Final ID: MP1285
Radiomics-Based Coronary Heart Disease Classification Using Cine Cardiac MRI in a Bi-Racial Cohort
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Coronary heart disease (CHD) remains a leading global health burden. Cine cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR), the gold standard for evaluating left ventricular (LV) structure and function, avoids contrast but relies on human-derived clinical measures. Radiomics, a high-throughput image analysis method, offers a quantitative, agnostic approach to LV analysis. We hypothesized that radiomics could classify individuals with prevalent CHD in a large bi-racial cohort.
Methods
bSSFP cine CMR was performed in 2,629 participants from the Framingham Heart Offspring Study (n=1277, mean age 64.5 ± 10.0 years, 53.0% female, CHD = 93) and the Jackson Heart Study (n=1352, mean age 59.1 ± 10.3 years, 62.1% female, CHD = 37) using 1.5T scanners (FHS: Philips Achieva and Siemens Espree; JHS: Philips Medical Systems HS). 130 participants had prevalent CHD, 2,499 did not. LV myocardium was segmented from 5 short-axis slices (base to apex), and 939 shape & texture radiomic features were extracted using PyRadiomics. After restricting to previously published reproducible features and principal component analysis, 92 radiomic features were retained. XGBoost with 5-fold cross-validation selected the top 5 based on mean feature importance (average gain across folds), and used in all radiomics-based models. CHD was defined as prior coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, or unstable angina. Logistic regression models were developed to classify CHD using five configurations: (1) radiomics-only, (2) demographics only (age, sex, race), (3) demographics + LVEF (ejection fraction), and combined models: (4) demographics + radiomics, and (5) demographics + LVEF + radiomics. Model performance was compared using the DeLong test.
Results
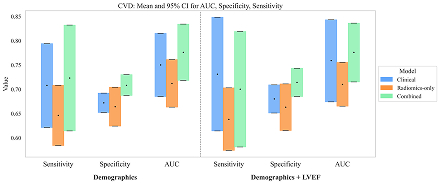
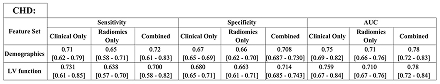
Radiomics-only models performed similarly to Demographics (AUC = 0.71 [0.66–0.76], p = 0.20) and Demographics + LVEF (AUC = 0.71 [0.67–0.76], p = 0.14), with overlapping confidence intervals and p-values for comparison ≥ 0.14 (Figure, Table), indicating no significant difference. Classification performance improved with combined radiomics, demographics, and LVEF (AUC = 0.78 [0.72–0.82], p = 0.38).
Conclusion
Radiomics-only models from routine cine CMR performed comparably to models using key demographic and functional factors(LVEF) for CHD. These findings underscore that cine images alone hold valuable information about underlying disease and may enhance the discriminative ability of agnostic image interrogation in CHD classification.
Coronary heart disease (CHD) remains a leading global health burden. Cine cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR), the gold standard for evaluating left ventricular (LV) structure and function, avoids contrast but relies on human-derived clinical measures. Radiomics, a high-throughput image analysis method, offers a quantitative, agnostic approach to LV analysis. We hypothesized that radiomics could classify individuals with prevalent CHD in a large bi-racial cohort.
Methods
bSSFP cine CMR was performed in 2,629 participants from the Framingham Heart Offspring Study (n=1277, mean age 64.5 ± 10.0 years, 53.0% female, CHD = 93) and the Jackson Heart Study (n=1352, mean age 59.1 ± 10.3 years, 62.1% female, CHD = 37) using 1.5T scanners (FHS: Philips Achieva and Siemens Espree; JHS: Philips Medical Systems HS). 130 participants had prevalent CHD, 2,499 did not. LV myocardium was segmented from 5 short-axis slices (base to apex), and 939 shape & texture radiomic features were extracted using PyRadiomics. After restricting to previously published reproducible features and principal component analysis, 92 radiomic features were retained. XGBoost with 5-fold cross-validation selected the top 5 based on mean feature importance (average gain across folds), and used in all radiomics-based models. CHD was defined as prior coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, or unstable angina. Logistic regression models were developed to classify CHD using five configurations: (1) radiomics-only, (2) demographics only (age, sex, race), (3) demographics + LVEF (ejection fraction), and combined models: (4) demographics + radiomics, and (5) demographics + LVEF + radiomics. Model performance was compared using the DeLong test.
Results
Radiomics-only models performed similarly to Demographics (AUC = 0.71 [0.66–0.76], p = 0.20) and Demographics + LVEF (AUC = 0.71 [0.67–0.76], p = 0.14), with overlapping confidence intervals and p-values for comparison ≥ 0.14 (Figure, Table), indicating no significant difference. Classification performance improved with combined radiomics, demographics, and LVEF (AUC = 0.78 [0.72–0.82], p = 0.38).
Conclusion
Radiomics-only models from routine cine CMR performed comparably to models using key demographic and functional factors(LVEF) for CHD. These findings underscore that cine images alone hold valuable information about underlying disease and may enhance the discriminative ability of agnostic image interrogation in CHD classification.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Machine Learning Approach to Predict Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients with Critical Illness and Signs of Myocardial Injury
Mueller Joshua, Stepanova Daria, Chidambaram Vignesh, Nakarmi Ukash, Al'aref Subhi
A Deep Learning Digital Biomarker for Mitral Valve Prolapse using Echocardiogram VideosAl-alusi Mostafa, Khurshid Shaan, Sanborn Danita, Picard Michael, Ho Jennifer, Maddah Mahnaz, Ellinor Patrick, Lau Emily, Small Aeron, Reeder Christopher, Shnitzer Dery Tal, Andrews Carl, Kany Shinwan, Ramo Joel, Haimovich Julian