Final ID: Su2131
The Statin Shortfall: Lower Statin Use in Autoimmune Disease Despite Elevated Cardiovascular Risk Across LDL-C Levels.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
It is well known that patients with autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus are at increased risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. However, contemporary patterns of lipid-lowering therapy in autoimmune disease, especially among those with low LDL-C, remain inadequately defined.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that statin therapy is underutilized in autoimmune patients with lower LDL-C levels despite similar or elevated risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE).
Methods:
Using the TriNetX platform, which provides real-time, deidentified clinical data from the electronic medical records, we conducted a nationwide retrospective cohort analysis of adult patients (≥18 years) with rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus, stratified by LDL-C into seven groups: <60, 60–79, 80–99, 100–119, 120–139, 140–159, and ≥160 mg/dL. The MACE outcomes defined as myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization, or cardiovascular death and the respective statin usage were compared between each group and the ≥160 mg/dL reference group using odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals.
Results:
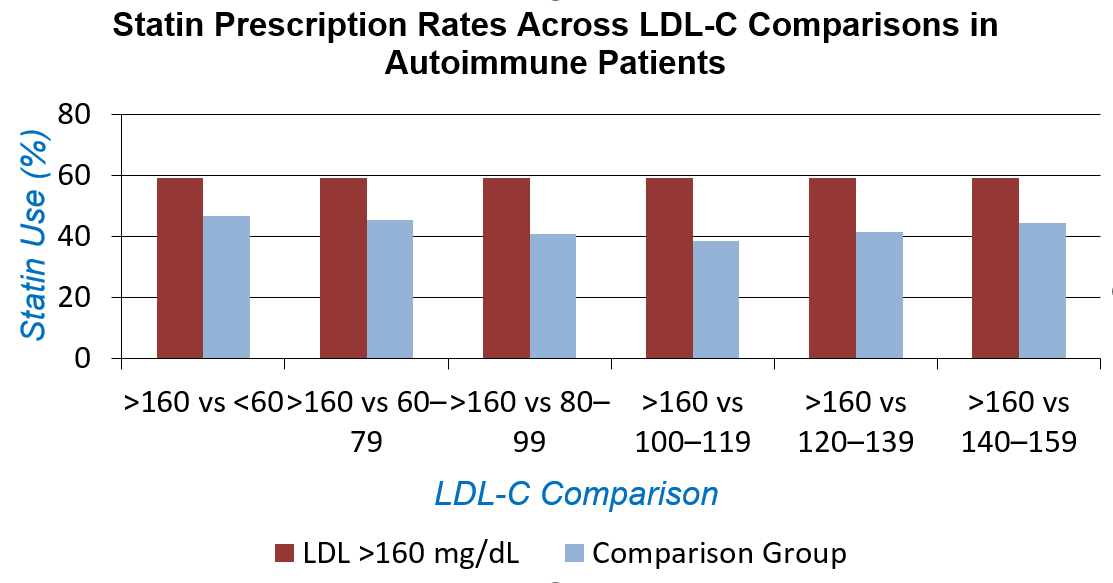
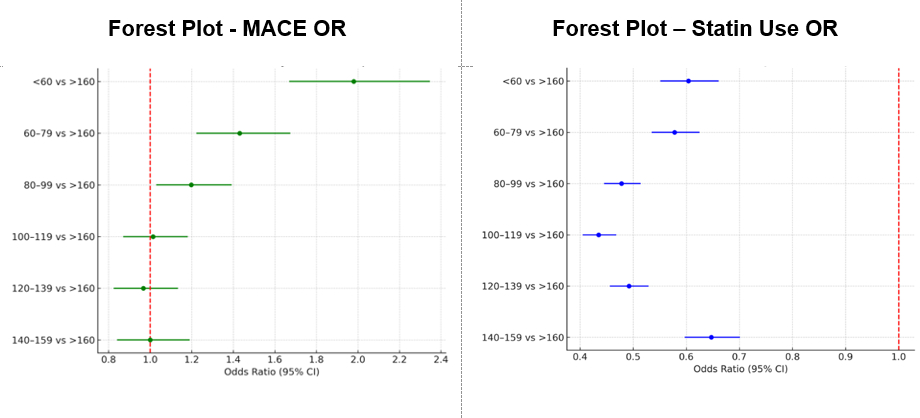
A total of 50,436 autoimmune patients were included. Among patients with autoimmune disease, statin use was consistently lower across all lower LDL-C strata when compared to those with LDL-C >160 mg/dL. The odds ratios (OR) for statin use ranged from 0.435 (95% CI: 0.405–0.468) in the 100–119 mg/dL group to 0.647 (95% CI: 0.597–0.701) in the 140–159 mg/dL group, indicating a substantial treatment gap.
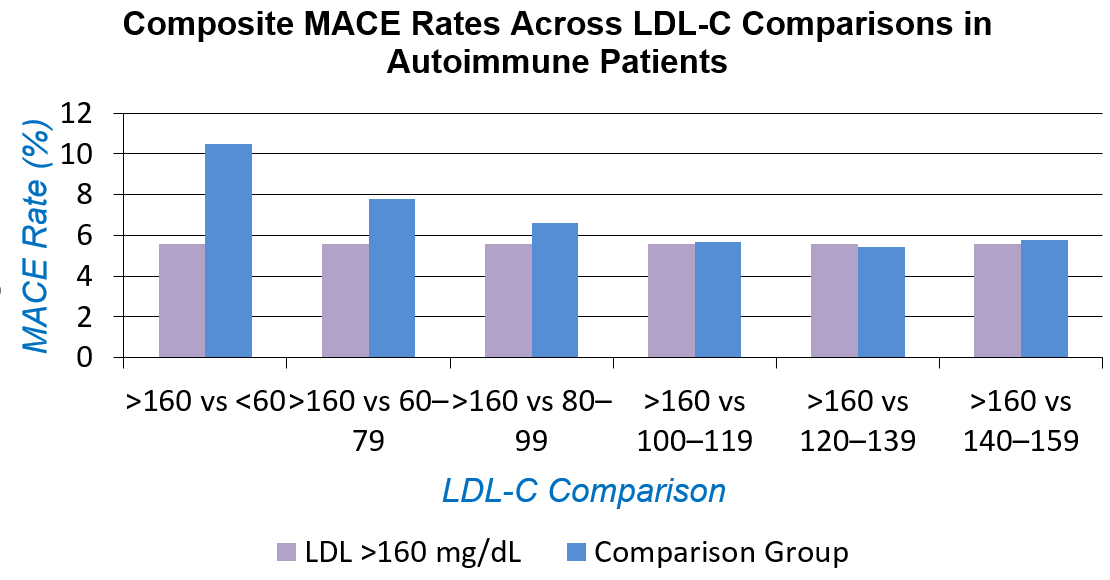
In contrast, the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) was significantly higher among autoimmune patients with lower LDL-C levels relative to those with LDL-C >160 mg/dL. The highest odds were observed in the <60 mg/dL group (OR 1.980, 95% CI: 1.669–2.347), followed by the 60–79 mg/dL (OR 1.431, 95% CI: 1.222–1.675) and 80–99 mg/dL (OR 1.198, 95% CI: 1.029–1.393) groups. No statistically significant differences in MACE risk were observed in the higher LDL-C strata.
Conclusion:
Among autoimmune patients, statin therapy is markedly underprescribed in those with lower LDL-C levels, despite persistent or elevated cardiovascular risk. These findings suggest that current LDL-C–based thresholds may inadequately capture cardiovascular risk in autoimmune populations and support the need for broader risk-based treatment strategies.
It is well known that patients with autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus are at increased risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. However, contemporary patterns of lipid-lowering therapy in autoimmune disease, especially among those with low LDL-C, remain inadequately defined.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that statin therapy is underutilized in autoimmune patients with lower LDL-C levels despite similar or elevated risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE).
Methods:
Using the TriNetX platform, which provides real-time, deidentified clinical data from the electronic medical records, we conducted a nationwide retrospective cohort analysis of adult patients (≥18 years) with rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus, stratified by LDL-C into seven groups: <60, 60–79, 80–99, 100–119, 120–139, 140–159, and ≥160 mg/dL. The MACE outcomes defined as myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization, or cardiovascular death and the respective statin usage were compared between each group and the ≥160 mg/dL reference group using odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals.
Results:
A total of 50,436 autoimmune patients were included. Among patients with autoimmune disease, statin use was consistently lower across all lower LDL-C strata when compared to those with LDL-C >160 mg/dL. The odds ratios (OR) for statin use ranged from 0.435 (95% CI: 0.405–0.468) in the 100–119 mg/dL group to 0.647 (95% CI: 0.597–0.701) in the 140–159 mg/dL group, indicating a substantial treatment gap.
In contrast, the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) was significantly higher among autoimmune patients with lower LDL-C levels relative to those with LDL-C >160 mg/dL. The highest odds were observed in the <60 mg/dL group (OR 1.980, 95% CI: 1.669–2.347), followed by the 60–79 mg/dL (OR 1.431, 95% CI: 1.222–1.675) and 80–99 mg/dL (OR 1.198, 95% CI: 1.029–1.393) groups. No statistically significant differences in MACE risk were observed in the higher LDL-C strata.
Conclusion:
Among autoimmune patients, statin therapy is markedly underprescribed in those with lower LDL-C levels, despite persistent or elevated cardiovascular risk. These findings suggest that current LDL-C–based thresholds may inadequately capture cardiovascular risk in autoimmune populations and support the need for broader risk-based treatment strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adding a polygenic risk score to the PREVENT clinical risk tool significantly improves cardiovascular risk prediction
Euesden Jack, Absher Devin, Iribarren Carlos, Riveros-mckay Fernando, Rana Jamal, Rowell Sarah, Neogi Arpita, Harrison Seamus, Weale Michael, Donnelly Peter
Cardiac Autoimmunity in Pediatric Single Ventricle Congenital Heart DiseaseTomasso Federica, Du Yanmei, Abbott Jordan, Lin Daniel, Nakano Stephanie