Final ID: MP1528
Hybrid Rule-Based and Large Language Model Framework Extracts Statin-Related Information from Clinical Notes
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality; statin therapy reduces risk but adherence is suboptimal. Clinical notes contain details on statin intolerance, contraindications, and patient deferral that structured data miss, yet manual extraction is time-consuming.
Hypothesis: A hybrid AI framework combining rule-based NLP and LLM-based methods can accurately extract statin-related information from clinical notes to inform clinical decision support.
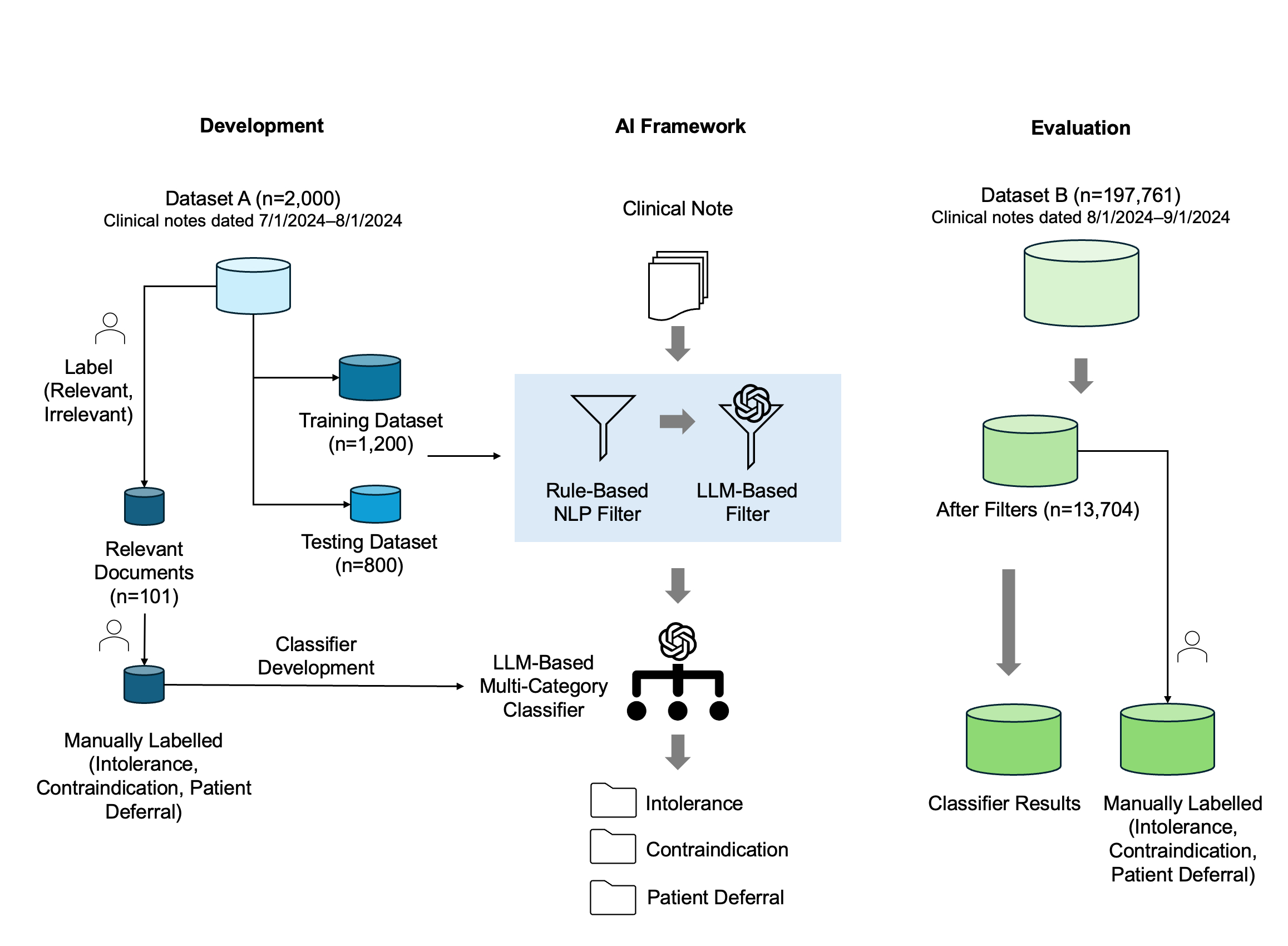
Methods: We developed a three-component framework: (1) a rule-based NLP filter to exclude irrelevant notes, (2) an LLM-based refinement filter to identify notes likely containing relevant information, and (3) an LLM-based multicategory classifier to categorize records into intolerance, contraindications, and deferral. Dataset A (2,000 notes; July 1–August 1, 2024) from adult primary care visits at Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) was split into training (n = 1,200) and testing (n = 800) subsets for development and evaluation. Dataset B (197,761 notes; August 1–September 1, 2024) was used for retrospective evaluation. Performance metrics included precision, recall, F1, accuracy, and filter-out rate. Patient-level prevalence for each category was measured in Dataset B.
Results: In Dataset A, the rule-based NLP filter excluded 81% of notes while retaining all relevant ones (precision = 1.00). The LLM-based refinement filter achieved precision = 0.973, recall = 0.947, F1 = 0.960, accuracy = 0.996, and a filter-out rate of 95.4% on the testing subset. The multicategory classifier attained F1 scores of 0.99 (intolerance), 0.81 (contraindications), and 0.86 (deferral). In Dataset B, after sequential filtering, 45,253 of 197,761 notes remained; the classifier identified 3,027 patients (6.4%) with documented intolerance, 310 (0.7%) with contraindications, and 1,391 (2.9%) who deferred therapy.
Conclusions: The hybrid AI framework efficiently processes clinical notes, filtering out over 90% of irrelevant records while maintaining high precision for relevant content. This scalable approach enables extraction of actionable statin-related information and has potential to enhance clinical decision support by integrating patient-level insights to optimize statin therapy.
Hypothesis: A hybrid AI framework combining rule-based NLP and LLM-based methods can accurately extract statin-related information from clinical notes to inform clinical decision support.
Methods: We developed a three-component framework: (1) a rule-based NLP filter to exclude irrelevant notes, (2) an LLM-based refinement filter to identify notes likely containing relevant information, and (3) an LLM-based multicategory classifier to categorize records into intolerance, contraindications, and deferral. Dataset A (2,000 notes; July 1–August 1, 2024) from adult primary care visits at Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) was split into training (n = 1,200) and testing (n = 800) subsets for development and evaluation. Dataset B (197,761 notes; August 1–September 1, 2024) was used for retrospective evaluation. Performance metrics included precision, recall, F1, accuracy, and filter-out rate. Patient-level prevalence for each category was measured in Dataset B.
Results: In Dataset A, the rule-based NLP filter excluded 81% of notes while retaining all relevant ones (precision = 1.00). The LLM-based refinement filter achieved precision = 0.973, recall = 0.947, F1 = 0.960, accuracy = 0.996, and a filter-out rate of 95.4% on the testing subset. The multicategory classifier attained F1 scores of 0.99 (intolerance), 0.81 (contraindications), and 0.86 (deferral). In Dataset B, after sequential filtering, 45,253 of 197,761 notes remained; the classifier identified 3,027 patients (6.4%) with documented intolerance, 310 (0.7%) with contraindications, and 1,391 (2.9%) who deferred therapy.
Conclusions: The hybrid AI framework efficiently processes clinical notes, filtering out over 90% of irrelevant records while maintaining high precision for relevant content. This scalable approach enables extraction of actionable statin-related information and has potential to enhance clinical decision support by integrating patient-level insights to optimize statin therapy.
More abstracts on this topic:
Digital Biomarkers Associated With Coronary Artery Calcium And Traditional Risk Factors Extracted From Facial Photos Through Multi-Label Deep Learning For Detecting Coronary Artery Disease
Zeng Juntong, Lin Shen, Sun Runchen, Li Zhongchen, Zheng Zhe
An Electronic Health Record Multimodal Data Integration Platform for Comprehensive Analysis of Single Ventricle PhysiologyXu Hang, Aboulhosn Jamil, Christodoulou Anthony, Finn Paul, Hsu William, Nguyen Kimlien, Zhang Hinn, Sisniega Carlos, Renella Pierangelo, Morris Connor, Husain Majid, Satou Gary, Zhu Bing, Van Arsdell Glen