Final ID: MP1209
Vascular Leak Index Predicts Postoperative Fluid Accumulation Following Cardiac Surgery
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Postoperative vascular leak and the associated fluid retention are frequent and clinically significant complications in patients following cardiac surgery. Despite their substantial impact on mortality and morbidity, no easily accessible and validated diagnostic tools exist to quantify endothelial dysfunction and predict fluid shifts. The Vascular Leak Index (VLI) was introduced as a straightforward yet effective tool to assess vascular leak in septic ICU patients. Our study aims to evaluate the applicability and prognostic value of VLI in adult patients following cardiac surgery, specifically evaluating its association with postoperative fluid accumulation.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesize that the VLI is a valid prognostic marker in patients after cardiac surgery and that elevated VLI values are associated with increased postoperative fluid accumulation.
Methods:
This retrospective cohort study included adult patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting, excluding those who received diuretics on the day of surgery or the first postoperative day, as well as those who died within the first four postoperative days. The VLI was calculated using changes in hematocrit from 0-36 h after ICU admission, normalized to net fluid balance and body surface area. The primary outcome was the fluid balance between 36-84 h post-ICU admission. Generalized additive models (GAMs) and linear regression were applied to assess associations.
Results:
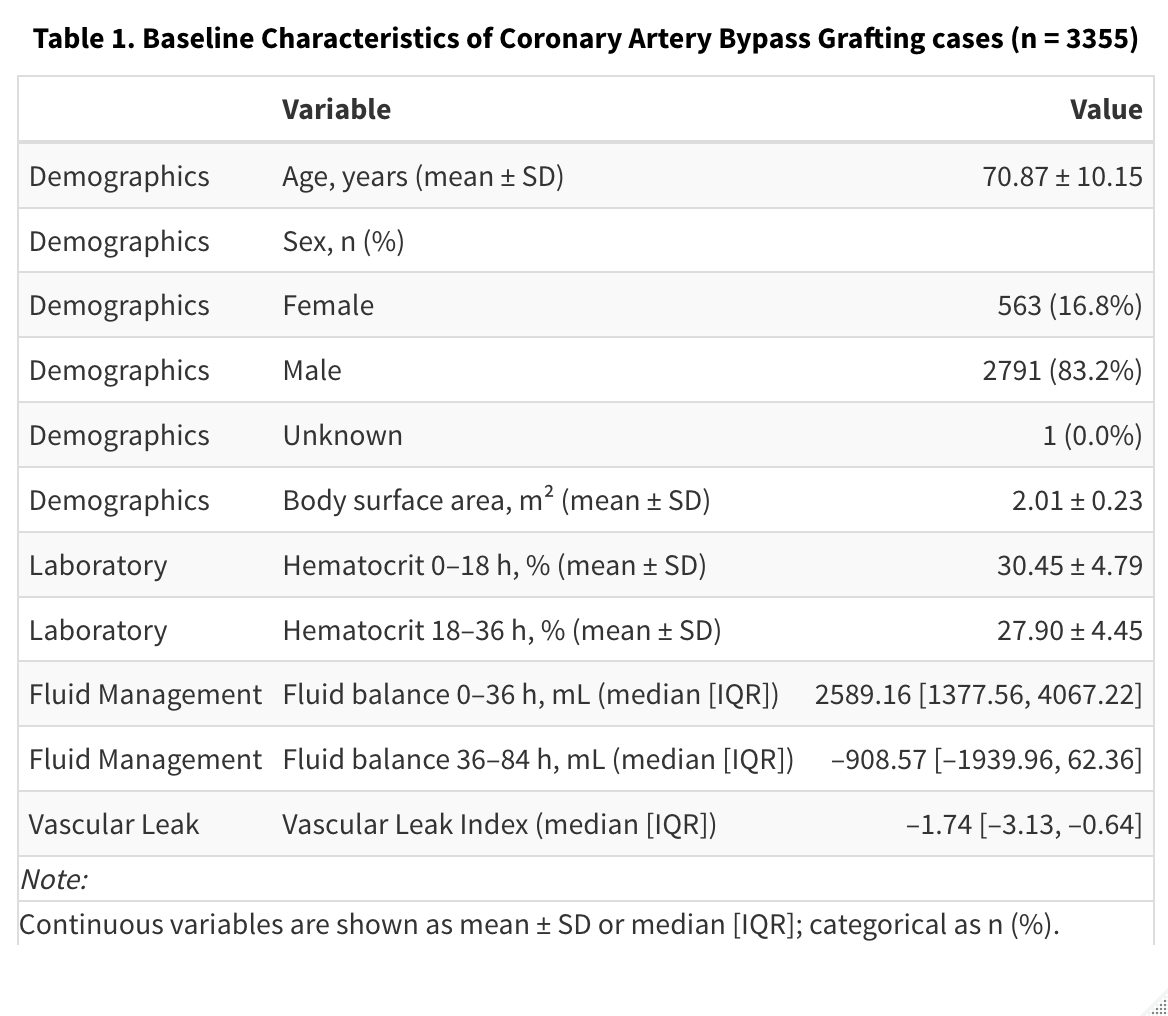
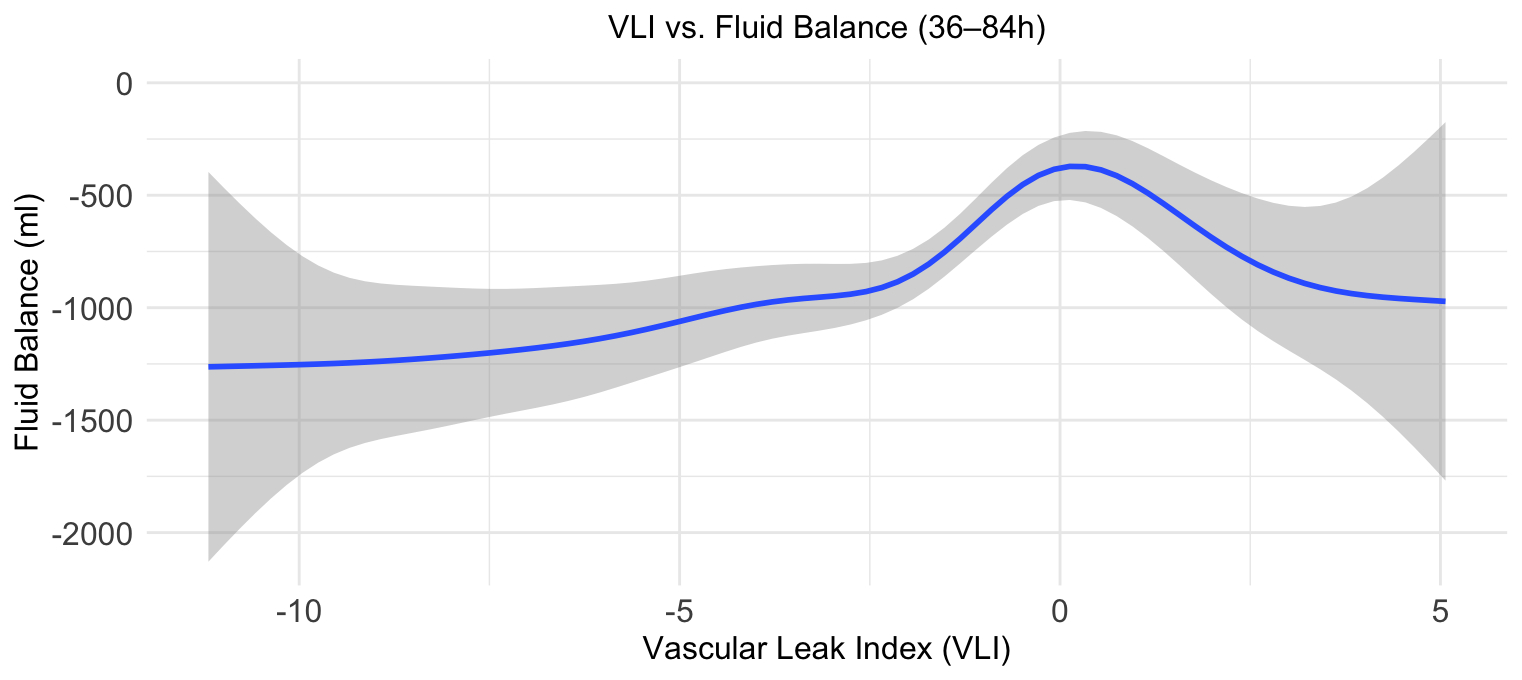
A total of 3,355 cases were included (mean age 70.9 years, 16.8% female). The GAM model revealed a significant non-linear association between VLI and subsequent fluid accumulation during ICU hours 36-84 (p<0.001). To further examine the association, patients were stratified into VLI quartiles. Compared to the lowest quartile (Q1), fluid balance was significantly higher in Q3 (β=+313.5 mL, p=0.002) and Q4 (β=+610.8 mL, p<0.001). The linear model demonstrated a significant overall effect of VLI quartile on fluid accumulation (p<0.0001), independent of age and sex.
Conclusion:
Our findings suggest that the VLI, originally developed for sepsis, may also serve as a predictive tool to identify patients at risk of fluid accumulation after cardiac surgery. This highlights the potential of the VLI as a non-invasive stratification and monitoring tool for guiding postoperative ICU fluid management and identifying patients at risk for complications related to fluid accumulation.
Postoperative vascular leak and the associated fluid retention are frequent and clinically significant complications in patients following cardiac surgery. Despite their substantial impact on mortality and morbidity, no easily accessible and validated diagnostic tools exist to quantify endothelial dysfunction and predict fluid shifts. The Vascular Leak Index (VLI) was introduced as a straightforward yet effective tool to assess vascular leak in septic ICU patients. Our study aims to evaluate the applicability and prognostic value of VLI in adult patients following cardiac surgery, specifically evaluating its association with postoperative fluid accumulation.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesize that the VLI is a valid prognostic marker in patients after cardiac surgery and that elevated VLI values are associated with increased postoperative fluid accumulation.
Methods:
This retrospective cohort study included adult patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting, excluding those who received diuretics on the day of surgery or the first postoperative day, as well as those who died within the first four postoperative days. The VLI was calculated using changes in hematocrit from 0-36 h after ICU admission, normalized to net fluid balance and body surface area. The primary outcome was the fluid balance between 36-84 h post-ICU admission. Generalized additive models (GAMs) and linear regression were applied to assess associations.
Results:
A total of 3,355 cases were included (mean age 70.9 years, 16.8% female). The GAM model revealed a significant non-linear association between VLI and subsequent fluid accumulation during ICU hours 36-84 (p<0.001). To further examine the association, patients were stratified into VLI quartiles. Compared to the lowest quartile (Q1), fluid balance was significantly higher in Q3 (β=+313.5 mL, p=0.002) and Q4 (β=+610.8 mL, p<0.001). The linear model demonstrated a significant overall effect of VLI quartile on fluid accumulation (p<0.0001), independent of age and sex.
Conclusion:
Our findings suggest that the VLI, originally developed for sepsis, may also serve as a predictive tool to identify patients at risk of fluid accumulation after cardiac surgery. This highlights the potential of the VLI as a non-invasive stratification and monitoring tool for guiding postoperative ICU fluid management and identifying patients at risk for complications related to fluid accumulation.
More abstracts on this topic:
Impacts of perioperative cyclohexanone exposure on systemic inflammatory response
Zheng Christie, Helmbrecht Hawley, Ellis Greg, Everett Allen, Graham David, Jantzie Lauren, Graham Eric, Kuiper Jordan
Discontinuation vs Continuation of Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibition Before Non-Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisQueiroz Ivo, Guida Camila, Defante Maria Luiza Rodrigues, Barbosa Lucas, Antunes Vanio Do Livramento Junior, X. Mendes Beatriz, Mazetto Roberto, Bulhões Elísio Bulhões, Silva Catarina, Romeiro Pedro