs can provide life-saving therapy and identify actionable new clinical arrhythmias.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acoustic Biomarkers Harvested from 911 Calls Differ among Patients with Cardiac and Non-Cardiac Chest Pain
Mazhar Harris, Zegre-hemsey Jessica, Lee Kyungbok, Tian Baotong, Heydari Mojtaba, Cushman Jeremy, Duan Zhiyao, Dzikowicz Dillon
Adverse Clinical Events Due to the Safety Mode in Implantable DefibrillatorsDesouki Mariam, Abdelsayed Kerollos, Witt Dawn, Sengupta Jay, Hauser Robert