Final ID: MP815
Pulmonary congestion assessment by automated quantitative computer tomography in heart failure patients
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Heart failure (HF) affects interstitial lung structure and function. AI-assisted quantitative computed tomography (qCT) offers possibility of objective assesment of lung structure, allowing to detect the presence and the severity of HF.
Hypothesis: Can automated qCT analysis discriminate HF from controls and identify tissue structures most linked to degree of congestion ?
Methods: Subjects underwent right heart catheterization (RHC), native CT chest imaging (full inspiration/expiration) by Naeotom-α photon-counting CT scanner (Siemens), lab testing, echocardiography. Automated AI-based analysis (VIDA Diagnostics) was employed to evaluate lung volumes, densities and tissue texture. Image series were used in mediastinal and lung window reconstruction with slice thickness 0,8 mm and increments 0,5 mm.
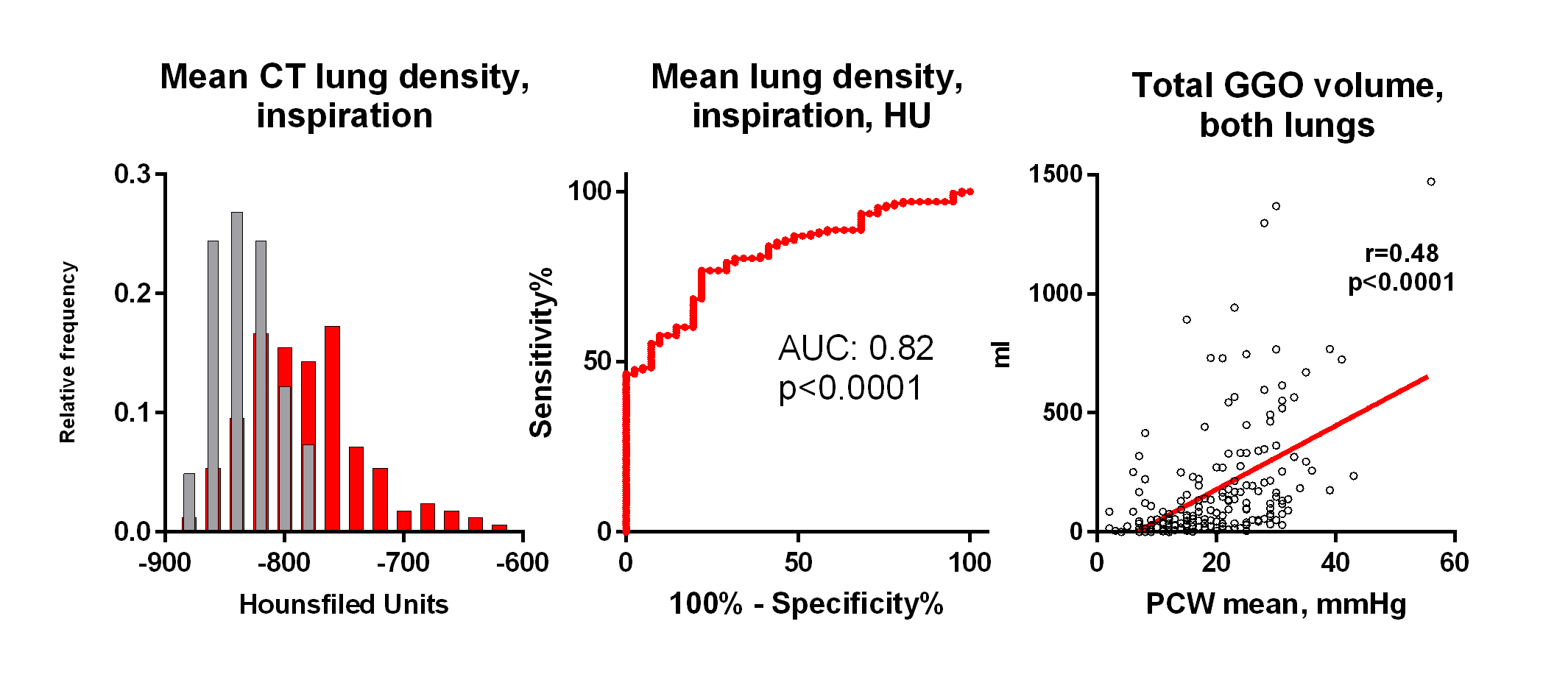
Results: 186 HF patients (85% HFrEF, NYHA 2.8±0.5, 58 y, 80% males, NTproBNP 4491 pg/ml, LVEF 26%) and 43 controls of similar sex and BMI were analyzed; both groups free of primary lung disease. In HF, 85 % had PH (mPAP>20mmHg). HF patients had comparable inspiratory lung volume, reduced air volume and increased lung tissue volume, compared to controls. Mean lung density (-782±50 vs -832±25 HU, p<0.0001), density variability and estimated lung fluid content (21.3 vs 16.7%, p<0.0001) were all higher in HF compared to controls. Across various density cut-offs, the most notable difference was at lung tissue density < -856 HU at inspiration. Lung tissue density corelated with mean PA pressure (r=0.49, p<0.0001), and less with pulmonary vascular resistance (r=0.21, p=0.006). Insp/exp scan analysis showed no difference in air trapping, but reduced lung tissue compliance (Jacobian strain: 1.8±0.4 vs 1.6±0.3, p=0.0005) in HF.
Lung texture analysis showed increased ground-glass opacity (GGO) mass (48.8 g vs 9.1 g; p < 0.001), reticulation (42.2 g vs. 8.4 g; p < 0.001) and consolidation (0.5 g vs 0.2 g; p=0.0011) in HF compared to controls, with no difference in honeycombing. GGO mass correlated strongly with pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) (r=0.48, p<0.001) and mitral regurgitation grade (r=0.28,<0.0001), but not with inflammation (hsCRP, IL6, WBC), smoking exposure or oncotic pressure.
Conclusions: qCT distinguished HF patients from controls by increased lung tissue mass, reduced air volume, increased lung density and increased mass of GGO and reticulation. GGO mass in HF strongly reflects increased hydrostatic pressure, but not inflammation.
Hypothesis: Can automated qCT analysis discriminate HF from controls and identify tissue structures most linked to degree of congestion ?
Methods: Subjects underwent right heart catheterization (RHC), native CT chest imaging (full inspiration/expiration) by Naeotom-α photon-counting CT scanner (Siemens), lab testing, echocardiography. Automated AI-based analysis (VIDA Diagnostics) was employed to evaluate lung volumes, densities and tissue texture. Image series were used in mediastinal and lung window reconstruction with slice thickness 0,8 mm and increments 0,5 mm.
Results: 186 HF patients (85% HFrEF, NYHA 2.8±0.5, 58 y, 80% males, NTproBNP 4491 pg/ml, LVEF 26%) and 43 controls of similar sex and BMI were analyzed; both groups free of primary lung disease. In HF, 85 % had PH (mPAP>20mmHg). HF patients had comparable inspiratory lung volume, reduced air volume and increased lung tissue volume, compared to controls. Mean lung density (-782±50 vs -832±25 HU, p<0.0001), density variability and estimated lung fluid content (21.3 vs 16.7%, p<0.0001) were all higher in HF compared to controls. Across various density cut-offs, the most notable difference was at lung tissue density < -856 HU at inspiration. Lung tissue density corelated with mean PA pressure (r=0.49, p<0.0001), and less with pulmonary vascular resistance (r=0.21, p=0.006). Insp/exp scan analysis showed no difference in air trapping, but reduced lung tissue compliance (Jacobian strain: 1.8±0.4 vs 1.6±0.3, p=0.0005) in HF.
Lung texture analysis showed increased ground-glass opacity (GGO) mass (48.8 g vs 9.1 g; p < 0.001), reticulation (42.2 g vs. 8.4 g; p < 0.001) and consolidation (0.5 g vs 0.2 g; p=0.0011) in HF compared to controls, with no difference in honeycombing. GGO mass correlated strongly with pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) (r=0.48, p<0.001) and mitral regurgitation grade (r=0.28,<0.0001), but not with inflammation (hsCRP, IL6, WBC), smoking exposure or oncotic pressure.
Conclusions: qCT distinguished HF patients from controls by increased lung tissue mass, reduced air volume, increased lung density and increased mass of GGO and reticulation. GGO mass in HF strongly reflects increased hydrostatic pressure, but not inflammation.
More abstracts on this topic:
9-Year Longitudinal Assessment of the 12-lead Electrocardiogram of Volunteer Firefighters
Bae Alexander, Dzikowicz Dillon, Lai Chi-ju, Brunner Wendy, Krupa Nicole, Carey Mary, Tam Wai Cheong, Yu Yichen
Age- and Sex-Related Coronary Atherosclerosis by Artificial Intelligence Quantitative Coronary CT Angiography from the INVICTUS RegistryOkubo Ryo, Ichikawa Keishi, Abe Mitsunori, Kitagawa Toshiro, Ikenaga Hiroki, Osawa Kazuhiro, Saji Mike, Iguchi Nobuo, Nakazawa Gaku, Takahashi Kuniaki, Ijichi Takeshi, Matsuo Hitoshi, Mikamo Hiroshi, Kurata Akira, Moroi Masao, Iijima Raisuke, Crabtree Tami, Min James, Earls James, Nakanishi Rine, Sobue Yoshihiro, Kaneko Umihiko, Sato Hideyuki, Fujimoto Shinichiro, Nozaki Yui, Kajiya Takashi, Miyoshi Toru