Final ID: 4369799
AI-enhanced ECG for diastolic dysfunction: development, validation and prognosis across five international cohorts
Evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function is integral to diagnosing heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), but echocardiography is resource-intensive and not always available, leading to delayed detection. We developed an AI-enhanced ECG (AI-ECG) model to detect echocardiography-determined diastolic dysfunction (DD).
Methods
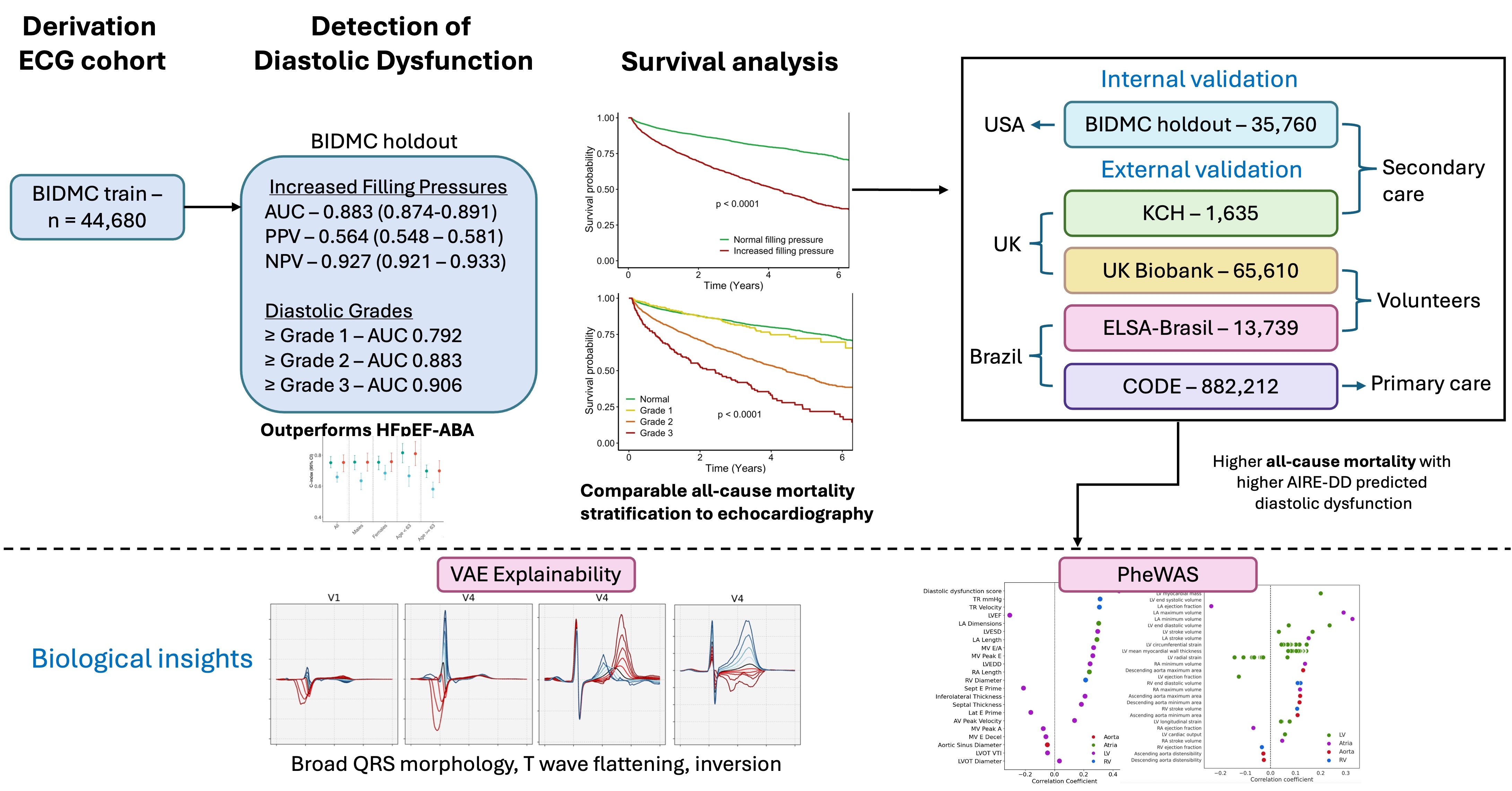
The AI-Risk Estimator for DD (AIRE-DD) is a residual neural network with a discrete-time survival loss function. It was trained on 89,100 ECG-echocardiography (ECG–TTE) pairs from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and externally validated in four cohorts: King’s College Hospital (KCH; n=1 635), CODE (Brazil; n=882,212), ELSA-Brasil (n=13,739) and UK Biobank (UKB; n = 65 610).
Results
In the BIDMC holdout set (n = 35,760 ECG–TTE pairs), AIRE-DD detected increased LV filling pressures with an AUC of 0.883 (95 % CI 0.874–0.891), sensitivity 0.780, specificity 0.822, PPV 0.564 and NPV 0.927. AIRE-DD also detected grades of diastolic dysfunction with AUCs of 0.792 (≥ grade I), 0.882 (≥ grade II) and 0.906 (grade III). For incident DD prediction in BIDMC participants without baseline DD and LVEF ≥ 50 %, AIRE-DD achieved a C-index of 0.751 (95 % CI 0.719–0.791). In KCH, AIRE-DD identified clinician-confirmed HFpEF with an AUC of 0.850 (0.809–0.887).
In BIDMC, increased filling pressures predicted by AIRE-DD stratified incident outcomes at least as well as echocardiography (age- and sex-adjusted hazard ratios [HRs]: mortality 2.09 vs 1.98; atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease 2.02 vs 1.70; atrial fibrillation 2.12 vs 1.79; heart failure 2.24 vs 2.40; chronic kidney disease 1.93 vs 1.70). Across BIDMC, CODE, ELSA-Brasil and UKB, AIRE-DD-predicted increased filling pressures were associated with age- and sex-adjusted HRs for all-cause mortality of 2.05 (1.87–2.26), 2.83 (2.75–2.92), 4.38 (3.46–5.52) and 1.67 (1.33–2.09), respectively.
Explainability analyses showed that AIRE-DD predictions correlated with broad QRS morphology, T-wave inversion/flattening and poor precordial R-wave progression, and were associated with echocardiographic metrics of impaired relaxation, chamber enlargement and myocardial remodelling.
Conclusion
AIRE-DD provides a non-invasive, scalable method for detection and prediction of diastolic dysfunction and stratification of mortality risk, supporting its potential as a first-line screening tool to prioritise patients for confirmatory imaging and early intervention.
- Pastika, Libor ( Imperial College London , London , United Kingdom )
- O Gallagher, Kevin ( KINGS COLLEGE LONDON , London , United Kingdom )
- Shah, Ajay ( KINGS COLLEGE LONDON , London , United Kingdom )
- Barreto, Sandhi Maria ( Universidade Federal Minas Gerais , Belo Horizonte , Brazil )
- Foppa, Murilo ( HCPA , PortoAlegre , Brazil )
- Paixao, Gabriela ( FEDERAL UNIVERSITY OF MINAS GERAIS , Belo Horizonte , Brazil )
- Khan, Sadia ( Chelsea and Westminster NHS Foundation Trust , London , United Kingdom )
- Brant, Luisa ( FEDERAL UNIVERSITY of MINAS GERAIS , Belo Horizonte , Brazil )
- Kramer, Daniel ( Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Cente , Newton Center , Massachusetts , United States )
- Waks, Jonathan ( Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Cente , Newton Center , Massachusetts , United States )
- Peters, Nicholas ( Imperial College London , London , United Kingdom )
- Zeidaabadi, Boroumand ( Imperial College London , London , United Kingdom )
- Ribeiro, Antonio Luiz ( UFMG , Belo Horizonte , Brazil )
- Sau, Arunashis ( Imperial College London , London , United Kingdom )
- Ng, Fu Siong ( Imperial College , London , United Kingdom )
- Patlatzoglou, Konstantinos ( Imperial College London , London , United Kingdom )
- Khattak, Gul Rukh ( Imperial College London , London , United Kingdom )
- Barker, Joseph ( Imperial College London , London , United Kingdom )
- Aggour, Hesham ( Imperial College London , London , United Kingdom )
- El-medany, Ahmed ( Imperial College London , London , United Kingdom )
- Bernstein, Brett ( KINGS COLLEGE LONDON , London , United Kingdom )
- Wu, Jack ( KINGS COLLEGE LONDON , London , United Kingdom )
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
Sunday, 11/09/2025 , 09:45AM - 11:10AM
Abstract Oral Session
More abstracts on this topic:
Wexler Yehuda, Grinstein Harel, Landesberg Michal, Glatstein Shany, Huber Irit, Arbel Gil, Gepstein Lior
A Machine Learning Algorithm to Detect Pediatric Supraventricular Tachycardia Risk from Baseline ECGsArezoumand Amirhossein, Danala Gopichandh, Masnadi Khiabani Parisa, Ebert David, Behere Shashank
More abstracts from these authors:
Pastika Libor, Peters Nicholas, Kramer Daniel, Waks Jonathan, Sau Arunashis, Ng Fu Siong, Patlatzoglou Konstantinos, Sieliwonczyk Ewa, Barker Joseph, Zeidaabadi Boroumand, Mcgurk Kathryn, Khan Sadia, Mandic Danilo, Ware James
Artificial Intelligence-enhanced Electrocardiography Sex-Discordance is Associated with Cardiovascular Events and Risk Factors in Women: from the ELSA-Brasil studyCamelo Lidyane, Zeidaabadi Boroumand, Pinto Filho Marcelo, Ribeiro Antonio Luiz, Ng Fu, Brant Luisa, Sau Arunashis, Barreto Sandhi, Giatti Luana, Oliveira Clara, Paixao Gabriela, Barker Joseph, Pastika Libor, Patlatzoglou Konstantinos