Final ID: MP994
Myocardial Tuberculosis Presenting as Ventricular Tachycardia Along with Heart Failure Mimicking Sarcoidosis: A Case Report
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Myocardial tuberculosis (TB) is an extremely rare form of extrapulmonary TB with a reported prevalence of less than 2%. It is often diagnosed late due to subtle systemic or pulmonary manifestations or even absence of it. We report a case of myocardial TB presented with ventricular tachycardia (VT) along with heart failure was the sole clinical manifestation in an immunocompetent adult.
Case Description:
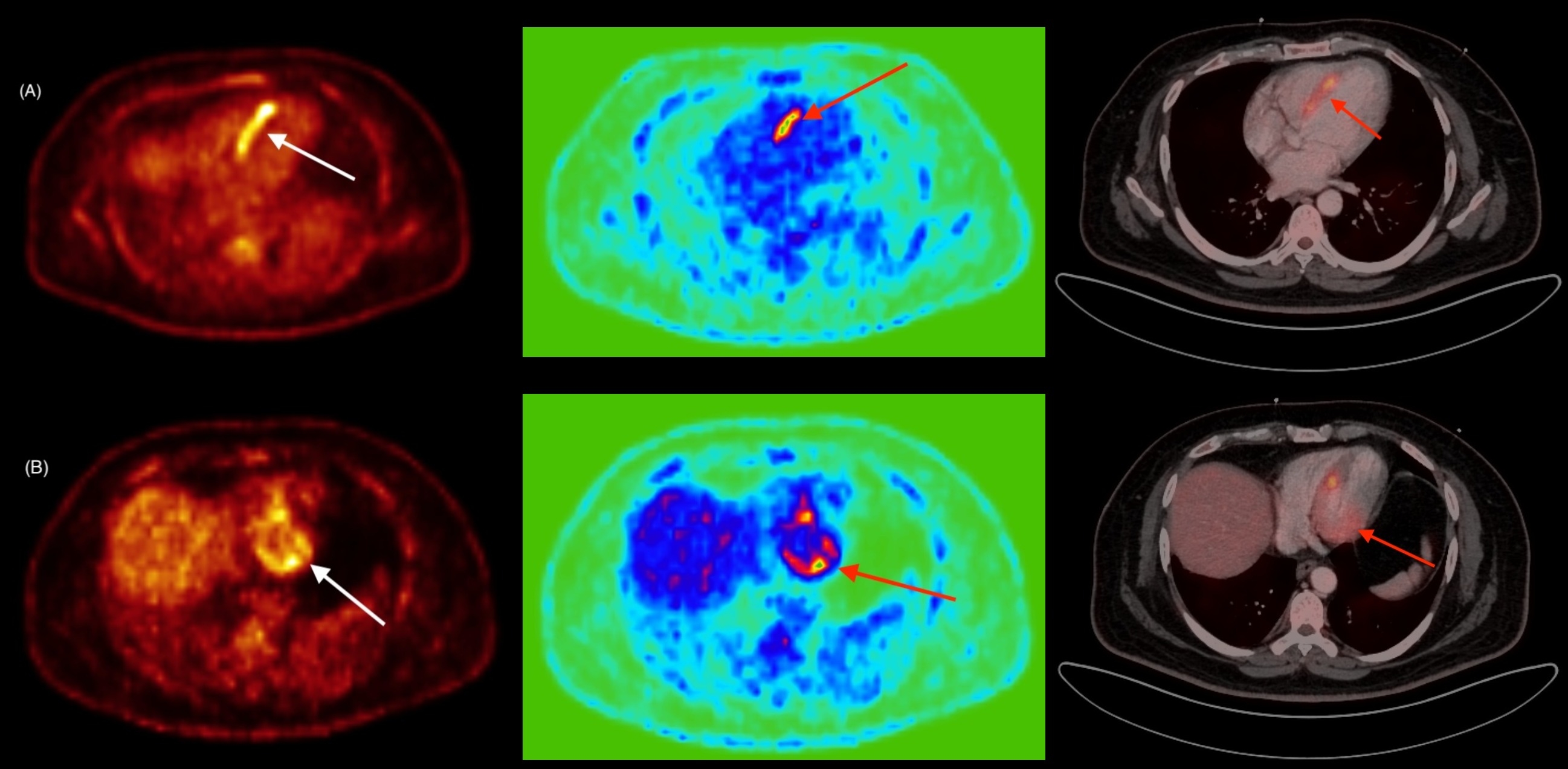
A 46-year-old male with poorly controlled type-2 diabetes mellites (T2DM) and without any significant past cardiac history presented with acute-onset palpitations, dry cough, and dyspnea. He developed sustained VT, which was reverted with IV amiodarone. On evaluation, he was found to have non-sustained monomorphic VT, a reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 30%, and moderate coronary artery disease without significant stenosis. NT-proBNP levels were elevated. Due to presence of metallic implant in arms, PET-CT was performed instead of conventional cardiac-MRI (CMR), revealing focal FDG uptake in the interventricular septum and lateral left ventricle (SUV max 11.3) (figure 1) along with widespread necrotic lymphadenopathy involving bilateral axillary, retroperitoneal, and right iliac and inguinal nodes (SUV max 29.3) suggestive of TB more than sarcoidosis (figure 2). Initially, the patient showed clinical improvement with no VT recurrence; however, he was later readmitted twice with episodes of VT. Subsequent Mantoux test and Quantiferon-TB Gold test were positive for TB infection, and lymph node biopsy confirmed the diagnosis. The patient was initiated with five-drug anti-tubercular therapy (ATT) along with guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) for heart failure. On recent visit, patient was clinically stable.
Conclusion:
This case highlights the importance of considering tuberculosis as a differential diagnosis in cases of idiopathic VT with severe LV dysfunction without significance coronary artery disease especially in TB-endemic regions. PET-CT played a crucial role in identifying myocardial involvement when conventional imaging was limited and CMR not possible in presence of metallic implant. Early diagnosis and initiation of ATT played a key role in arrhythmia control and clinical stabilization.
Myocardial tuberculosis (TB) is an extremely rare form of extrapulmonary TB with a reported prevalence of less than 2%. It is often diagnosed late due to subtle systemic or pulmonary manifestations or even absence of it. We report a case of myocardial TB presented with ventricular tachycardia (VT) along with heart failure was the sole clinical manifestation in an immunocompetent adult.
Case Description:
A 46-year-old male with poorly controlled type-2 diabetes mellites (T2DM) and without any significant past cardiac history presented with acute-onset palpitations, dry cough, and dyspnea. He developed sustained VT, which was reverted with IV amiodarone. On evaluation, he was found to have non-sustained monomorphic VT, a reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 30%, and moderate coronary artery disease without significant stenosis. NT-proBNP levels were elevated. Due to presence of metallic implant in arms, PET-CT was performed instead of conventional cardiac-MRI (CMR), revealing focal FDG uptake in the interventricular septum and lateral left ventricle (SUV max 11.3) (figure 1) along with widespread necrotic lymphadenopathy involving bilateral axillary, retroperitoneal, and right iliac and inguinal nodes (SUV max 29.3) suggestive of TB more than sarcoidosis (figure 2). Initially, the patient showed clinical improvement with no VT recurrence; however, he was later readmitted twice with episodes of VT. Subsequent Mantoux test and Quantiferon-TB Gold test were positive for TB infection, and lymph node biopsy confirmed the diagnosis. The patient was initiated with five-drug anti-tubercular therapy (ATT) along with guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) for heart failure. On recent visit, patient was clinically stable.
Conclusion:
This case highlights the importance of considering tuberculosis as a differential diagnosis in cases of idiopathic VT with severe LV dysfunction without significance coronary artery disease especially in TB-endemic regions. PET-CT played a crucial role in identifying myocardial involvement when conventional imaging was limited and CMR not possible in presence of metallic implant. Early diagnosis and initiation of ATT played a key role in arrhythmia control and clinical stabilization.
More abstracts on this topic:
5-oxoproline/ OPLAH Axis Alleviates Doxorubicin-induced Cardiomyopathy By Inhibiting Ferroptosis
Jiang Meng, Guo Xinning
Arrhythmic Risk Stratification of Patients with Suspected Cardiac Sarcoidosis, High-Grade Atrioventricular Block, and No Late Gadolinium Enhancement on Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Multicenter StudyBawaskar Parag, De Leeuw Beverly, Rochlani Yogita, Mathijssen Harold, Markowitz Jeremy, Von Wald Lisa, Roukoz Henri, Post Marco, Shenoy Chetan