Final ID: MP2412
Social Network Analysis for Clinical Phenotyping of Complex Relationships of Cardiac Cycle Phases Represented in Tissue Doppler Echocardiography of Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: We used Social Network Analysis (SNA) to phenotypic and clinical characterization of tissue Doppler (TD)signals representing different phases of the cardiac cycle in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Methods: Retrospectively, 275 HFpEF patients (64±18 years, 54% females, EF: 57±7%, followed for median 2.8 years for heart failure hospitalization and mortality) were studied. TD signals were measured [Positive and negative pre systolic (PREp and PREn) and ejection systolic (S'), negative and positive post systolic velocities (POEn and POEp) and early diastolic (e’) velocities]. PREp/n, POEn/p, PREp/S’ and POEn/e’ were calculated to represent relationships between the biphasic PRE and POE and different parts of systole and diastole. SNA was done using Python and google Colab. The above parameters were treated as the edges and patients as the nodes. Cosine similarity and Louvain clustering were used for SNA..
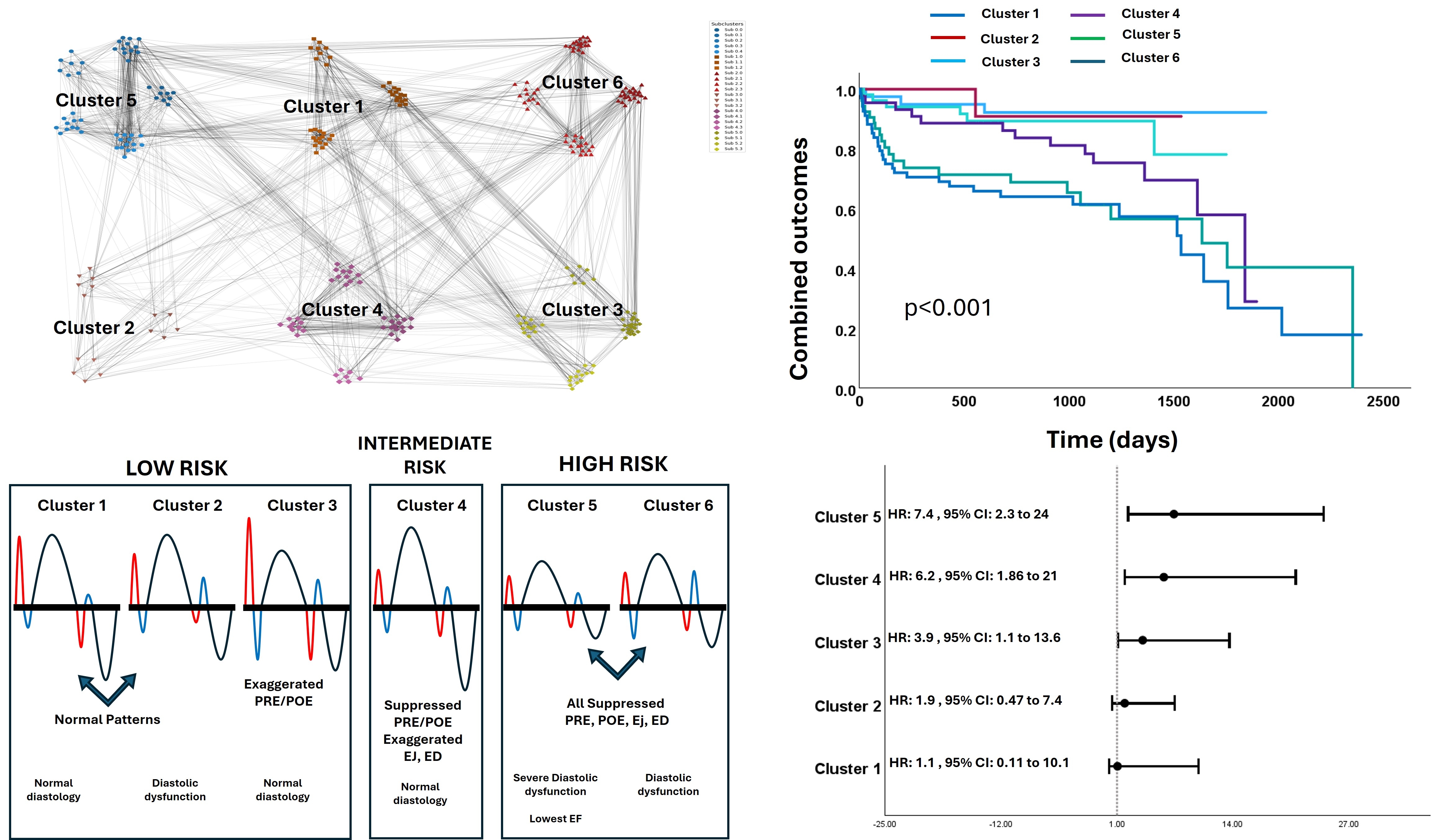
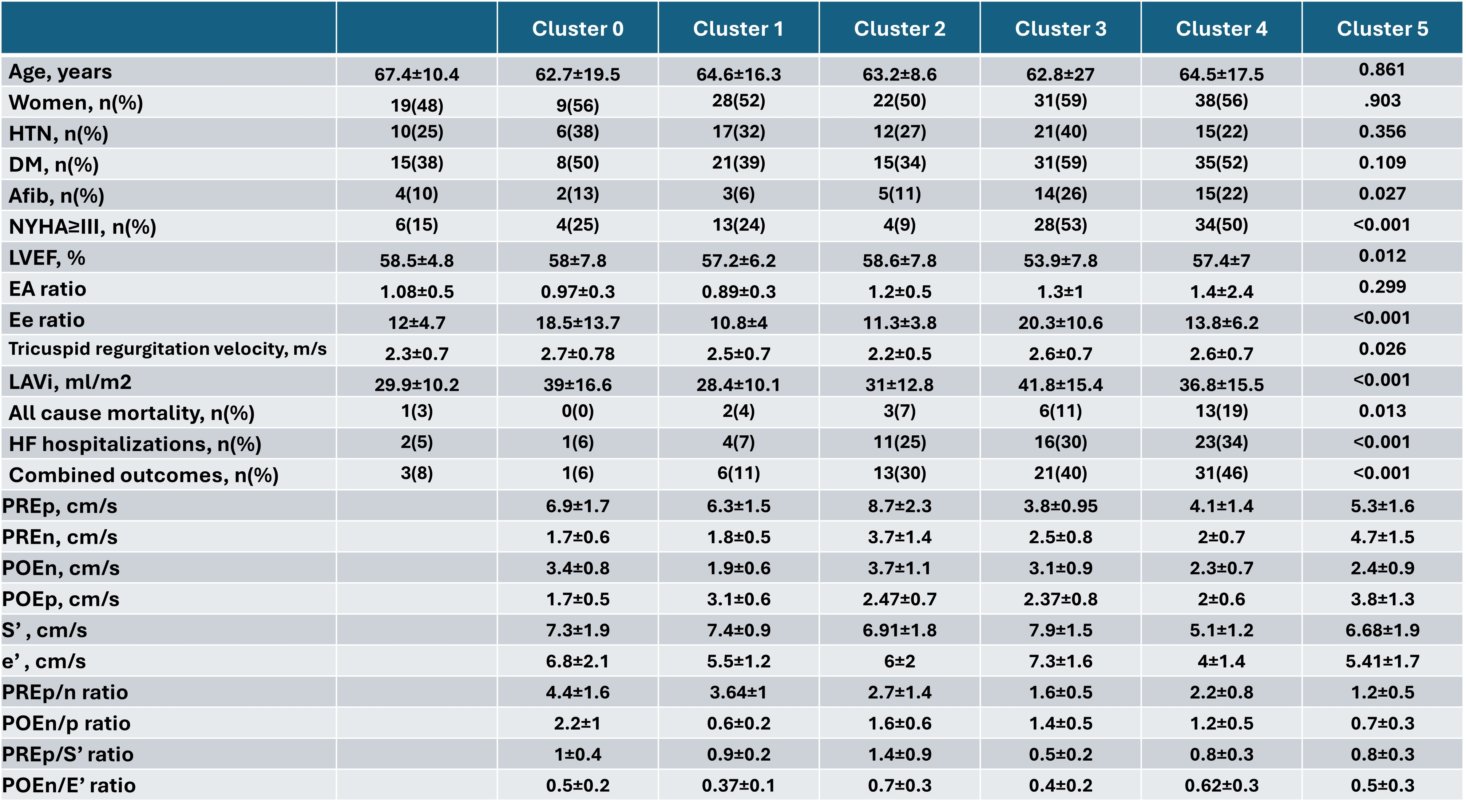
Results: SNA yielded 6 clusters (edges: 2654, density 0.1, average degree: 19.3, average clustering coefficient: 0.42, assortativity: .165, path length: 2.77, figure 1, table 1). Cluster 1 (40 patients) and 2 (16 patients) had preserved TD signals relationships. Cluster 3 (54 patients) exaggerated PRE and POE with mild S’ depression, cluster 4 (44 patients) had depressed PRE and POE despite preserved S’ and e’. Cluster 5 (53 patients) and 6 (68 patients) showed all signals depressed. Clusters were not different for age, sex, risk factors or co-morbidities. NYHA class was worst in clusters 4 and 5, while clusters 1 and 5 had the worst diastolic profiles, and cluster 5 had intermediate diastolic profiles. Survival analyses suggested clusters 0,1, and 2 as low risk, cluster 3 was intermediate, and clusters 4 and 5 as high risk. Moreover, clusters were subdivided into smaller clusters that differentiate TD relationships further; in addition to specific clinical and echocardiographic features (Cluster 3 differentiates based on E/A ratio, Cluster 5 differentiates based on E/e’ and symptoms, Cluster 6 differentiates based on LAVi).
Conclusions: In HFpEF patients PRE, ejection, POE, and early diastolic TD signals share complex clinically meaningful relationships that are difficult to express using traditional statistical techniques. Clustering using SNA can help computationally and visually stratify such relationships. Exploring such relationships in larger studies can unlock phenotypic characterization and management strategies.
Methods: Retrospectively, 275 HFpEF patients (64±18 years, 54% females, EF: 57±7%, followed for median 2.8 years for heart failure hospitalization and mortality) were studied. TD signals were measured [Positive and negative pre systolic (PREp and PREn) and ejection systolic (S'), negative and positive post systolic velocities (POEn and POEp) and early diastolic (e’) velocities]. PREp/n, POEn/p, PREp/S’ and POEn/e’ were calculated to represent relationships between the biphasic PRE and POE and different parts of systole and diastole. SNA was done using Python and google Colab. The above parameters were treated as the edges and patients as the nodes. Cosine similarity and Louvain clustering were used for SNA..
Results: SNA yielded 6 clusters (edges: 2654, density 0.1, average degree: 19.3, average clustering coefficient: 0.42, assortativity: .165, path length: 2.77, figure 1, table 1). Cluster 1 (40 patients) and 2 (16 patients) had preserved TD signals relationships. Cluster 3 (54 patients) exaggerated PRE and POE with mild S’ depression, cluster 4 (44 patients) had depressed PRE and POE despite preserved S’ and e’. Cluster 5 (53 patients) and 6 (68 patients) showed all signals depressed. Clusters were not different for age, sex, risk factors or co-morbidities. NYHA class was worst in clusters 4 and 5, while clusters 1 and 5 had the worst diastolic profiles, and cluster 5 had intermediate diastolic profiles. Survival analyses suggested clusters 0,1, and 2 as low risk, cluster 3 was intermediate, and clusters 4 and 5 as high risk. Moreover, clusters were subdivided into smaller clusters that differentiate TD relationships further; in addition to specific clinical and echocardiographic features (Cluster 3 differentiates based on E/A ratio, Cluster 5 differentiates based on E/e’ and symptoms, Cluster 6 differentiates based on LAVi).
Conclusions: In HFpEF patients PRE, ejection, POE, and early diastolic TD signals share complex clinically meaningful relationships that are difficult to express using traditional statistical techniques. Clustering using SNA can help computationally and visually stratify such relationships. Exploring such relationships in larger studies can unlock phenotypic characterization and management strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
12-lead electrocardiograms predict adverse cardiovascular outcomes of emergency department patients
Haimovich Julian, Kolossvary Marton, Alam Ridwan, Padros I Valls Raimon, Lu Michael, Aguirre Aaron
A DHX38 Spliceosomal Mutation Impairs MYC Signaling, Cardiac Transcriptome Splicing, and Leads to Diastolic DysfunctionIwanski Jessika, Sarvagalla Sailu, Methawasin Mei, Van Den Berg Marloes, Churko Jared