Final ID: MP305
Prostate Cancer Imposes Significant Risk for Cardiovascular Events: Insights from the CLARIFY Registry
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Prostate cancer tends to be a slow-growing malignancy, and oftentimes patient mortality is the result of non-cancerous disease processes. Recent studies have identified an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in prostate cancer (PCa) patients—this may relate to increased cardiovascular susceptibility compared to the average population.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that prostate cancer patients had a higher propensity for major adverse cardiac events (MACE) than patients with similar cardiovascular risk factors.
Aims:
Our study aimed to assess CVD susceptibility in PCa patients by evaluating MACE rates in PCa and non-PCa patients within similar baseline cardiovascular risk categories, as determined by coronary artery calcium (CAC) score.
Methods:
Using data obtained from the CLARIFY registry (Clinicaltrials.gov NCT04075162), a large prospective study of no-charge CAC testing, we identified 1,942 patients with PCa and 50,511 non-PCa patients over 9 years of the program (January 2014-September 2023). Patients were divided by CAC group (CAC = 0, 1-99, 100-399, ≥ 400) and followed for MACE (myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure admission, revascularization, and death). Cohort analyses compared cumulative MACE probability using Kaplan-Meier and Mantel-Cox test and hazard ratios (HR) from Cox-proportional hazard regression adjusted for race, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and obesity.
Results:
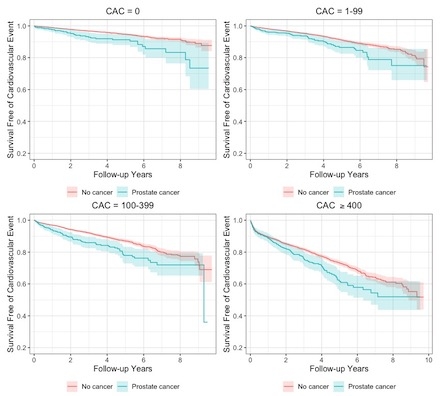
Median follow-up time was 1.7 years with 289 MACE (15%) in PCa and 2930 MACE (6%) in non-PCa patients. PCa was associated with significantly increased MACE (p < .01) in all CAC groups (Figure). PCa patients had significantly increased hazard for MACE compared to non-PCa patients in CAC = 0 (HR 1.63 [1.14, 2.35], p < .01), CAC = 100-399 (HR 1.53 [1.20, 1.95], p < .01), and CAC ≥ 400 (HR 1.25 [1.04, 1.50], p = 0.02).
Conclusion:
PCa patients with no prior history of MACE are at a significantly increased risk for MACE in almost all CAC groups after adjustment for multiple factors. These data suggest mechanisms unique to PCa and/or its treatment that confers higher CVD events. Thus, there should be a lower threshold to implement cardiac risk reduction measures, including lifestyle modifications, statins, and other medical therapy, in PCa patients.
Prostate cancer tends to be a slow-growing malignancy, and oftentimes patient mortality is the result of non-cancerous disease processes. Recent studies have identified an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in prostate cancer (PCa) patients—this may relate to increased cardiovascular susceptibility compared to the average population.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that prostate cancer patients had a higher propensity for major adverse cardiac events (MACE) than patients with similar cardiovascular risk factors.
Aims:
Our study aimed to assess CVD susceptibility in PCa patients by evaluating MACE rates in PCa and non-PCa patients within similar baseline cardiovascular risk categories, as determined by coronary artery calcium (CAC) score.
Methods:
Using data obtained from the CLARIFY registry (Clinicaltrials.gov NCT04075162), a large prospective study of no-charge CAC testing, we identified 1,942 patients with PCa and 50,511 non-PCa patients over 9 years of the program (January 2014-September 2023). Patients were divided by CAC group (CAC = 0, 1-99, 100-399, ≥ 400) and followed for MACE (myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure admission, revascularization, and death). Cohort analyses compared cumulative MACE probability using Kaplan-Meier and Mantel-Cox test and hazard ratios (HR) from Cox-proportional hazard regression adjusted for race, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and obesity.
Results:
Median follow-up time was 1.7 years with 289 MACE (15%) in PCa and 2930 MACE (6%) in non-PCa patients. PCa was associated with significantly increased MACE (p < .01) in all CAC groups (Figure). PCa patients had significantly increased hazard for MACE compared to non-PCa patients in CAC = 0 (HR 1.63 [1.14, 2.35], p < .01), CAC = 100-399 (HR 1.53 [1.20, 1.95], p < .01), and CAC ≥ 400 (HR 1.25 [1.04, 1.50], p = 0.02).
Conclusion:
PCa patients with no prior history of MACE are at a significantly increased risk for MACE in almost all CAC groups after adjustment for multiple factors. These data suggest mechanisms unique to PCa and/or its treatment that confers higher CVD events. Thus, there should be a lower threshold to implement cardiac risk reduction measures, including lifestyle modifications, statins, and other medical therapy, in PCa patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Comparison Between Global Longitudinal Strain (GLS) Derived with CMR Feature-Tracking (CMR-FT) and 2D Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography (2D-STE) to Monitor Cancer Therapy-Related Cardiac Dysfunction (CTRCD)
Kar Julia, Cohen Michael, Revere Cherie, Mcquiston Samuel, Malozzi Christopher
Age-stratified Monogenic and Polygenic Contributions for Atrial Fibrillation in the All of Us Research ProgramChen Zhanlin, Gordon Adam, Webster Gregory