Final ID: MP2048
Signals of Cardioprotection with Colchicine in Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy: A Propensity-Matched Real-World Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (TCM), a transient myocardial disorder, is increasingly recognized to involve heightened inflammatory activation. Elevated inflammatory markers have been associated with worse outcomes in TCM. Colchicine, an anti-inflammatory agent, may have therapeutic potential in TCM, but supporting evidence remains limited.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that Colchicine therapy in TCM is associated with reduced mortality, cardiovascular events, and renal complications compared to no Colchicine treatment.
Methods:
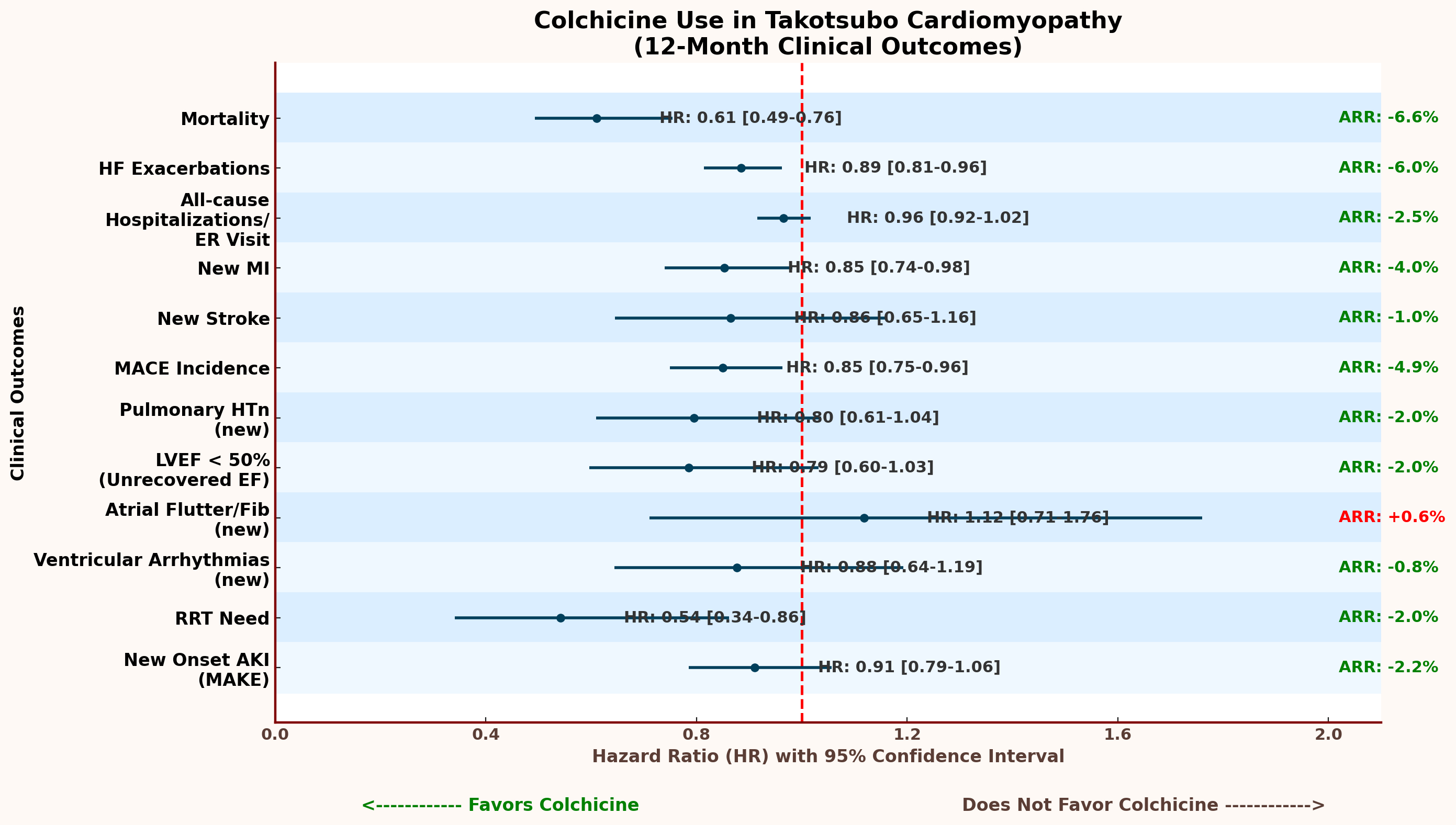
A retrospective cohort study was conducted using the Global Collaborative Network, a large multi-institutional electronic health record database. Adults aged 15–70 years diagnosed with TCM who received colchicine (n=1,149) were 1:1 propensity score–matched to TCM patients who did not receive colchicine (n=1,149), balancing on demographics, comorbidities, cardiac risk factors, medications, inflammatory biomarkers, and other labs. Outcomes were assessed over 12 months. The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes included heart failure (HF) exacerbations, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, arrhythmias, acute kidney injury (AKI), and renal replacement therapy (RRT). Hazard ratios (HRs), 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and absolute risk reductions (ARRs) were calculated.
Results:
Colchicine was associated with significantly lower all-cause mortality (10.4% vs. 17.0%; HR 0.61 [95% CI: 0.49–0.76]; ARR −6.6%; p<0.001), HF exacerbations (46.2% vs. 52.2%; HR 0.89; ARR −6.0%; p=0.004), and MACE (27.6% vs. 32.5%; HR 0.85; ARR −4.9%; p=0.011). MI risk was reduced (23.2% vs. 27.2%; HR 0.85; p=0.027), as was RRT use (2.5% vs. 4.5%; HR 0.54; p=0.008). Stroke (HR 0.87), AKI (HR 0.91), and arrhythmias showed non-significant trends favoring Colchicine. LVEF recovery was more common in the Colchicine group (7.3% vs. 9.3% unrecovered; HR 0.79; p=0.082).
Conclusion:
In this large, matched real-world cohort, Colchicine use in TCM was associated with improved survival and cardiovascular outcomes. These findings raise the possibility of a therapeutic benefit, given the role of inflammation in TCM. Prospective studies and randomized trials are warranted to further explore its clinical utility and mechanistic impact in this unique cardiomyopathy.
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (TCM), a transient myocardial disorder, is increasingly recognized to involve heightened inflammatory activation. Elevated inflammatory markers have been associated with worse outcomes in TCM. Colchicine, an anti-inflammatory agent, may have therapeutic potential in TCM, but supporting evidence remains limited.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that Colchicine therapy in TCM is associated with reduced mortality, cardiovascular events, and renal complications compared to no Colchicine treatment.
Methods:
A retrospective cohort study was conducted using the Global Collaborative Network, a large multi-institutional electronic health record database. Adults aged 15–70 years diagnosed with TCM who received colchicine (n=1,149) were 1:1 propensity score–matched to TCM patients who did not receive colchicine (n=1,149), balancing on demographics, comorbidities, cardiac risk factors, medications, inflammatory biomarkers, and other labs. Outcomes were assessed over 12 months. The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes included heart failure (HF) exacerbations, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, arrhythmias, acute kidney injury (AKI), and renal replacement therapy (RRT). Hazard ratios (HRs), 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and absolute risk reductions (ARRs) were calculated.
Results:
Colchicine was associated with significantly lower all-cause mortality (10.4% vs. 17.0%; HR 0.61 [95% CI: 0.49–0.76]; ARR −6.6%; p<0.001), HF exacerbations (46.2% vs. 52.2%; HR 0.89; ARR −6.0%; p=0.004), and MACE (27.6% vs. 32.5%; HR 0.85; ARR −4.9%; p=0.011). MI risk was reduced (23.2% vs. 27.2%; HR 0.85; p=0.027), as was RRT use (2.5% vs. 4.5%; HR 0.54; p=0.008). Stroke (HR 0.87), AKI (HR 0.91), and arrhythmias showed non-significant trends favoring Colchicine. LVEF recovery was more common in the Colchicine group (7.3% vs. 9.3% unrecovered; HR 0.79; p=0.082).
Conclusion:
In this large, matched real-world cohort, Colchicine use in TCM was associated with improved survival and cardiovascular outcomes. These findings raise the possibility of a therapeutic benefit, given the role of inflammation in TCM. Prospective studies and randomized trials are warranted to further explore its clinical utility and mechanistic impact in this unique cardiomyopathy.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Beta Tubulin Mutation Suppresses Arrhythmias and Improves Connexin 43 Localization in Heart of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Mice
Zhou Delong, Liu Tong, Yehia Ghassan, Romanienko Peter, Rodney George, Wehrens Xander, Lampe Paul, Gourdie Robert, Xie Lai-hua, Fraidenraich Diego, Nouet Julie, Mesa Elam, Yegneshwaran Vasisht, Geukgeuzian Geovanni, Adibemma Ifeanyichukwu, Nandakumar Swetha, Ramirez Edwin, Li Hong
A Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy-Based Model Estimate of the Prevalence of Danon Disease in the United StatesMaron Martin, Massera Daniele, Manganaro Susan, Bailey Miranda, Rehbein Fletcher, Taylor Matthew