Final ID: Su1006
Targeting Cerebrovascular Risk in Diabetes: GLP-1 Receptor Agonists as Neuroprotective Agents
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are established therapies for type 2 diabetes (T2D) that lower major adverse cardiovascular events. Their specific impact on stroke incidence and stroke-related death remains unclear.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that treatment with GLP-1 RAs reduces the risk of nonfatal stroke in T2D patients and may also influence stroke-related mortality.
Methods:
A systematic search of PubMed (2010–June 2025) identified randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of GLP-1 RAs in adults with T2D reporting stroke outcomes. Trials without separate stroke data were excluded. The primary outcome was first occurrence of nonfatal stroke; the secondary outcome was fatal stroke. A total of thirteen RCTs (n = 58 432) met inclusion criteria. Hazard ratios (HRs) for each outcome were pooled using a random-effects model. Study quality was assessed using Cochrane Risk of Bias tools. Agent-specific effects and subgroup analyses in patients with established cardiovascular disease (CVD) were also evaluated.
Results:
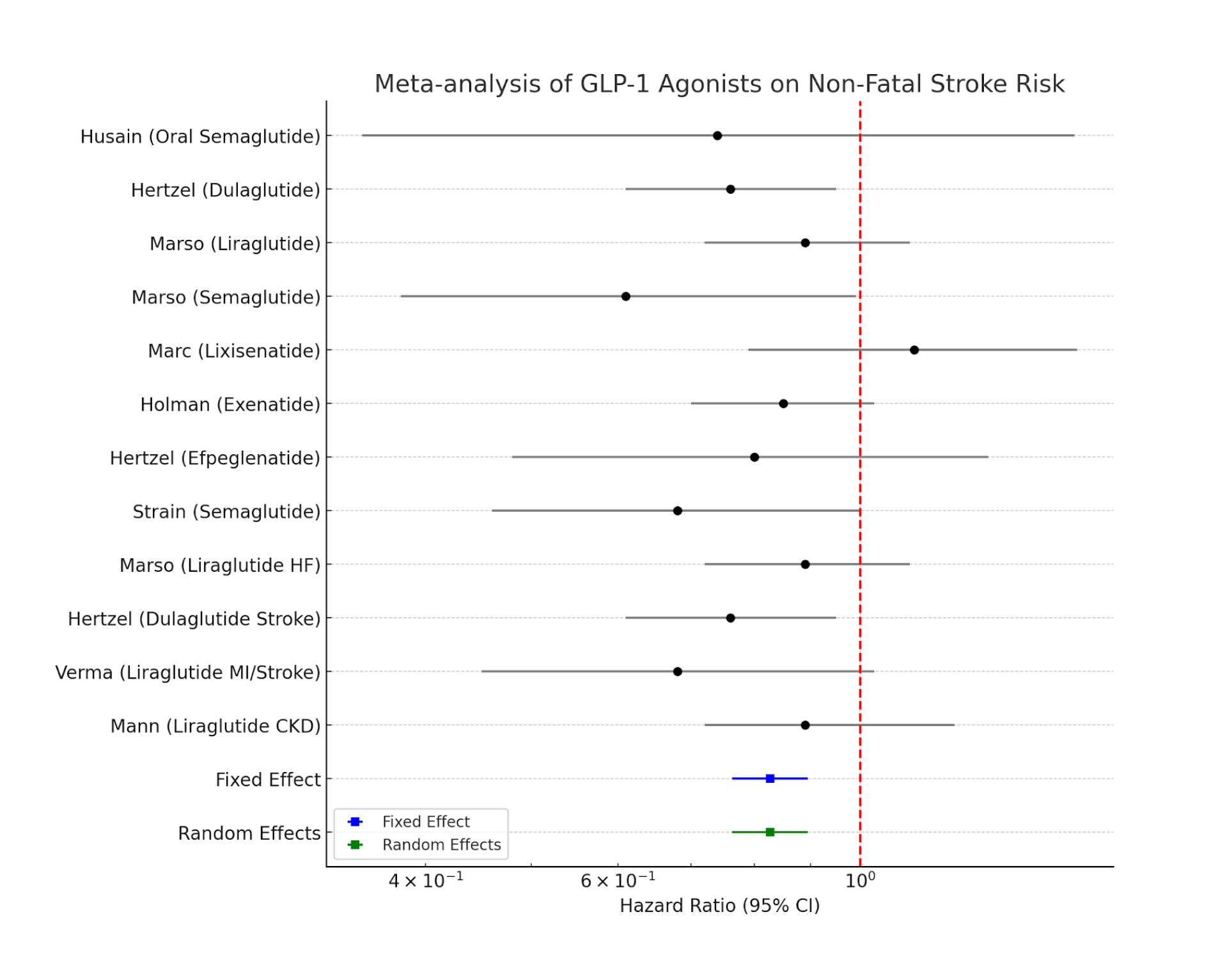
A total of thirteen trials involving liraglutide, semaglutide, dulaglutide, exenatide, lixisenatide, and efpeglenatide were analyzed. The median follow-up was 3.4 years (range 0.5–5.4 years). Overall, GLP-1 RA therapy was associated with an 18 percent reduction in nonfatal stroke risk (pooled HR 0.82; 95 percent CI 0.75–0.90; I^2 = 25 percent; p < 0.001). Dulaglutide achieved a significant reduction (HR 0.76; 0.61–0.95), as did semaglutide (HR 0.61; 0.38–0.99), while lixisenatide showed no benefit (HR 1.12; 0.79–1.58). Patients with prior CVD experienced an amplified benefit (HR 0.68; 0.45–1.03). No statistically significant effect on fatal stroke was observed (HR 0.71; 0.47–1.07; based on three trials). Stroke subtypes were reported in seven of thirteen trials; 100 percent reported nonfatal stroke separately, and 32 percent reported fatal stroke separately. The event rate in control arms averaged 2.1 percent per year.
Conclusions:
In adults with T2D, GLP-1 RA therapy significantly lowers the risk of nonfatal stroke, especially with dulaglutide and semaglutide, while no definitive reduction in stroke-related death was detected. These findings support preferential GLP-1 RA selection for cerebrovascular risk reduction in high-risk diabetic populations
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are established therapies for type 2 diabetes (T2D) that lower major adverse cardiovascular events. Their specific impact on stroke incidence and stroke-related death remains unclear.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that treatment with GLP-1 RAs reduces the risk of nonfatal stroke in T2D patients and may also influence stroke-related mortality.
Methods:
A systematic search of PubMed (2010–June 2025) identified randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of GLP-1 RAs in adults with T2D reporting stroke outcomes. Trials without separate stroke data were excluded. The primary outcome was first occurrence of nonfatal stroke; the secondary outcome was fatal stroke. A total of thirteen RCTs (n = 58 432) met inclusion criteria. Hazard ratios (HRs) for each outcome were pooled using a random-effects model. Study quality was assessed using Cochrane Risk of Bias tools. Agent-specific effects and subgroup analyses in patients with established cardiovascular disease (CVD) were also evaluated.
Results:
A total of thirteen trials involving liraglutide, semaglutide, dulaglutide, exenatide, lixisenatide, and efpeglenatide were analyzed. The median follow-up was 3.4 years (range 0.5–5.4 years). Overall, GLP-1 RA therapy was associated with an 18 percent reduction in nonfatal stroke risk (pooled HR 0.82; 95 percent CI 0.75–0.90; I^2 = 25 percent; p < 0.001). Dulaglutide achieved a significant reduction (HR 0.76; 0.61–0.95), as did semaglutide (HR 0.61; 0.38–0.99), while lixisenatide showed no benefit (HR 1.12; 0.79–1.58). Patients with prior CVD experienced an amplified benefit (HR 0.68; 0.45–1.03). No statistically significant effect on fatal stroke was observed (HR 0.71; 0.47–1.07; based on three trials). Stroke subtypes were reported in seven of thirteen trials; 100 percent reported nonfatal stroke separately, and 32 percent reported fatal stroke separately. The event rate in control arms averaged 2.1 percent per year.
Conclusions:
In adults with T2D, GLP-1 RA therapy significantly lowers the risk of nonfatal stroke, especially with dulaglutide and semaglutide, while no definitive reduction in stroke-related death was detected. These findings support preferential GLP-1 RA selection for cerebrovascular risk reduction in high-risk diabetic populations
More abstracts on this topic:
Added Value of Clinical Data Over Claims Data in Controlling for Confounding by Indication: A Case Example Assessing the Effectiveness of Community-Based Rehabilitation Therapy After Stroke
Zhang Shuqi, Freburger Janet, Trogdon Justin, Patterson Charity, Wen Molly, Jones Sara
A ChatGLM-based stroke diagnosis and prediction toolSong Xiaowei, Wang Jiayi, Ma Weizhi, Wu Jian, Wang Yueming, Gao Ceshu, Wei Chenming, Pi Jingtao