Final ID: MP2325
Camera is All You Need: Low-cost Atrial Fibrillation Detection using Facial Remote Photoplethysmography
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the most prevalent cardiac arrhythmias, yet current screening and monitoring methods require contact-based electrocardiographic (ECG) equipment, leading to higher costs and potential diagnostic delays. Facial remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) uses video to capture subtle light absorption changes in the skin and is a promising avenue for accessible AF monitoring. While algorithms exist for detecting AF from R-R intervals extracted from ECG, the inherent noisiness of rPPG signals makes direct application difficult. Deep learning models have been proposed; however, they require high computational costs and offer limited explainability.
Aims
This study aimed to develop and validate a low-cost, explainable approach to detect AF from beat-to-beat (B-B) intervals extracted from facial rPPG. Our goal was to avoid complex model architectures and to instead train a simple model using only R-R intervals extracted from ECG data.
Methods
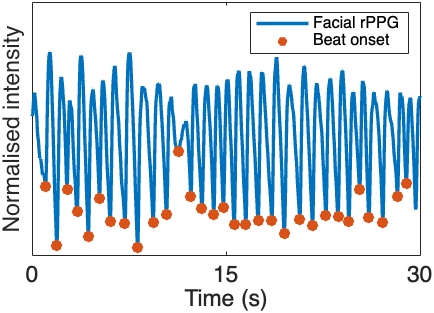
We first trained a model using 1172 single-lead recordings from the 2017 CinC Challenge dataset, of which 567 were labeled as AF. From these recordings, R-R intervals were extracted and then used for computing seven handcrafted features. We then trained a support vector machine (SVM) model solely on this dataset. For external validation, we conducted a prospective clinical study in which facial video (320×240 pixels, 150 Hz) and 12-lead ECG were recorded from 15 AF and 52 normal sinus rhythm (NSR) patients. ECGs were annotated by board-certified physicians. Videos were segmented into 30-second clips. The green channel was isolated, bandpass filtered and then temporally smoothed. Signals from the forehead and cheek regions were averaged to produce a representative rPPG signal. A heuristic algorithm was used to assess signal quality. Beat onsets were detected using an adaptive thresholding algorithm and then used to compute the B-B intervals for classification.
Results
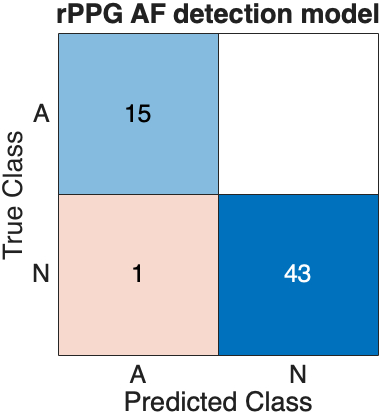
The model has achieved a sensitivity of 100.00%, a specificity of 97.73% and an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.9773. The indeterminate rate due to low signal quality was 11.94%.
Conclusion
We haved successfully demonstrated that an interpretable, low-cost machine learning model trained solely on ECG data can accurately detect AF from facial rPPG. This shows significant promise for developing accessible, low-cost, non-contact rPPG-based systems for AF screening and monitoring, with possible future applications to other arrhythmias.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the most prevalent cardiac arrhythmias, yet current screening and monitoring methods require contact-based electrocardiographic (ECG) equipment, leading to higher costs and potential diagnostic delays. Facial remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) uses video to capture subtle light absorption changes in the skin and is a promising avenue for accessible AF monitoring. While algorithms exist for detecting AF from R-R intervals extracted from ECG, the inherent noisiness of rPPG signals makes direct application difficult. Deep learning models have been proposed; however, they require high computational costs and offer limited explainability.
Aims
This study aimed to develop and validate a low-cost, explainable approach to detect AF from beat-to-beat (B-B) intervals extracted from facial rPPG. Our goal was to avoid complex model architectures and to instead train a simple model using only R-R intervals extracted from ECG data.
Methods
We first trained a model using 1172 single-lead recordings from the 2017 CinC Challenge dataset, of which 567 were labeled as AF. From these recordings, R-R intervals were extracted and then used for computing seven handcrafted features. We then trained a support vector machine (SVM) model solely on this dataset. For external validation, we conducted a prospective clinical study in which facial video (320×240 pixels, 150 Hz) and 12-lead ECG were recorded from 15 AF and 52 normal sinus rhythm (NSR) patients. ECGs were annotated by board-certified physicians. Videos were segmented into 30-second clips. The green channel was isolated, bandpass filtered and then temporally smoothed. Signals from the forehead and cheek regions were averaged to produce a representative rPPG signal. A heuristic algorithm was used to assess signal quality. Beat onsets were detected using an adaptive thresholding algorithm and then used to compute the B-B intervals for classification.
Results
The model has achieved a sensitivity of 100.00%, a specificity of 97.73% and an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.9773. The indeterminate rate due to low signal quality was 11.94%.
Conclusion
We haved successfully demonstrated that an interpretable, low-cost machine learning model trained solely on ECG data can accurately detect AF from facial rPPG. This shows significant promise for developing accessible, low-cost, non-contact rPPG-based systems for AF screening and monitoring, with possible future applications to other arrhythmias.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Heart-pounding Case of Cardiomyopathy in Pregnancy
Tran Linh, Everitt Ian, Vaught Arthur, Barth Andreas, Minhas Anum
3D Statistical Shape Analysis Predicts Type A Aortic Dissection Better Than Aortic DiametersMarway Prabhvir, Campello Jorge Carlos Alberto, Wagner Catherine, Baker Timothy, Burris Nicholas