Final ID: Mo2103
Dynamic Autonomic Adaptation During Cognitive Load: Heart Rate Variability Changes from Resting State to Visuo-Spatial Working Memory Task
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The autonomic nervous system dynamically adjusts cardiac regulation during cognitive challenges, reflecting the interplay between sympathetic and parasympathetic branches to support task performance.
Objective: To investigate within-subject changes in heart rate variability (HRV) in healthy individuals transitioning from eyes-open resting baseline to performance of a visuo-spatial working memory task (VSWMT) with increasing cognitive demand.
Methods: Thirty healthy control participants completed five-minute ECG recordings during eyes-open resting conditions and during VSWMT. HRV analysis included time-domain measures (SDNN, RMSSD, pNN50) and frequency-domain metrics (LF power, HF power, LF/HF ratio). Statistical analyses compared HRV indices between resting and task conditions within subjects.
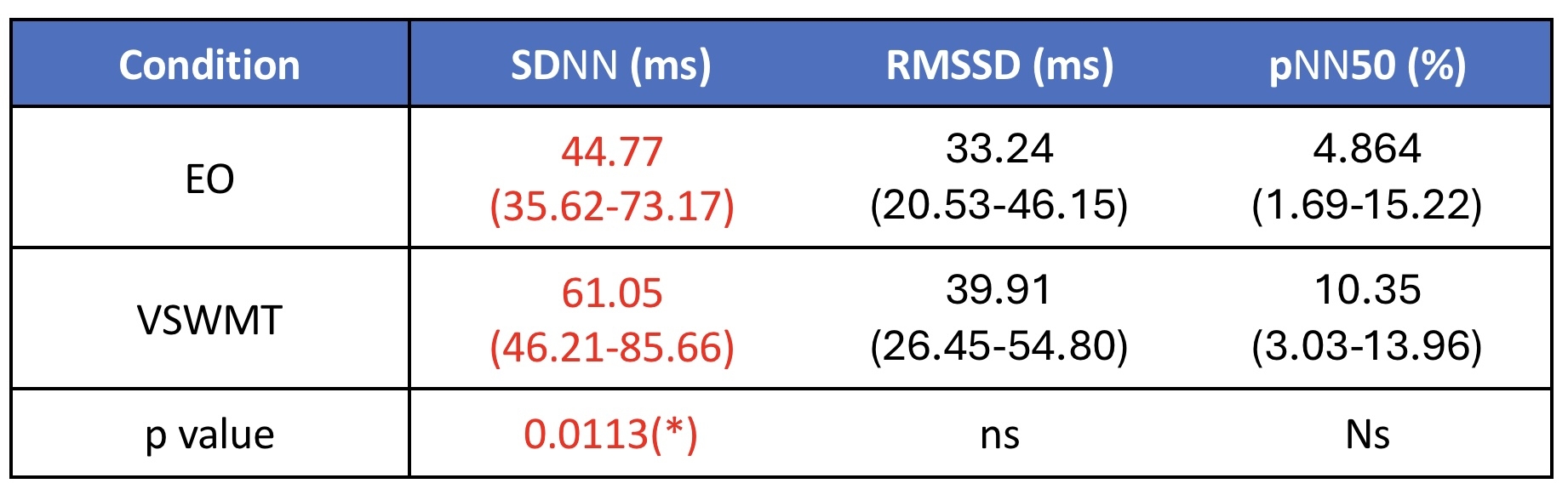
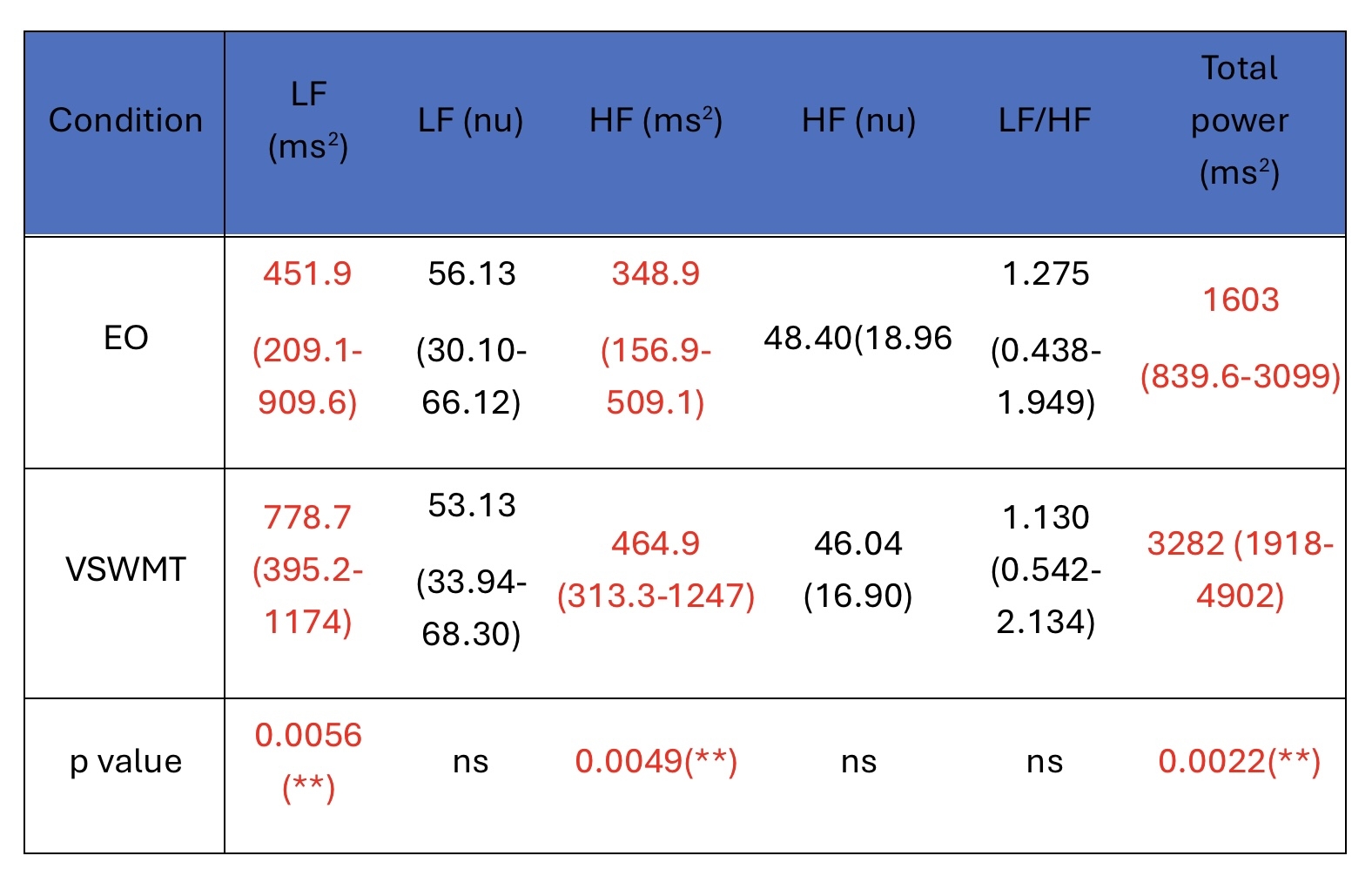
Results: Compared to baseline, controls exhibited significant increases in time-domain HRV parameter, SDNN, indicating enhanced parasympathetic modulation and greater beat-to-beat variability during task engagement. Frequency-domain analysis showed significant elevations in both LF and HF power (p < 0.05), with a stable LF/HF ratio, reflecting balanced sympathetic and parasympathetic activation. Total power of HRV increased significantly, supporting the notion of increased autonomic flexibility and adaptive regulation during cognitive load.
Conclusion: Healthy individuals display robust autonomic modulation characterized by increased variability and balanced autonomic activity during visuo-spatial working memory demands. These physiological adaptations likely facilitate optimal cognitive function and resilience to stress during challenging mental tasks.
Objective: To investigate within-subject changes in heart rate variability (HRV) in healthy individuals transitioning from eyes-open resting baseline to performance of a visuo-spatial working memory task (VSWMT) with increasing cognitive demand.
Methods: Thirty healthy control participants completed five-minute ECG recordings during eyes-open resting conditions and during VSWMT. HRV analysis included time-domain measures (SDNN, RMSSD, pNN50) and frequency-domain metrics (LF power, HF power, LF/HF ratio). Statistical analyses compared HRV indices between resting and task conditions within subjects.
Results: Compared to baseline, controls exhibited significant increases in time-domain HRV parameter, SDNN, indicating enhanced parasympathetic modulation and greater beat-to-beat variability during task engagement. Frequency-domain analysis showed significant elevations in both LF and HF power (p < 0.05), with a stable LF/HF ratio, reflecting balanced sympathetic and parasympathetic activation. Total power of HRV increased significantly, supporting the notion of increased autonomic flexibility and adaptive regulation during cognitive load.
Conclusion: Healthy individuals display robust autonomic modulation characterized by increased variability and balanced autonomic activity during visuo-spatial working memory demands. These physiological adaptations likely facilitate optimal cognitive function and resilience to stress during challenging mental tasks.
More abstracts on this topic:
Glycemic Changes After Peer Group Exergaming and Step Goal Activities Among Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes
IMPACT OF A MOBILE HEALTH CARDIOVASCULAR RISK SELF MANAGEMENT PROGRAM AMONG MEDICARE ADVANTAGE BENEFICIARIES
Lukasik James, Nally Laura, Jeon Sangchoon, Granados Alvaro, Weinzimer Stuart, Ash Garrett
IMPACT OF A MOBILE HEALTH CARDIOVASCULAR RISK SELF MANAGEMENT PROGRAM AMONG MEDICARE ADVANTAGE BENEFICIARIES
Gurumoorthy Vivek, Roberts Walter, Speer Clint, Paz Edo