Final ID: Mo4006
Sex-specific differences in the mechano-metabolic behavior of the myocardium in mice
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Introduction: The pathophysiological mechanisms of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) involve impaired relaxation and restricted filling of the left ventricle (LV). Both mechanical and metabolic impairments are expected to occur in the myocardium in LVDD. The mechano-metabolic interplay underlying LVDD-related remodeling remains understudied. Understanding this interplay is especially important for identifying sex-specific susceptibilities to LVDD. In this study, we present an approach to assess key biomechanical and energetic differences through ex-vivo benchtop assays of cardiac mechanoenergetics.
Methods: Male (n=8) and female (n=8) 8-10-week-old wild-type mice were used. The LV free wall (LVFW) was harvested from the mice and immediately placed in PBS at 1°C. Mechanical testing was performed to measure passive stiffness and viscoelastic relaxation time (M and F; n = 4 each). The ex-vivo tissue was subjected to equibiaxial stretch at 1% per second and allowed to relax for a period of 10 minutes. Energetics were quantified by homogenizing 10 mg of LVFW tissue using buffer A and analyzing the supernatant ATP concentration (M and F; n = 4 each).
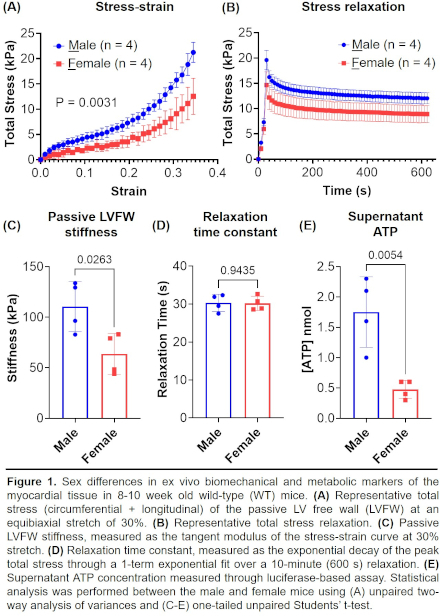
Results: Sex differences were evident in both passive mechanical and metabolic indices of LVFW tissues. Stress-strain analysis revealed significantly higher total stress in male mice compared to females at various stages of equibiaxial stretching (Fig. 1A). However, a very similar viscoelastic relaxation behavior was observed between male and female (Fig. 1B). Despite the presence of increased LVFW stiffness in the male mice (Fig. 1C), consistent relaxation time constants were maintained between all mice, evidenced via similar standard deviation (Fig. 1D). Energetic analysis showed a significant difference between male and female mice (M vs. F: 1.75 ± 0.58 vs. 0.48 ± 0.15 nmol) (Fig. 1E).
Conclusion: This study provided ex vivo insights into sex-specific mechano-metabolic markers of the myocardial tissue in mice. Our findings demonstrate that male mice possess stiffer myocardial tissue and higher basal ATP concentrations compared to females, despite similar stress relaxation kinetics. Future work using this approach will investigate the mechano-metabolic remodeling in LVDD that accounts for sex-based physiological differences in myocardial stiffening and metabolic impairments.
Introduction: The pathophysiological mechanisms of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) involve impaired relaxation and restricted filling of the left ventricle (LV). Both mechanical and metabolic impairments are expected to occur in the myocardium in LVDD. The mechano-metabolic interplay underlying LVDD-related remodeling remains understudied. Understanding this interplay is especially important for identifying sex-specific susceptibilities to LVDD. In this study, we present an approach to assess key biomechanical and energetic differences through ex-vivo benchtop assays of cardiac mechanoenergetics.
Methods: Male (n=8) and female (n=8) 8-10-week-old wild-type mice were used. The LV free wall (LVFW) was harvested from the mice and immediately placed in PBS at 1°C. Mechanical testing was performed to measure passive stiffness and viscoelastic relaxation time (M and F; n = 4 each). The ex-vivo tissue was subjected to equibiaxial stretch at 1% per second and allowed to relax for a period of 10 minutes. Energetics were quantified by homogenizing 10 mg of LVFW tissue using buffer A and analyzing the supernatant ATP concentration (M and F; n = 4 each).
Results: Sex differences were evident in both passive mechanical and metabolic indices of LVFW tissues. Stress-strain analysis revealed significantly higher total stress in male mice compared to females at various stages of equibiaxial stretching (Fig. 1A). However, a very similar viscoelastic relaxation behavior was observed between male and female (Fig. 1B). Despite the presence of increased LVFW stiffness in the male mice (Fig. 1C), consistent relaxation time constants were maintained between all mice, evidenced via similar standard deviation (Fig. 1D). Energetic analysis showed a significant difference between male and female mice (M vs. F: 1.75 ± 0.58 vs. 0.48 ± 0.15 nmol) (Fig. 1E).
Conclusion: This study provided ex vivo insights into sex-specific mechano-metabolic markers of the myocardial tissue in mice. Our findings demonstrate that male mice possess stiffer myocardial tissue and higher basal ATP concentrations compared to females, despite similar stress relaxation kinetics. Future work using this approach will investigate the mechano-metabolic remodeling in LVDD that accounts for sex-based physiological differences in myocardial stiffening and metabolic impairments.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Community Outreach Program Focused on Hypertension Awareness Reaches 600+ People in Rural Georgia and Works to Build the Next Generation of Biomedical Scientists
Dent Elena, Ilatovskaya Daria, Pinkerton Brittany, Crider Emily, Ryan Michael, Sullivan Jennifer
Ambulatory Atrial Fibrillation Ablation is Underutilized Among Women and Racial/Ethnic Minority GroupsMakmal Noam, Koplan Bruce