Final ID: MP777
In-Hospital Outcomes of Acute Noncardiac Organ Failure among Non-Acute Myocardial Infarction Cardiogenic Shock: A Nationwide Cohort Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Noncardiac organ failure is a frequent complication in non–acute myocardial infarction (non-AMI) cardiogenic shock (CS), yet its impact on in-hospital outcomes remains understudied.
Methods
We analyzed data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (2016–2021) to identify hospitalizations for non-AMI CS among patients ≥18 years. We assessed the incidence of acute kidney injury (AKI), acute neurological failure, acute hematologic failure, acute respiratory failure, and acute liver failure during hospitalization. Patients were stratified into three groups: no organ failure, single-organ failure, and multi-organ failure (≥2 systems).
Primary outcomes included in-hospital mortality (IHM) and total hospitalization costs. Univariable and multivariable survey weighted logistic regression was used to evaluate the association between organ failure and IHM.
Results
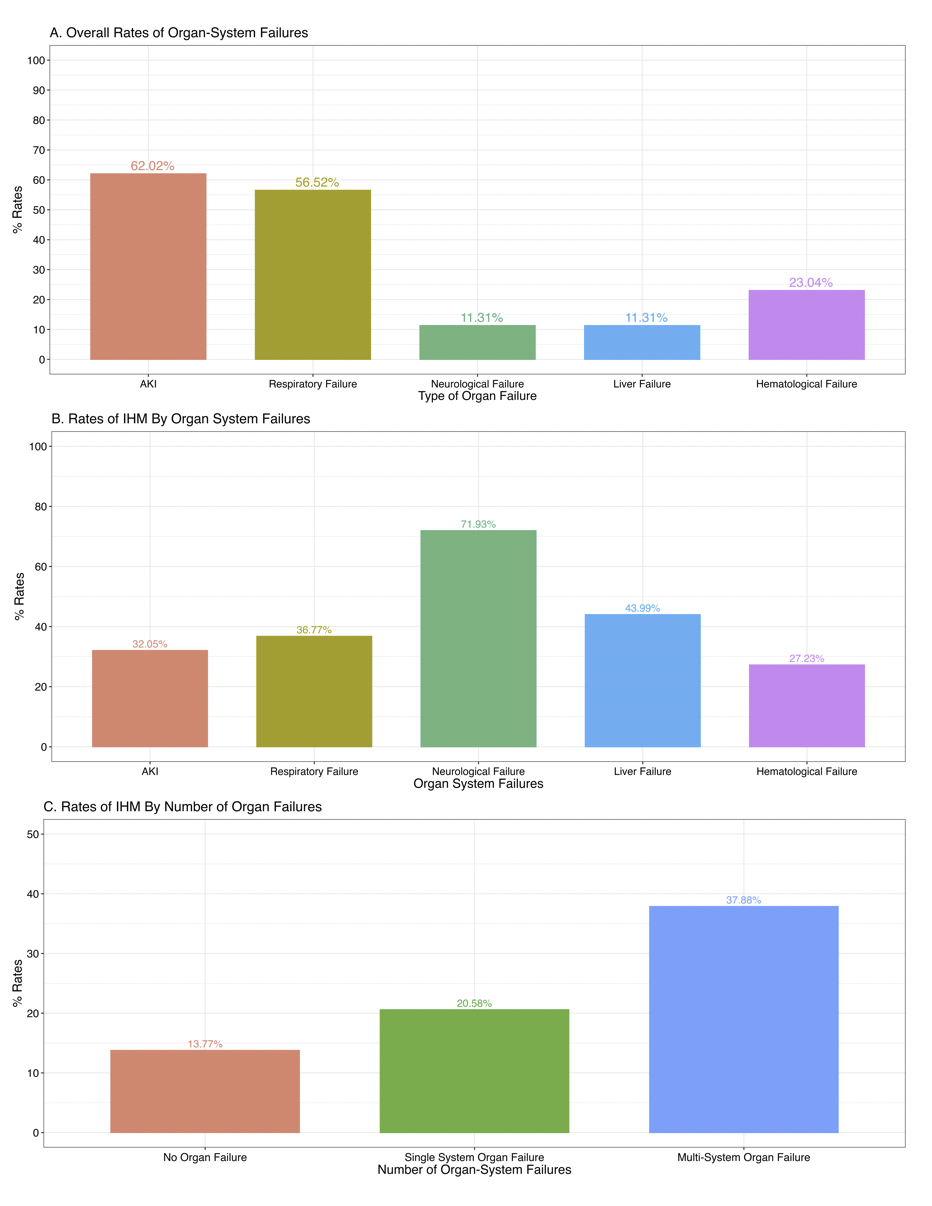
We identified 258,022 adult non-AMI CS hospitalizations. The median age was 67 years (IQR: 56–76), 63% were male, and 64% had chronic heart failure. AKI (62.0%) was the most common organ failure, followed by acute respiratory failure (56.6%) (Figure 1.A). Overall, 53.8% developed multi-organ failure, 31.8% had single-organ failure, and 14.4% had no organ failure.
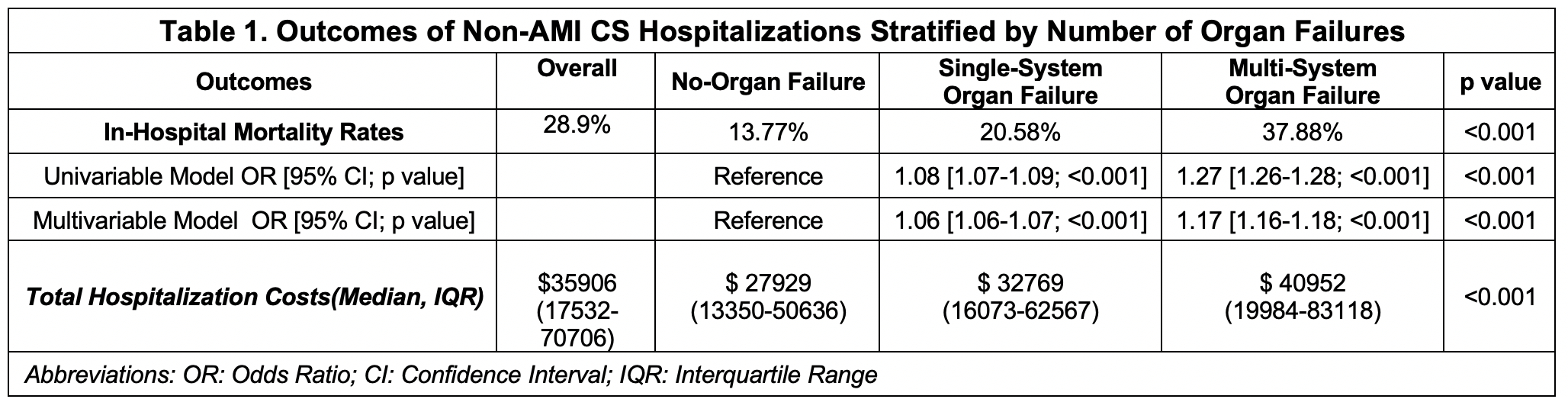
The overall IHM rate was 28.9%. Neurological failure had the highest IHM (71.9%), followed by liver failure (44.0%) (Figure 1.B). IHM was significantly higher in patients with multi-organ failure (37.9%) compared to single-organ (20.6%) and no organ failure (13.8%) (p < 0.001) (Figure 1.C). After adjustment, both multi-organ failure (aOR 1.17; 95% CI 1.16–1.18) and single-organ failure (aOR 1.06; 95% CI 1.06–1.07) were associated with increased odds of IHM (p < 0.001). The median hospitalization cost was $35,906 (IQR: $17,532–$70,706), and was significantly higher in those with multi-organ ($40,952; IQR: 19984-83118) and single-organ failure ($32,769; IQR: 16073-62567) (p < 0.001) (Table 1).
Conclusion
Noncardiac organ failure is common in non-AMI CS hospitalizations, with AKI being the most frequent and over half of patients experiencing multi-organ failure. Neurological failure was associated with the highest mortality. Both single and multi-organ failure were independently linked to increased IHM and higher healthcare costs, emphasizing the need for early recognition and targeted management strategies in this population.
Noncardiac organ failure is a frequent complication in non–acute myocardial infarction (non-AMI) cardiogenic shock (CS), yet its impact on in-hospital outcomes remains understudied.
Methods
We analyzed data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (2016–2021) to identify hospitalizations for non-AMI CS among patients ≥18 years. We assessed the incidence of acute kidney injury (AKI), acute neurological failure, acute hematologic failure, acute respiratory failure, and acute liver failure during hospitalization. Patients were stratified into three groups: no organ failure, single-organ failure, and multi-organ failure (≥2 systems).
Primary outcomes included in-hospital mortality (IHM) and total hospitalization costs. Univariable and multivariable survey weighted logistic regression was used to evaluate the association between organ failure and IHM.
Results
We identified 258,022 adult non-AMI CS hospitalizations. The median age was 67 years (IQR: 56–76), 63% were male, and 64% had chronic heart failure. AKI (62.0%) was the most common organ failure, followed by acute respiratory failure (56.6%) (Figure 1.A). Overall, 53.8% developed multi-organ failure, 31.8% had single-organ failure, and 14.4% had no organ failure.
The overall IHM rate was 28.9%. Neurological failure had the highest IHM (71.9%), followed by liver failure (44.0%) (Figure 1.B). IHM was significantly higher in patients with multi-organ failure (37.9%) compared to single-organ (20.6%) and no organ failure (13.8%) (p < 0.001) (Figure 1.C). After adjustment, both multi-organ failure (aOR 1.17; 95% CI 1.16–1.18) and single-organ failure (aOR 1.06; 95% CI 1.06–1.07) were associated with increased odds of IHM (p < 0.001). The median hospitalization cost was $35,906 (IQR: $17,532–$70,706), and was significantly higher in those with multi-organ ($40,952; IQR: 19984-83118) and single-organ failure ($32,769; IQR: 16073-62567) (p < 0.001) (Table 1).
Conclusion
Noncardiac organ failure is common in non-AMI CS hospitalizations, with AKI being the most frequent and over half of patients experiencing multi-organ failure. Neurological failure was associated with the highest mortality. Both single and multi-organ failure were independently linked to increased IHM and higher healthcare costs, emphasizing the need for early recognition and targeted management strategies in this population.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Bridge from Sweet to Sour: A Case of Recurrent Myocardial Stunning in Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Satish Vikyath, Pargaonkar Sumant, Slipczuk Leandro, Schenone Aldo, Maliha Maisha, Chi Kuan Yu, Sunil Kumar Sriram, Borkowski Pawel, Vyas Rhea, Rodriguez Szaszdi David Jose Javier, Kharawala Amrin, Seo Jiyoung
β1 Adrenergic Receptor Autoantibodies Promote Heart Failure Though Activation of Prostaglandin E2 Receptor EP1/Phosphodiesterase 4B PathwayCao Ning, Qiu Hui, Li Hongwei