Final ID: LBP6
Exosome-loaded with Small Cajal Body Associated RNA20: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain the leading global cause of morbidity and mortality. While mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have shown regenerative promise, limitations such as heterogeneity and poor tissue retention have driven interest in cell-free, exosome-based therapies. Emerging evidence highlights the role of small Cajal body-associated RNAs (scaRNAs)—a subclass of non-coding RNAs—in cardiac development and disease, yet their therapeutic potential remains underexplored.
Objective: To investigate the role of exosomes loaded with scaRNA20 (scaRNA20) in cardiomyocyte differentiation its therapeutic potential in mitigating inflammatory stress responses.
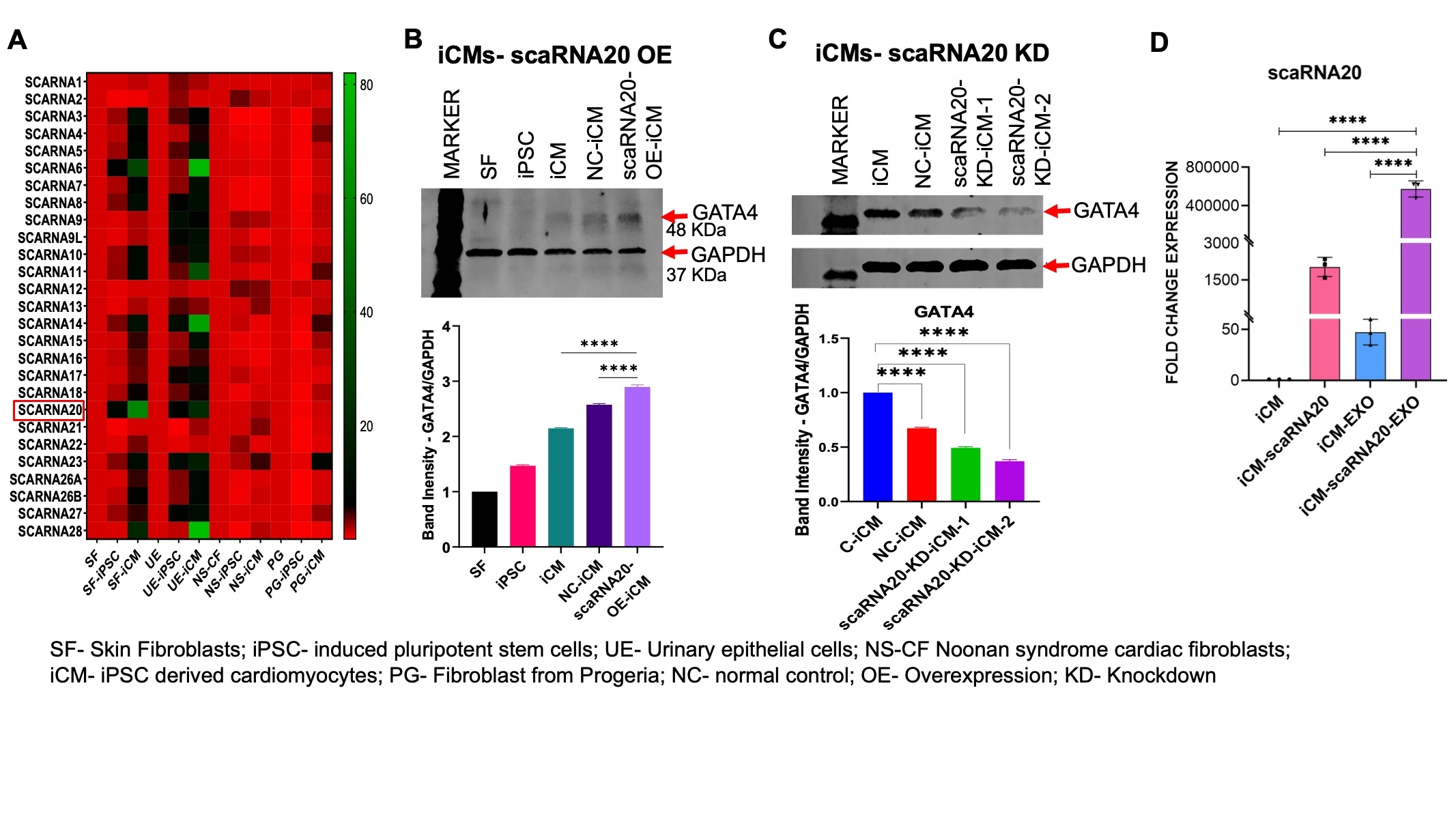
Methods and Results: Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) were generated from healthy and disease-specific donors, differentiated into cardiomyocytes (iCMs), and profiled for scaRNA expression. scaRNA20 levels were significantly reduced in iCMs derived from patients with Noonan and Progeria syndromes (Fig. A). Overexpression of scaRNA20 enhanced cardiac differentiation and upregulated GATA4 and TNNT2 expression, while knockdown impaired differentiation and downregulated GATA4 (Fig. B, C). Exosomes (EXOs) derived from iPSC-derived MSCs (iMSCs) were successfully engineered to carry synthetic scaRNA20 transcripts (EXO-scaRNA20) (Fig. D). These exosomes efficiently delivered scaRNA20 to iCMs, resulting in elevated expression of cardiac-specific genes. Moreover, EXO and EXO-scaRNA20 treatments attenuated Angiotensin II-induced proinflammatory responses (TNFα, IL6) and upregulated NRF2, a key regulator of cellular stress resistance.
Conclusion: Exosome-mediated delivery of scaRNA20 promotes cardiac gene expression, improves differentiation, and enhances resistance to inflammatory stress. These findings support the therapeutic potential of EXO-scaRNA20 as a novel, cell-free intervention for treating cardiovascular disease.
Objective: To investigate the role of exosomes loaded with scaRNA20 (scaRNA20) in cardiomyocyte differentiation its therapeutic potential in mitigating inflammatory stress responses.
Methods and Results: Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) were generated from healthy and disease-specific donors, differentiated into cardiomyocytes (iCMs), and profiled for scaRNA expression. scaRNA20 levels were significantly reduced in iCMs derived from patients with Noonan and Progeria syndromes (Fig. A). Overexpression of scaRNA20 enhanced cardiac differentiation and upregulated GATA4 and TNNT2 expression, while knockdown impaired differentiation and downregulated GATA4 (Fig. B, C). Exosomes (EXOs) derived from iPSC-derived MSCs (iMSCs) were successfully engineered to carry synthetic scaRNA20 transcripts (EXO-scaRNA20) (Fig. D). These exosomes efficiently delivered scaRNA20 to iCMs, resulting in elevated expression of cardiac-specific genes. Moreover, EXO and EXO-scaRNA20 treatments attenuated Angiotensin II-induced proinflammatory responses (TNFα, IL6) and upregulated NRF2, a key regulator of cellular stress resistance.
Conclusion: Exosome-mediated delivery of scaRNA20 promotes cardiac gene expression, improves differentiation, and enhances resistance to inflammatory stress. These findings support the therapeutic potential of EXO-scaRNA20 as a novel, cell-free intervention for treating cardiovascular disease.
More abstracts on this topic:
Cardiac protection of hiPSC-CMs loaded chitosan cardiac patch in myocardial infarcted swine
Zheng Zilong, Li Yichen, Tang Weijie, Chen Wangping, Yang Jinfu, Fan Chengming
Blood Pressure Magnitude as a Modulator of Perivascular Adipose Tissue Fibrotic ResponseRendon C. Javier, Lefkowitz Rebecca, Garver Hannah, Lauver Adam, Fink Gregory, Krieger-burke Teresa, Watts Stephanie, Contreras Andres