Final ID: MP1898
Hyperammonemia during exercise as a cause of prolonged post-exertional fatigue in a Post- COVID Patient
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Post-COVID syndrome may present with exertional symptoms that are not explained by noninvasive testing. Invasive cardiopulmonary exercise testing (iCPET) can identify unique hemodynamic and metabolic impairments.
Case Presentation:
A 52-year-old man with prior COVID-19 infection (2020) and obstructive sleep apnea presented with exertional fatigue, dizziness, and presyncope. Routine investigations, including echocardiogram, stress testing, spirometry, and lab examinations were normal. Neurologic workup revealed preserved epidermal nerve fiber density in skin biopsy, normal quantitative sudomotor axon reflex test (QSART), and normal cardiovascular autonomic reflex testing with tilt, without orthostatic intolerance. Given persistent symptoms, he underwent iCPET with right heart catheterization and arterial line placement.
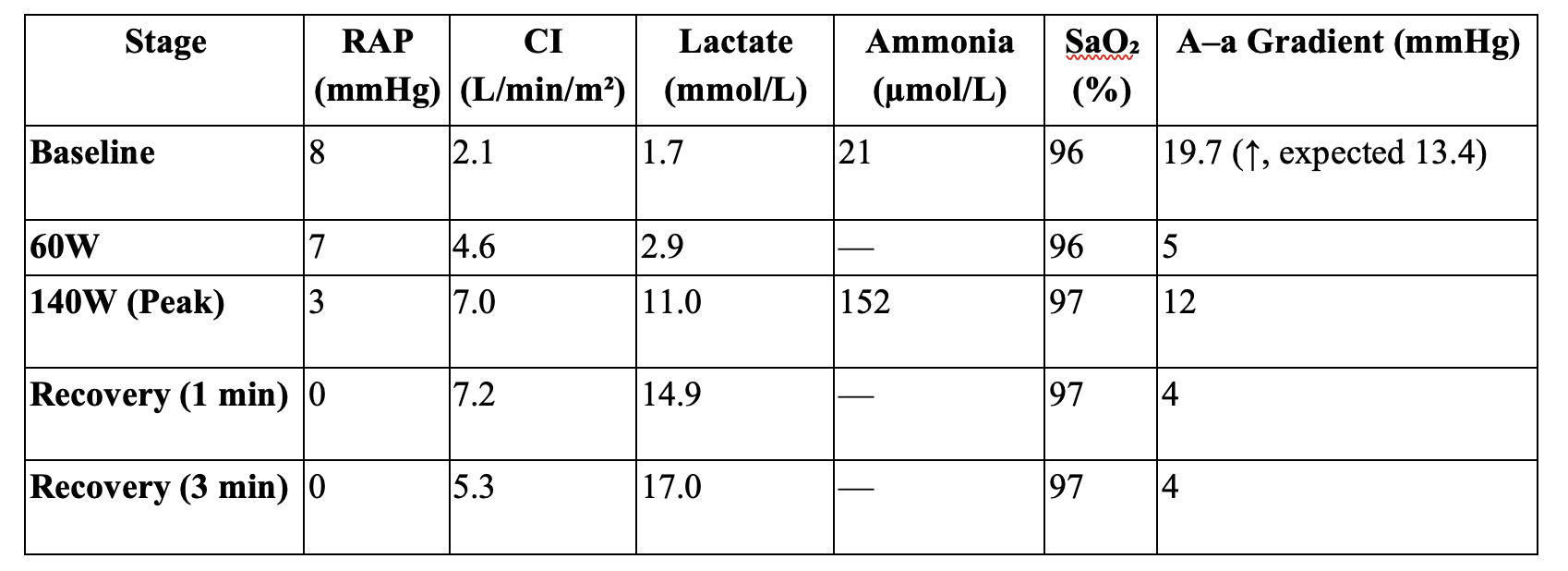
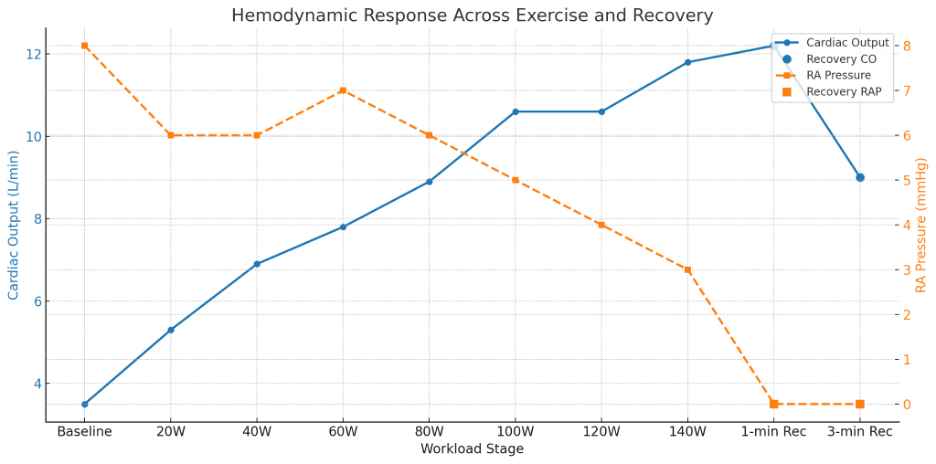
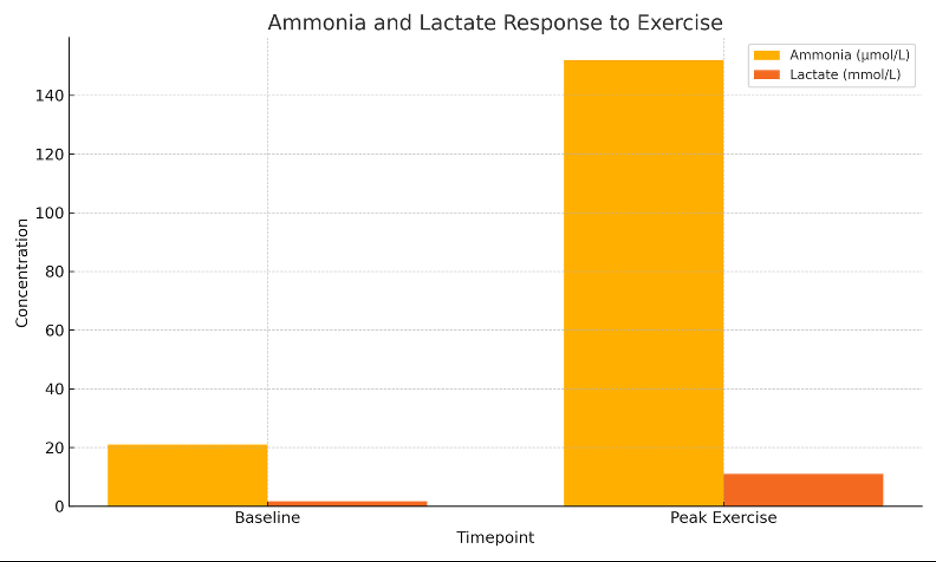
At baseline, right atrial pressure (RAP) was 4 mmHg and cardiac index 2.54 L/min/m2. During exercise to 140 watts (91% predicted VO2), RAP fell to 3 mmHg, and cardiac index rose to 7.0 L/min/m2. Stroke volume declined in late stages. Cardiac output reached 77.4% of predicted. Ammonia rose from 21 to 152 µmol/L and lactate from 1.7 to 11 mmol/L. [Fig 1, Fig 2, Fig 3] Breathing reserve was exhausted (-18.2%). Counterpressure maneuvers improved cardiac output and blood pressure. Oxygenation remained normal.
Discussion:
This case highlights a potential novel mechanism of post-exertional fatigue: exertional hyperammonemia due to impaired ammonia clearance. The patient’s preserved ventilatory and autonomic profiles, alongside a marked rise in ammonia and lactate, suggest a metabolic dysregulation independent of oxygenation or cardiac output capacity. The sustained hyperammonemia may be attributable to delayed urea cycle clearance or excessive gut production by urease-positive bacteria, possibly due to small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). While rare, exercise-induced hyperammonemia has been described in disorders of nitrogen metabolism. In our evolving clinical experience, such patients show improvement with empiric rifaximin therapy and are being studied using exhaled nitrogen breath tests for SIBO, although formal data is pending.
Conclusion:
In a post-COVID patient with normal autonomic and neurologic testing, iCPET revealed preload insufficiency and exertional hyperammonemia likely contributing to post-exertional fatigue. iCPET can uncover functional and metabolic limitations not detected by standard evaluations.
Post-COVID syndrome may present with exertional symptoms that are not explained by noninvasive testing. Invasive cardiopulmonary exercise testing (iCPET) can identify unique hemodynamic and metabolic impairments.
Case Presentation:
A 52-year-old man with prior COVID-19 infection (2020) and obstructive sleep apnea presented with exertional fatigue, dizziness, and presyncope. Routine investigations, including echocardiogram, stress testing, spirometry, and lab examinations were normal. Neurologic workup revealed preserved epidermal nerve fiber density in skin biopsy, normal quantitative sudomotor axon reflex test (QSART), and normal cardiovascular autonomic reflex testing with tilt, without orthostatic intolerance. Given persistent symptoms, he underwent iCPET with right heart catheterization and arterial line placement.
At baseline, right atrial pressure (RAP) was 4 mmHg and cardiac index 2.54 L/min/m2. During exercise to 140 watts (91% predicted VO2), RAP fell to 3 mmHg, and cardiac index rose to 7.0 L/min/m2. Stroke volume declined in late stages. Cardiac output reached 77.4% of predicted. Ammonia rose from 21 to 152 µmol/L and lactate from 1.7 to 11 mmol/L. [Fig 1, Fig 2, Fig 3] Breathing reserve was exhausted (-18.2%). Counterpressure maneuvers improved cardiac output and blood pressure. Oxygenation remained normal.
Discussion:
This case highlights a potential novel mechanism of post-exertional fatigue: exertional hyperammonemia due to impaired ammonia clearance. The patient’s preserved ventilatory and autonomic profiles, alongside a marked rise in ammonia and lactate, suggest a metabolic dysregulation independent of oxygenation or cardiac output capacity. The sustained hyperammonemia may be attributable to delayed urea cycle clearance or excessive gut production by urease-positive bacteria, possibly due to small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). While rare, exercise-induced hyperammonemia has been described in disorders of nitrogen metabolism. In our evolving clinical experience, such patients show improvement with empiric rifaximin therapy and are being studied using exhaled nitrogen breath tests for SIBO, although formal data is pending.
Conclusion:
In a post-COVID patient with normal autonomic and neurologic testing, iCPET revealed preload insufficiency and exertional hyperammonemia likely contributing to post-exertional fatigue. iCPET can uncover functional and metabolic limitations not detected by standard evaluations.
More abstracts on this topic:
Persistent Vascular Dysfunction and Blood Pressure Elevation Over 12 Months After COVID-19 Recovery in Non-Hypertensive Adults – LOCHINVAR Study
Lip Stefanie, Padmanabhan Sandosh, Tran Tran Qb, Hanna Rebecca, Nichol Sarah, Mcclure John, Delles Christian, Mccallum Linsay, Berry Colin, Touyz Rhian
Clinical and Hemodynamic Correlates of Supranormal Ejection Fraction in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF)Dhruve Ritika, Koshy Thomas, Pandey Ambarish, Patel Lajjaben, Subramanian Vinayak, Segar Matthew, Miller James, Lokesh Nidhish, Keshvani Neil, Tong Dan, Chandra Alvin