Final ID: MP2192
New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation Exacerbates Mortality and Healthcare Burden in Orthotopic Liver Transplant Recipients Readmitted Within 90 Days
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction/Background:
Atrial fibrillation (AF), a common postoperative arrhythmia, is associated with increased morbidity and mortality across various surgical populations. In patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation (LT), the presence of AF has been linked to poorer clinical outcomes. However, data on the prognostic significance of new-onset AF during early post-transplant readmissions in orthotopic LT recipients remain limited.
Hypothesis:
We postulated that incident AF occurring during 90-day post-LT readmissions is independently associated with increased in-hospital mortality, prolonged length of stay, and higher healthcare costs.
Methods:
We conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the National Readmission Database (2016–2019). Adult LT recipients (aged >18 years) readmitted within 90 days were identified via ICD-10 coding. Patients who developed new-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) during readmission were compared to those without AF. Primary outcomes included in-hospital mortality, length of stay (LOS), and total hospitalization costs. Multivariable logistic and linear regression models, adjusted for demographic and clinical confounders, were used.
Results:
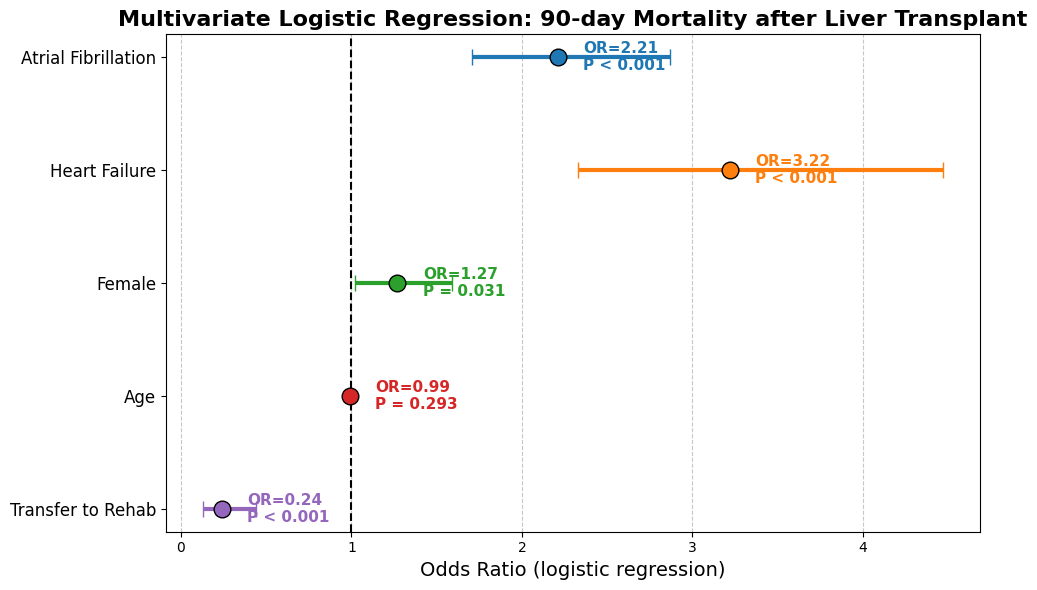
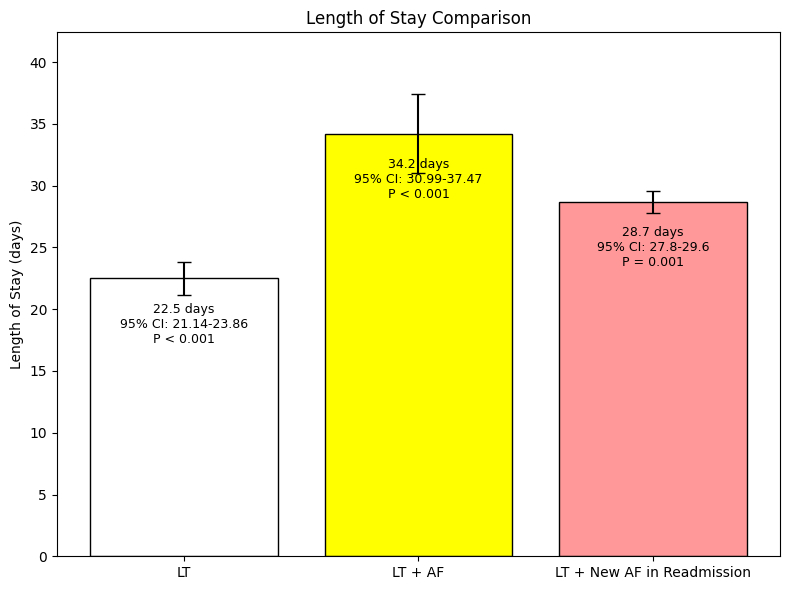
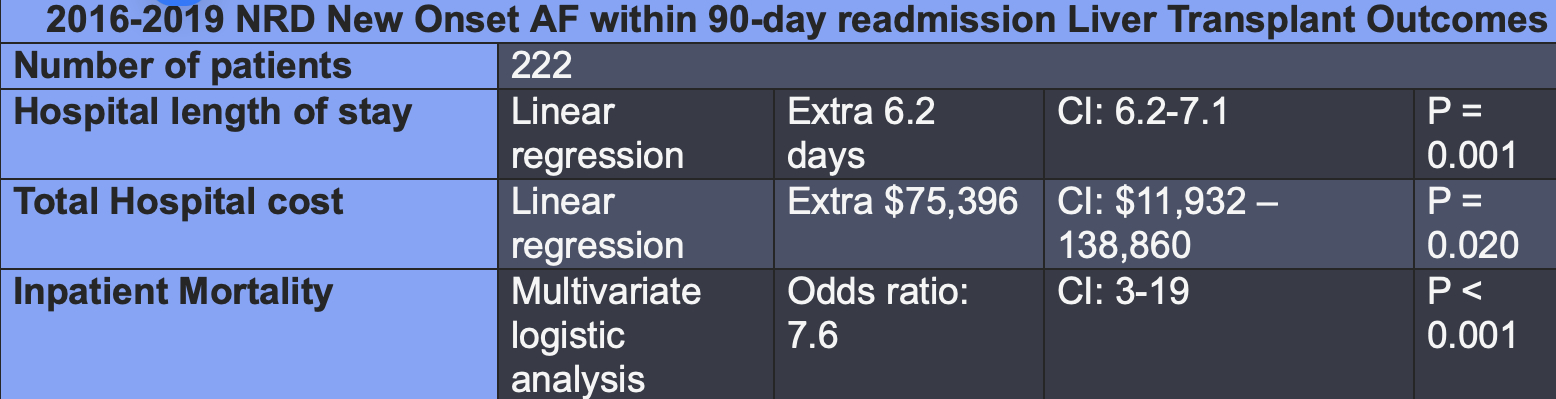
Of 31,557 adult LT recipients (mean age 55.5 years, 35% female), 8,449 (27.6%) (mean age 55.3 years, 36.7% women) were readmitted within 90 days. Among those readmitted, 222 patients (2.6%) developed new-onset atrial fibrillation (AF), and 84 (1.0%) died during the readmission period. New-onset AF was associated with a 7.6-fold increased risk of in-hospital mortality (95% CI: 3.0–19.0; P < 0.05). Additionally, AF onset was linked to a mean increase in LOS of 6.2 days (95% CI: 6.2–7.1; P = 0.001) and an average increase in hospitalization costs of $75,396 (95% CI: $11,932–$138,860; P = 0.02). All associations achieved statistical significance.
Conclusion(s):
New-onset AF during early post-transplant readmissions is associated with significantly worse clinical outcomes and increased healthcare utilization. These findings underscore the need for proactive rhythm monitoring and risk-stratified arrhythmia management during the liver transplant recovery period.
Atrial fibrillation (AF), a common postoperative arrhythmia, is associated with increased morbidity and mortality across various surgical populations. In patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation (LT), the presence of AF has been linked to poorer clinical outcomes. However, data on the prognostic significance of new-onset AF during early post-transplant readmissions in orthotopic LT recipients remain limited.
Hypothesis:
We postulated that incident AF occurring during 90-day post-LT readmissions is independently associated with increased in-hospital mortality, prolonged length of stay, and higher healthcare costs.
Methods:
We conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the National Readmission Database (2016–2019). Adult LT recipients (aged >18 years) readmitted within 90 days were identified via ICD-10 coding. Patients who developed new-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) during readmission were compared to those without AF. Primary outcomes included in-hospital mortality, length of stay (LOS), and total hospitalization costs. Multivariable logistic and linear regression models, adjusted for demographic and clinical confounders, were used.
Results:
Of 31,557 adult LT recipients (mean age 55.5 years, 35% female), 8,449 (27.6%) (mean age 55.3 years, 36.7% women) were readmitted within 90 days. Among those readmitted, 222 patients (2.6%) developed new-onset atrial fibrillation (AF), and 84 (1.0%) died during the readmission period. New-onset AF was associated with a 7.6-fold increased risk of in-hospital mortality (95% CI: 3.0–19.0; P < 0.05). Additionally, AF onset was linked to a mean increase in LOS of 6.2 days (95% CI: 6.2–7.1; P = 0.001) and an average increase in hospitalization costs of $75,396 (95% CI: $11,932–$138,860; P = 0.02). All associations achieved statistical significance.
Conclusion(s):
New-onset AF during early post-transplant readmissions is associated with significantly worse clinical outcomes and increased healthcare utilization. These findings underscore the need for proactive rhythm monitoring and risk-stratified arrhythmia management during the liver transplant recovery period.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Body Shape Index at Age 25-64 Predicts Mortality and CHD Hospitalization
Shafran Itamar, Krakauer Nir, Krakauer Jesse, Cohen Gali, Gerber Yariv
Acoramidis Reduces All-Cause Mortality (ACM) and Cardiovascular-Related Hospitalization (CVH): Initial Outcomes From the ATTRibute-CM Open-Label Extension (OLE) StudyJudge Daniel, Masri Ahmad, Obici Laura, Poulsen Steen, Sarswat Nitasha, Shah Keyur, Soman Prem, Cao Xiaofan, Wang Kevin, Pecoraro Maria, Tamby Jean-francois, Gillmore Julian, Katz Leonid, Fox Jonathan, Maurer Mathew, Alexander Kevin, Ambardekar Amrut, Cappelli Francesco, Fontana Marianna, Garcia-pavia Pablo, Grogan Martha, Hanna Mazen