Final ID: MP1319
Individualized mHealth Intervention and 12-Month Health Behavior Trajectories for Coronary Artery Disease: An Open-label, Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Coronary heart disease (CHD), the global leading cause of death (8.9 million annual fatalities), requires combined lifestyle and medication management. We developed iCARE - a personalized mHealth system delivering visualized recommendations to improve health behaviors and medication adherence.
Purpose: To investigate health behavior trajectories and evaluate effectiveness of iCARE in CHD patients.
Methods: This multicenter randomized controlled trial enrolled CHD patients (≥18 years, angiography-confirmed, Android smartphone owners) from two Chinese tertiary hospitals, randomizing them (1:1:1) to: 1) iCARE group receiving personalized mHealth interventions via visualized content (comics/videos/images) plus usual care, 2) text message group receiving text-based interventions, or 3) control group with usual care and daily logging. Primary outcomes were 12-month health behavior trajectories (medication adherence, physical activity, diet, smoking cessation) assessed at discharge, 3-, 6-, and 12-month intervals using validated scales and digital biomarkers, analyzed via generalized linear mixed models (GLMM) to identify temporal patterns and group×time interactions.
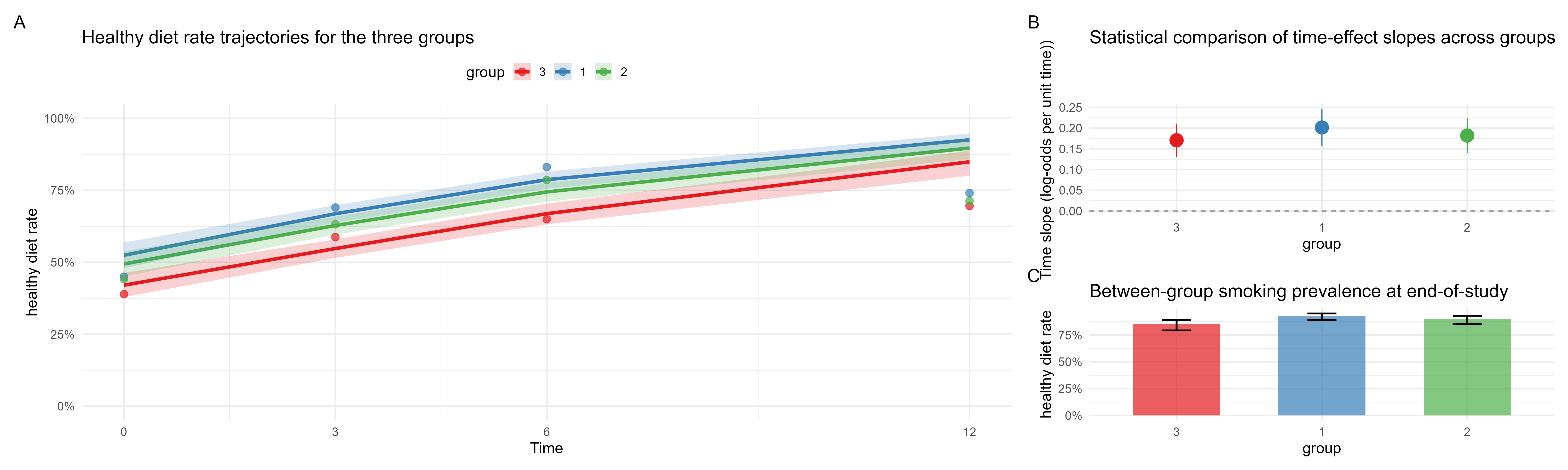
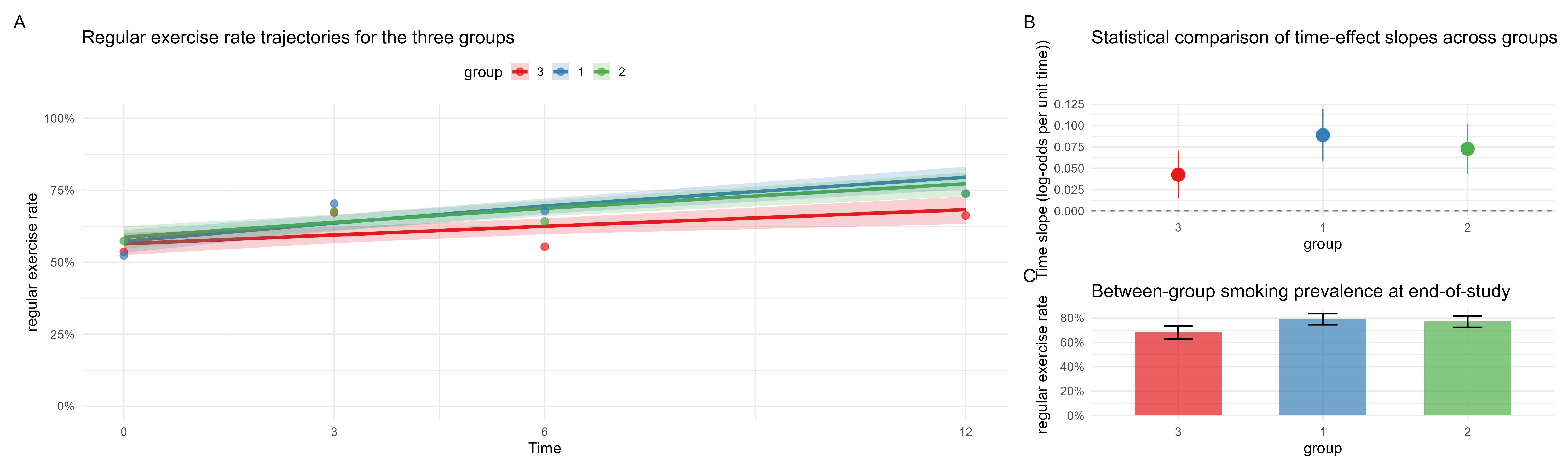
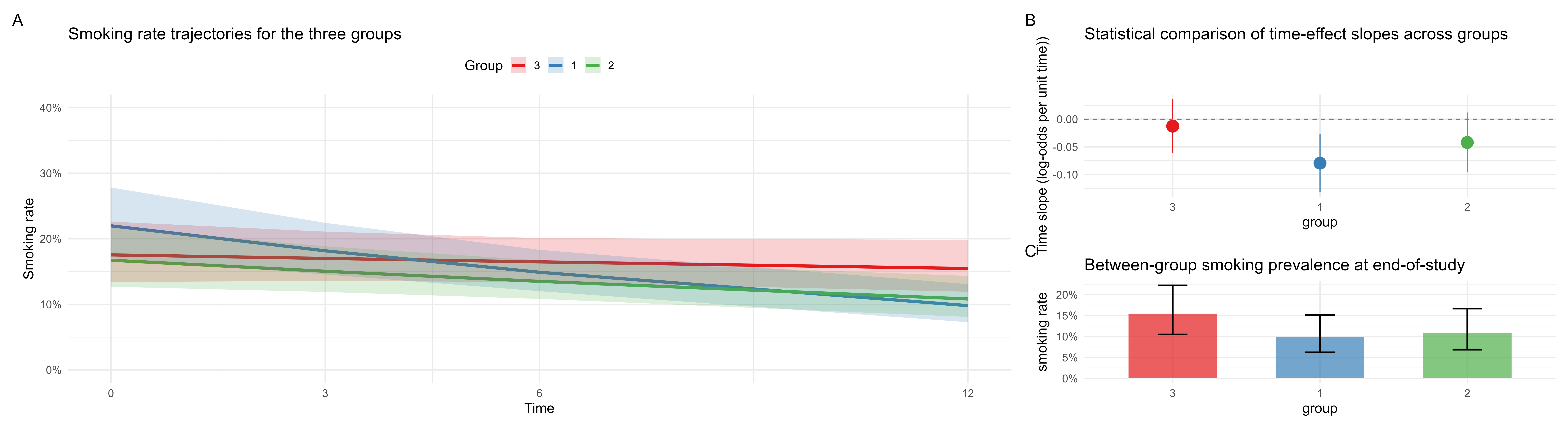
Results: Between September 2019 and May 2024, we screened 3,000 patients, enrolling 1,149 participants: 378 in the iCARE intervention group, 383 in the text message group, and 388 in the control group. In this 12-month randomized controlled trial, trajectory analyses using generalized linear mixed models revealed significant Group × Time interactions for all continuous behavioral outcomes (all p<0.001). The iCARE group demonstrated greater monthly increases in healthy diet rate (β=0.41, 95%CI[0.25-0.57]) and medication adherence rate (β=0.38, 95%CI[0.22-0.54] ), while the text message group showed superior improvement in regular exercise rate (β=0.35, 95%CI[0.20-0.50]). Both interventions significantly reduced smoking rates versus control (iCARE: β=-0.43, 95%CI[-0.58,-0.28]; text: β=-0.31, 95%CI[-0.46,-0.16]). Peak improvements occurred at 6 months (e.g., maximum between-group difference in medication adherence: 12.4 percentage points, 95%CI[9.1-15.7]). Substantial between-individual variability was observed (slope variances: 0.12-0.19), particularly in smoking trajectories.
Conclusion: The iCARE system effectively improves dietary, exercise, and medication adherence in CHD patients, with the greatest behavior change typically occurring at 6 months.
Purpose: To investigate health behavior trajectories and evaluate effectiveness of iCARE in CHD patients.
Methods: This multicenter randomized controlled trial enrolled CHD patients (≥18 years, angiography-confirmed, Android smartphone owners) from two Chinese tertiary hospitals, randomizing them (1:1:1) to: 1) iCARE group receiving personalized mHealth interventions via visualized content (comics/videos/images) plus usual care, 2) text message group receiving text-based interventions, or 3) control group with usual care and daily logging. Primary outcomes were 12-month health behavior trajectories (medication adherence, physical activity, diet, smoking cessation) assessed at discharge, 3-, 6-, and 12-month intervals using validated scales and digital biomarkers, analyzed via generalized linear mixed models (GLMM) to identify temporal patterns and group×time interactions.
Results: Between September 2019 and May 2024, we screened 3,000 patients, enrolling 1,149 participants: 378 in the iCARE intervention group, 383 in the text message group, and 388 in the control group. In this 12-month randomized controlled trial, trajectory analyses using generalized linear mixed models revealed significant Group × Time interactions for all continuous behavioral outcomes (all p<0.001). The iCARE group demonstrated greater monthly increases in healthy diet rate (β=0.41, 95%CI[0.25-0.57]) and medication adherence rate (β=0.38, 95%CI[0.22-0.54] ), while the text message group showed superior improvement in regular exercise rate (β=0.35, 95%CI[0.20-0.50]). Both interventions significantly reduced smoking rates versus control (iCARE: β=-0.43, 95%CI[-0.58,-0.28]; text: β=-0.31, 95%CI[-0.46,-0.16]). Peak improvements occurred at 6 months (e.g., maximum between-group difference in medication adherence: 12.4 percentage points, 95%CI[9.1-15.7]). Substantial between-individual variability was observed (slope variances: 0.12-0.19), particularly in smoking trajectories.
Conclusion: The iCARE system effectively improves dietary, exercise, and medication adherence in CHD patients, with the greatest behavior change typically occurring at 6 months.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Clinical Trial of Healthy Food Subsidies and Behavioral Interventions to Increase Fruit and Vegetable Purchasing in an Online Store
Hua Sophia, Klaiman Tamar, Dixon Erica, Volpp Kevin, Putt Mary, Coratti Samantha, White Jenna, Hossain Mohammad, Posner Hannah, Wang Erkuan, Zhu Jingsan, John Aileen
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Drug-Coated Balloons in Coronary Artery Calcification: TNF-α Modulation and Clinical OutcomesTawde Poonam, Savage-lobeck David, George Augustine, Shah Rakesh Kumar