Final ID: MP2336
Deep Learning Segmentation for Automated Measurement of Infarct Size in Preclinical Myocardial Infarction Models
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Myocardial infarct size (IS) is the most robust endpoint for evaluating cardioprotective strategies in preclinical ischemia/reperfusion studies. The gold standard for IS quantification in preclinical studies (triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining) is traditionally performed manually and is prone to inter-operator variability. Here, we propose a deep learning segmentation pipeline to automate IS quantification in TTC-stained rat heart sections.
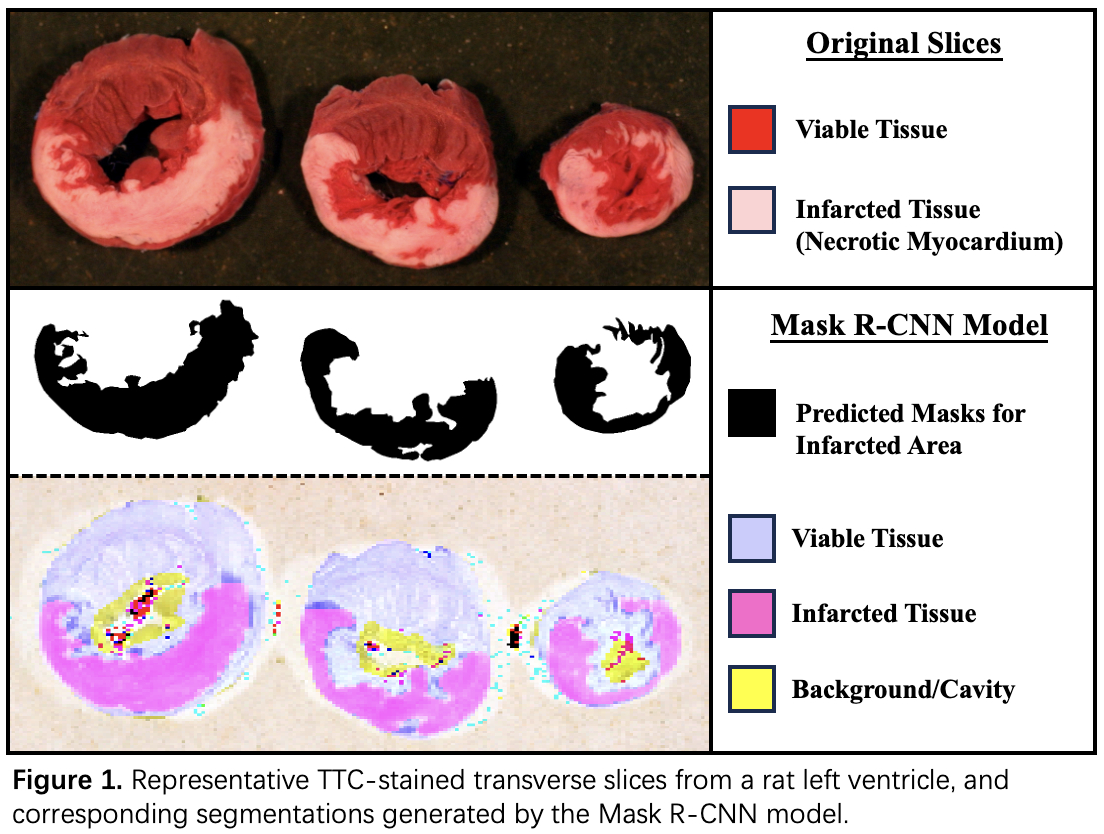
Methods: We used n=165 Sprague-Dawley rats (150–300 g, 1–2 months, 69% female). Myocardial infarction (MI) was induced using a standard occlusion/reperfusion model by occluding the proximal left coronary artery for 30 minutes, followed by 3 hours of reperfusion. After euthanasia, the left ventricle (LV) was excised, transversely sliced, and incubated in 1% TTC at 37 °C for 15 minutes to distinguish necrotic myocardium (pale white) from viable tissues (brick red, Fig. 1). Manual IS was quantified by contouring infarcted and total LV areas in each slice using ImageJ (NIH, USA). To automate the IS measurement from TTC-stained heart slices, we implemented a deep learning segmentation pipeline based on the mask region-based convolutional neural network (Mask R-CNN) architecture. Ground truth masks for infarcted regions and LV area were created using VGG Image Annotator. Images from n=140 rats were used for training, as well as an additional 1,400 images generated by data augmentation. All training and preprocessing pipelines were conducted in Python. Dice similarity coefficient (Dice score) was used to evaluate the model performance. The best-performing Mask R-CNN model was blindly tested on 25 additional MI rats.
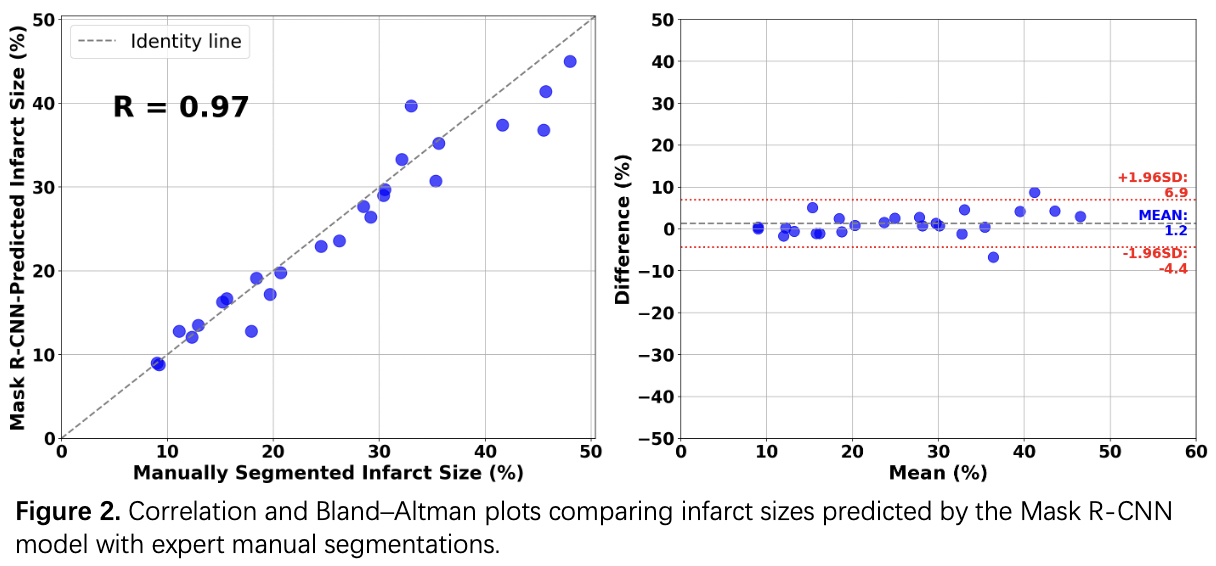
Results: Infarct sizes calculated from Mask R-CNN-generated segmentations showed strong agreement with the ones from expert-annotated manual segmentations from TTC-stained LV slices (R = 0.97, p < 0.0001) when tested on heart slices from 25 additional MI rats, supporting the model’s accuracy and validity.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that deep learning segmentation accurately and automatically quantifies infarct size from TTC-stained images without operator input. This automated approach is rapid, reproducible, and unbiased, significantly reducing inter-operator variability and manual workload in preclinical studies. By streamlining infarct size assessment in preclinical cardio-protection studies, it has the potential to improve consistency and translational value in cardiac research.
Methods: We used n=165 Sprague-Dawley rats (150–300 g, 1–2 months, 69% female). Myocardial infarction (MI) was induced using a standard occlusion/reperfusion model by occluding the proximal left coronary artery for 30 minutes, followed by 3 hours of reperfusion. After euthanasia, the left ventricle (LV) was excised, transversely sliced, and incubated in 1% TTC at 37 °C for 15 minutes to distinguish necrotic myocardium (pale white) from viable tissues (brick red, Fig. 1). Manual IS was quantified by contouring infarcted and total LV areas in each slice using ImageJ (NIH, USA). To automate the IS measurement from TTC-stained heart slices, we implemented a deep learning segmentation pipeline based on the mask region-based convolutional neural network (Mask R-CNN) architecture. Ground truth masks for infarcted regions and LV area were created using VGG Image Annotator. Images from n=140 rats were used for training, as well as an additional 1,400 images generated by data augmentation. All training and preprocessing pipelines were conducted in Python. Dice similarity coefficient (Dice score) was used to evaluate the model performance. The best-performing Mask R-CNN model was blindly tested on 25 additional MI rats.
Results: Infarct sizes calculated from Mask R-CNN-generated segmentations showed strong agreement with the ones from expert-annotated manual segmentations from TTC-stained LV slices (R = 0.97, p < 0.0001) when tested on heart slices from 25 additional MI rats, supporting the model’s accuracy and validity.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that deep learning segmentation accurately and automatically quantifies infarct size from TTC-stained images without operator input. This automated approach is rapid, reproducible, and unbiased, significantly reducing inter-operator variability and manual workload in preclinical studies. By streamlining infarct size assessment in preclinical cardio-protection studies, it has the potential to improve consistency and translational value in cardiac research.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel ECG Time-Frequency Eyeball Method for Robust Detection of Myocardial Infarction from Single-Channel ECG: A Preclinical Study
Alavi Rashid, Li Jiajun, Dai Wangde, Matthews Ray, Pahlevan Niema, Kloner Robert, Gharib Morteza
A Novel Multivariate Scoring System for Diagnosing Post-Myocardial Infarction Pericarditis Following Percutaneous Coronary InterventionBolaji Olayiwola, Omoru Okiemute, Upreti Prakash, Echari Blanche, Shoar Saeed, Basit Jawad, Alraies M Chadi