Final ID: MP1995
A Diagnosis Dilemma of Positional Hypoxia: Scoliosis-Mediated Platypnea-Orthodeoxia Syndrome
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Description of Case:
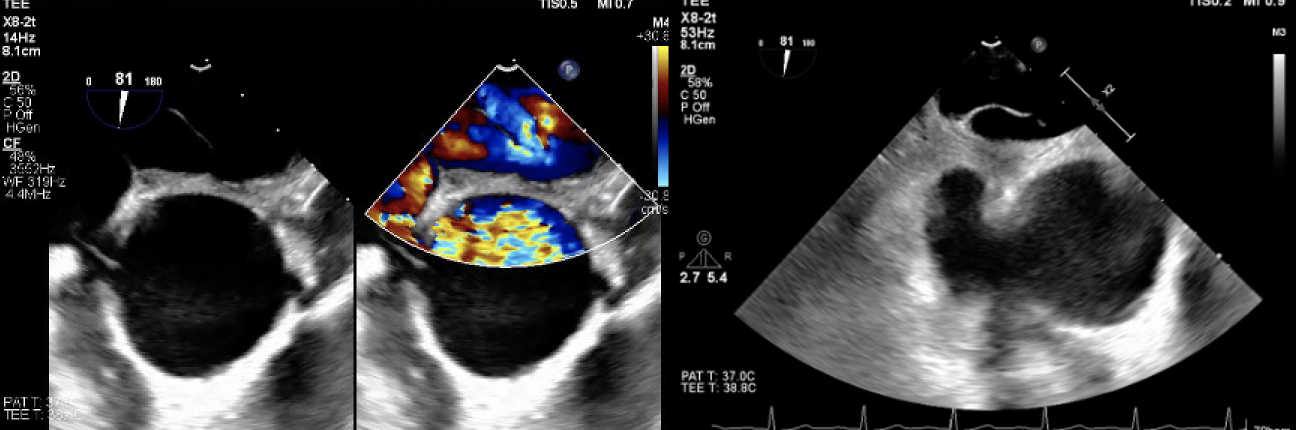
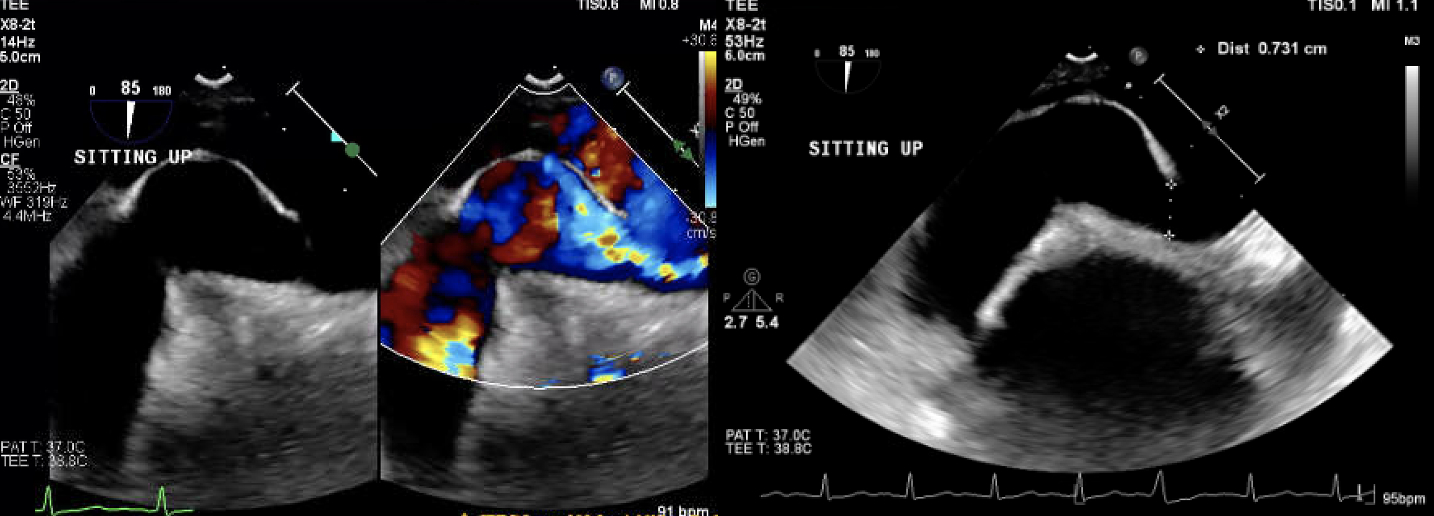
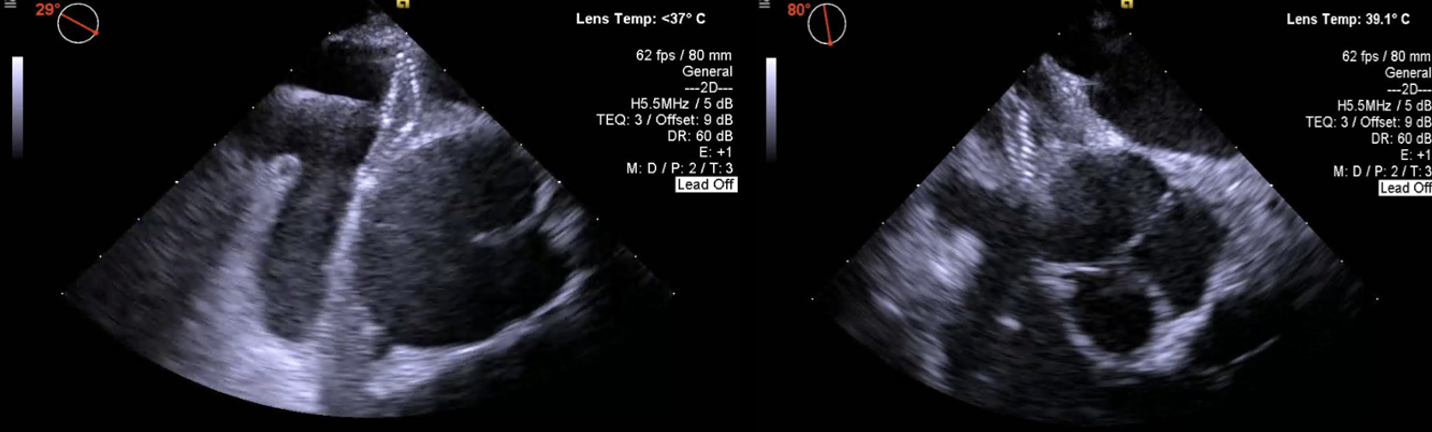
A 78-year-old man with a history of Parkinson’s, TIAs, and scoliosis presented with a sequalae of symptoms concerning for recurrent TIA, however extensive workup demonstrated no evidence of acute intracranial abnormalities. Subsequently, he developed acute hypoxic respiratory failure requiring high-flow nasal cannula. Initial chest CT angiography (CTA) and X-ray were negative for acute pulmonary pathology. A transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) with bubble study was positive for moderate right-to-left shunt through a patent foramen ovale (PFO). Subsequent imaging modalities, including right heart catheterization, transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) with bubble study, cardiac CT, and cardiac MRI, exhibited normal hemodynamics, positive PFO with left-to-right shunt, and no evidence of significant right-to-left shunt (normal Qp:Qs). Of note, he was discovered to have significant hypoxia while sitting up but remained on room air while supine. In order to evaluate for platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome (POS), TTE with agitated saline contrast was performed which was grossly positive after 5 cardiac cycles while in the supine position and 3 cardiac cycles while upright, raising concern for pulmonary arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). However, repeat CTA was negative for pulmonary AVMs. Finally, repeat TEE bubble study was performed while the patient was supine (Images A) and sitting up (Images B) which demonstrated a PFO with bidirectional shunting. While the patient was sitting up (Images B), there was stretching of the PFO with significant, continuous right-to-left shunting likely precipitated by the patient’s significant scoliosis. The patient underwent successful percutaneous PFO closure (Images C), which immediately resolved his hypoxia.
Discussion:
POS is a rare but important clinical phenomenon characterized by positional dyspnea and hypoxemia that worsen in the upright position and improve when supine. This syndrome is mostly associated with intracardiac shunts, such as a PFO, but may also be exacerbated by extrinsic anatomical factors. This rare case report of POS demonstrated a PFO that was exacerbated by vertebral deformity and mediastinal distortion (severe scoliosis) facilitating significant right-to-left shunting in the upright position. The case highlights the critical role of spinal anatomy in the pathophysiology of POS, especially with existing PFO, and the importance of multimodality imaging in diagnosing positional hypoxemia.
A 78-year-old man with a history of Parkinson’s, TIAs, and scoliosis presented with a sequalae of symptoms concerning for recurrent TIA, however extensive workup demonstrated no evidence of acute intracranial abnormalities. Subsequently, he developed acute hypoxic respiratory failure requiring high-flow nasal cannula. Initial chest CT angiography (CTA) and X-ray were negative for acute pulmonary pathology. A transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) with bubble study was positive for moderate right-to-left shunt through a patent foramen ovale (PFO). Subsequent imaging modalities, including right heart catheterization, transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) with bubble study, cardiac CT, and cardiac MRI, exhibited normal hemodynamics, positive PFO with left-to-right shunt, and no evidence of significant right-to-left shunt (normal Qp:Qs). Of note, he was discovered to have significant hypoxia while sitting up but remained on room air while supine. In order to evaluate for platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome (POS), TTE with agitated saline contrast was performed which was grossly positive after 5 cardiac cycles while in the supine position and 3 cardiac cycles while upright, raising concern for pulmonary arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). However, repeat CTA was negative for pulmonary AVMs. Finally, repeat TEE bubble study was performed while the patient was supine (Images A) and sitting up (Images B) which demonstrated a PFO with bidirectional shunting. While the patient was sitting up (Images B), there was stretching of the PFO with significant, continuous right-to-left shunting likely precipitated by the patient’s significant scoliosis. The patient underwent successful percutaneous PFO closure (Images C), which immediately resolved his hypoxia.
Discussion:
POS is a rare but important clinical phenomenon characterized by positional dyspnea and hypoxemia that worsen in the upright position and improve when supine. This syndrome is mostly associated with intracardiac shunts, such as a PFO, but may also be exacerbated by extrinsic anatomical factors. This rare case report of POS demonstrated a PFO that was exacerbated by vertebral deformity and mediastinal distortion (severe scoliosis) facilitating significant right-to-left shunting in the upright position. The case highlights the critical role of spinal anatomy in the pathophysiology of POS, especially with existing PFO, and the importance of multimodality imaging in diagnosing positional hypoxemia.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case Series of Papillary Fibroelastomas on the Coumadin ridge
Aboukhatwa Omar, Akiki Elias, Kurmann Reto, Larson Kathryn, Keeney Michael, Bois Melanie, Klarich Kyle
Chronic Suppression of the Renin-Angiotensin System Induces Renal Vascular Remodeling, Hypoxia, and Metabolic ReprogrammingAlmeida Lucas, Medrano Silvia, Smith Jason, Yamaguchi Hiroki, Yamaguchi Manako, Sequeira Maria Luisa, Gomez Ariel