Final ID: MP885
Efficacy evaluation of the novel concave supra-aortic branched stent-graft system and optimization scenarios for patient-specific endovascular total arch repair via hemodynamics
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Concave supra-aortic branched stent-graft (CSBSG) system offers a new option for managing aortic arch pathologies. However, therapeutic efficacy and appropriate implantation regimen of the innovative technique remain unclear.
Aims: This study aims to quantify hemodynamic outcomes to assess therapeutic efficacy of CSBSG and then to investigate patient-specific optimization scenarios for further improving CSBSG performance.
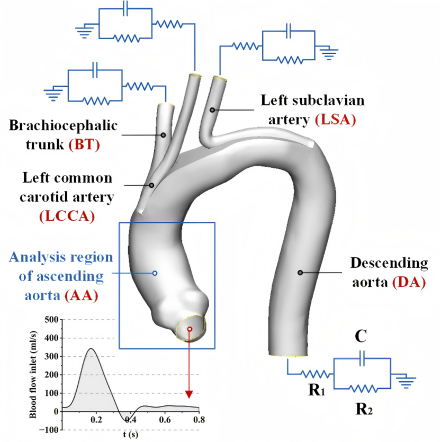
Methods: Numerical simulations are conducted via CTA datasets from first-in-human cases both before and after CSBSG implantation. Boundary conditions are obtained through three-element Windkessel model. Optimizations on concave degree (angle α) of CSBSG are analyzed in scenarios with patient-specific aortic diameter.
Results: Results show that CSBSG insertion can effectively maintain supra-aortic branches blood flow, and will not significantly influence pressure in ascending aorta (AA) and hemodynamic environments whether postoperative blood pressure is normotensive or hypertensive (from 120/80 to 180/140 mmHg). Larger concave angle improves supra-aortic branches perfusion, but also increases pressure and oscillatory shear index in AA. More notable variations are found in patients treated by CSBSG with α ranging from 150° to 180° than from 120° to 150°. Additionally, effects of CSBSG implantation on hemodynamic parameters, e.g., time-averaged wall shear stress, are more pronounced in patients with smaller aortic diameters compared to those with larger diameters. Patients who have (i) larger AA and descending aorta (DA) diameters or (ii) smaller diameter differences between AA and DA, exhibit lower AA pressure, supra-aortic branches perfusion and total energy loss after CSBSG deployment compared with others.
Conclusion: Results obtained can provide theoretical foundation in assessing CSBSG outcomes and guiding stent-graft design and determination.
Aims: This study aims to quantify hemodynamic outcomes to assess therapeutic efficacy of CSBSG and then to investigate patient-specific optimization scenarios for further improving CSBSG performance.
Methods: Numerical simulations are conducted via CTA datasets from first-in-human cases both before and after CSBSG implantation. Boundary conditions are obtained through three-element Windkessel model. Optimizations on concave degree (angle α) of CSBSG are analyzed in scenarios with patient-specific aortic diameter.
Results: Results show that CSBSG insertion can effectively maintain supra-aortic branches blood flow, and will not significantly influence pressure in ascending aorta (AA) and hemodynamic environments whether postoperative blood pressure is normotensive or hypertensive (from 120/80 to 180/140 mmHg). Larger concave angle improves supra-aortic branches perfusion, but also increases pressure and oscillatory shear index in AA. More notable variations are found in patients treated by CSBSG with α ranging from 150° to 180° than from 120° to 150°. Additionally, effects of CSBSG implantation on hemodynamic parameters, e.g., time-averaged wall shear stress, are more pronounced in patients with smaller aortic diameters compared to those with larger diameters. Patients who have (i) larger AA and descending aorta (DA) diameters or (ii) smaller diameter differences between AA and DA, exhibit lower AA pressure, supra-aortic branches perfusion and total energy loss after CSBSG deployment compared with others.
Conclusion: Results obtained can provide theoretical foundation in assessing CSBSG outcomes and guiding stent-graft design and determination.
More abstracts on this topic:
Co-localization of NCCT hypodensity and CTA spot sign to predict intracerebral hematoma expansion and severity: development and validation of the Black-&-White sign
Pensato Umberto, Banerjee Ankur, Kulkarni Girish, Menon Bijoy, Goyal Mayank, Hill Michael, Molina Carlos, Silva Yolanda, Boulanger Jean-martin, Gubitz Gord, Bhatia Rohit, Tanaka Koji, Srivastava Padma, Roy Jayanta, Dzialowski Imanuel, Kase Carlos, Kobayashi Adam, Rodriguez-luna David, Aviv Richard, Dowlatshahi Dar, Demchuk Andrew, Horn Mackenzie, Teleg Ericka, Al Sultan Abdulaziz, Kasickova Machova Linda, Ohara Tomoyuki, Ojha Piyush, Marzoughi Sina
Abnormal day-night blood pressure and systemic hemodynamics in heart failure compared to normotension and controlled hypertensionSrungavarapu Sambasiva Rao, Khatri Chander, Osmond Peter, Izzo Joseph