Final ID: MP2660
Simultaneous Heart-Kidney Transplantation Before and After the 2023 UNOS Policy Change
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Simultaneous heart-kidney transplantation (SHKT) is the preferred therapy for patients with combined heart and kidney failure. In 2023, the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) introduced policy changes to streamline SHKT allocation, including medical eligibility criteria and a safety net policy prioritizing kidney allocation for heart transplant (HT) recipients with irreversible renal dysfunction. The impact of these changes on recipient characteristics and outcomes remains unclear.
Methods:
We queried the UNOS database to identify patients who received SHKT from January 2021 to December 2024. Recipients were grouped into pre-policy (1/1/2021–9/26/2023) and post-policy (10/1/2023–12/31/2024) cohorts. Those transplanted between 9/27 and 9/30/2023 or who received HT with non-kidney organs were excluded. Kaplan-Meier and log-rank tests were used to assess graft and patient survival.
Results:
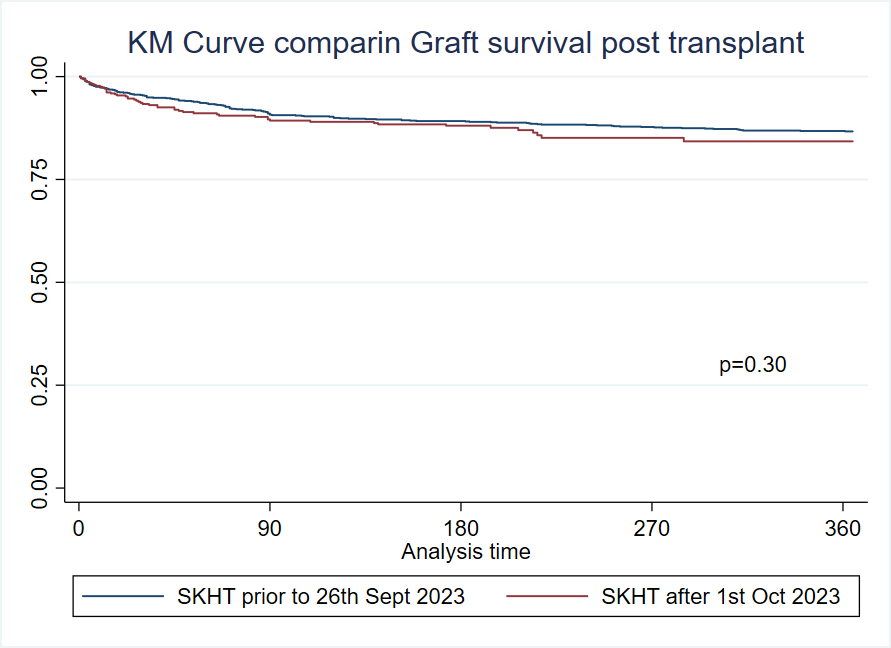
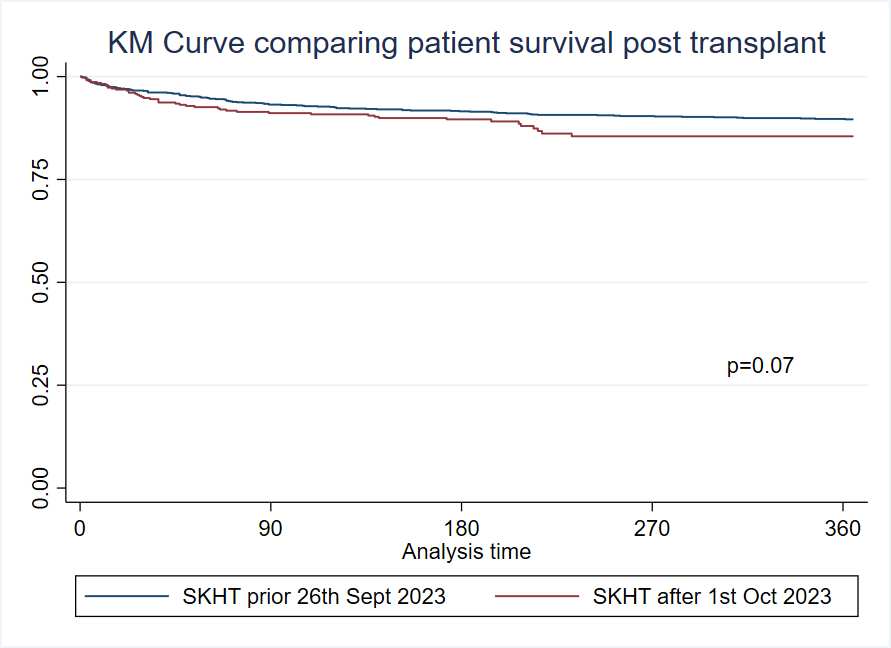
A total of 1,065 SHKT recipients were analyzed pre-policy and 464 post-policy. Median age was similar (58 years; p=0.90), but the proportion of male recipients declined post-policy (78.5% vs. 72.4%, p=0.01). Racial distribution was unchanged. Diabetes prevalence increased post-policy (51.7% vs. 45.1%, p=0.017). BMI and dialysis rates were comparable. Cold ischemia time increased post-policy (19.0 vs. 17.3 hours, p=0.0003). Fewer recipients received kidneys with KDPI ≤20% (53.4% vs. 59.8%, p=0.02), while KDPI 21–84% utilization increased (46.1% vs. 40.1%, p=0.03). Renal function among non-dialysis patients remained similar (median GFR 30.0 vs. 31.3 ml/min, p=0.14). GFR category distributions did not differ. One-year patient and graft survival were unchanged.
Conclusion:
The 2023 UNOS SHKT policy changes were associated with modest shifts in recipient comorbidities and kidney quality. Despite these changes, early renal outcomes and one-year survival remained stable, supporting the effectiveness of the new allocation strategy while potentially expanding access for higher-risk patients.
Simultaneous heart-kidney transplantation (SHKT) is the preferred therapy for patients with combined heart and kidney failure. In 2023, the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) introduced policy changes to streamline SHKT allocation, including medical eligibility criteria and a safety net policy prioritizing kidney allocation for heart transplant (HT) recipients with irreversible renal dysfunction. The impact of these changes on recipient characteristics and outcomes remains unclear.
Methods:
We queried the UNOS database to identify patients who received SHKT from January 2021 to December 2024. Recipients were grouped into pre-policy (1/1/2021–9/26/2023) and post-policy (10/1/2023–12/31/2024) cohorts. Those transplanted between 9/27 and 9/30/2023 or who received HT with non-kidney organs were excluded. Kaplan-Meier and log-rank tests were used to assess graft and patient survival.
Results:
A total of 1,065 SHKT recipients were analyzed pre-policy and 464 post-policy. Median age was similar (58 years; p=0.90), but the proportion of male recipients declined post-policy (78.5% vs. 72.4%, p=0.01). Racial distribution was unchanged. Diabetes prevalence increased post-policy (51.7% vs. 45.1%, p=0.017). BMI and dialysis rates were comparable. Cold ischemia time increased post-policy (19.0 vs. 17.3 hours, p=0.0003). Fewer recipients received kidneys with KDPI ≤20% (53.4% vs. 59.8%, p=0.02), while KDPI 21–84% utilization increased (46.1% vs. 40.1%, p=0.03). Renal function among non-dialysis patients remained similar (median GFR 30.0 vs. 31.3 ml/min, p=0.14). GFR category distributions did not differ. One-year patient and graft survival were unchanged.
Conclusion:
The 2023 UNOS SHKT policy changes were associated with modest shifts in recipient comorbidities and kidney quality. Despite these changes, early renal outcomes and one-year survival remained stable, supporting the effectiveness of the new allocation strategy while potentially expanding access for higher-risk patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Trial of Patients Receiving Remote Ischemic Conditioning in Early Stroke (PRICES) in a Tertiary Hospital in the Philippines: An Open Label Study
Ang Kevin Royce, Juangco Dan, Hernandez Maria Kim
A Case of Steroid-Refractory Immune-checkpoint-inhibitor Induced Myocarditis Responsive to Mycophenolate and Anti-thymocyte globulinDabdoub Jorge, Wilson Michael, Gottbrecht Matthew, Salazar Ryan, Shih Jeffrey