Final ID: MP2495
Cardiovascular Benefits of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Non-Obese Patients with Heart-Failure: A Real-World TriNetX Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), originally approved for glycemic control and weight loss in type 2 diabetes, have demonstrated cardiovascular (CV) benefit in obese individuals with Heart Failure (HF). However, their impact in non-obese patients with HF remains unclear. We aimed to evaluate the association between GLP-1 RAs use and cardiovascular outcomes in non-obese patients with HF with preserved (HFpEF) and reduced (HFrEF) ejection fraction.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective, observational cohort study using the TriNetX research network. Adults (>18 years) with a BMI <30 kg/m^2 and a diagnosis of HFpEF or HFrEF between 2014 and 2024 were included. Patients treated with GLP-1 RAs were propensity score–matched 1:1 to untreated controls based on 29 covariates including demographics, comorbidities, and baseline medications. The primary outcome was a composite of all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction (MI), and stroke at 1 and 5 years.
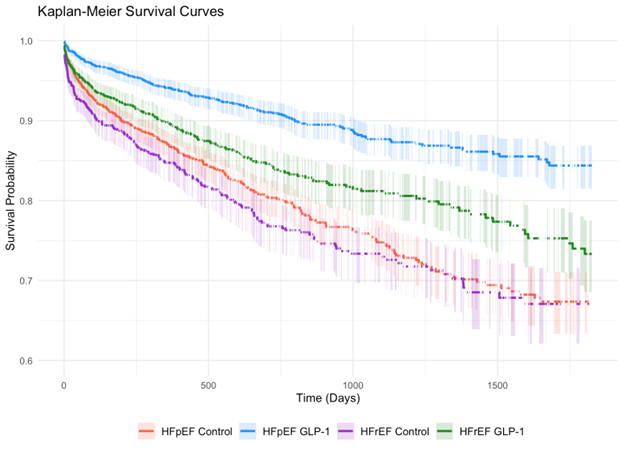
Results: We identified 1,987 non-obese HFpEF patients and 1,257 non-obese HFrEF patients treated with GLP-1 RAs. The mean age was 66 ± 12 years for HFpEF and 64 ± 13 years for HFrEF patients, with 41% and 63% being male, respectively. At 1 year, GLP-1 RA treatment was associated with a 58% reduction in the composite outcome in HFpEF patients (HR 0.42, 95% CI [0.35–0.50]) and a 35% reduction in HFrEF patients (HR 0.65, 95% CI [0.53–0.81]). The beneficial effect of GLP-1 RAs remained at 5 years, with greater relative reduction in HFpEF (HR 0.41; 95% CI [0.36–0.47]) compared to HFrEF patients (HR 0.64; 95% CI [0.54–0.76]) (Figure 1).
Conclusions: In this large real-world cohort of non-obese HF patients, GLP-1 RAs treatment was associated with significantly improved cardiovascular outcomes across HF phenotypes, with a more pronounced benefit in HFpEF. These findings suggest that GLP-1 RAs may offer therapeutic benefit beyond glycemic and weight control in HF, particularly in HFpEF, and support their further evaluation as potential guideline-directed medical therapy in this population, which warrants further investigation.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective, observational cohort study using the TriNetX research network. Adults (>18 years) with a BMI <30 kg/m^2 and a diagnosis of HFpEF or HFrEF between 2014 and 2024 were included. Patients treated with GLP-1 RAs were propensity score–matched 1:1 to untreated controls based on 29 covariates including demographics, comorbidities, and baseline medications. The primary outcome was a composite of all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction (MI), and stroke at 1 and 5 years.
Results: We identified 1,987 non-obese HFpEF patients and 1,257 non-obese HFrEF patients treated with GLP-1 RAs. The mean age was 66 ± 12 years for HFpEF and 64 ± 13 years for HFrEF patients, with 41% and 63% being male, respectively. At 1 year, GLP-1 RA treatment was associated with a 58% reduction in the composite outcome in HFpEF patients (HR 0.42, 95% CI [0.35–0.50]) and a 35% reduction in HFrEF patients (HR 0.65, 95% CI [0.53–0.81]). The beneficial effect of GLP-1 RAs remained at 5 years, with greater relative reduction in HFpEF (HR 0.41; 95% CI [0.36–0.47]) compared to HFrEF patients (HR 0.64; 95% CI [0.54–0.76]) (Figure 1).
Conclusions: In this large real-world cohort of non-obese HF patients, GLP-1 RAs treatment was associated with significantly improved cardiovascular outcomes across HF phenotypes, with a more pronounced benefit in HFpEF. These findings suggest that GLP-1 RAs may offer therapeutic benefit beyond glycemic and weight control in HF, particularly in HFpEF, and support their further evaluation as potential guideline-directed medical therapy in this population, which warrants further investigation.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adverse Maternal and Offspring Outcomes in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rat Pregnancies: Impact of a Maternal Hypertensive High-Fat Diet
Gomes Viviane, Watts Stephanie, Fink Gregory, Kim Lauren, Lopez Krystal, Gilbert Bryce, Bailey Victoria, Marques Bruno, Garver Hannah, Mckenzie Mckenzie, Lauver Adam
A Simple One-Item Nursing Falls Assessment Predicts Outcomes For Patients With Stage D Heart Failure Undergoing Surgical Advanced TherapiesSalvador Vincent, Perez Jaime Abraham, Hudec Paige, Gorodeski Eiran, Oneill Thomas