Final ID: MP1971
The predictive value of Atherogenic index of plasma and plaque characteristics after percutaneous coronary intervention in ST-elevated myocardial infarction patients: an intravascular optical coherence tomography study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background and Aim This prospective study investigated plaque morphologies based on the underlying culprit lesion pathology in relation to the Atherogenic Index of Plasma (AIP) in patients with acute ST-elevated myocardial infarction (STEMI) who underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention and optical coherence tomography (OCT) for assessment of culprit lesions. The aim of the study was to elucidate the effects of the AIP index and plaque type on the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs).
Methods A total of 274 patients with STEMI aged ≥ 18 years who underwent pre-intervention OCT imaging of culprit lesions between March 2017 and March 2019 were enrolled. AIP index was calculated using the formula: log 10 (triglycerides [TG]/ high-density lipoprotein cholesterol [HDL-C]). We stratified the cohort into four groups according to the presence of Thin-Cap Fibroatheroma (TCFA), as assessed by OCT, and the median value of AIP: Group I consisted of patients with AIP < median & without TCFA; Group II had AIP < median & with TCFA; Group III included those with AIP > median & without TCFA; and Group IV comprised patients with AIP > median & with TCFA.
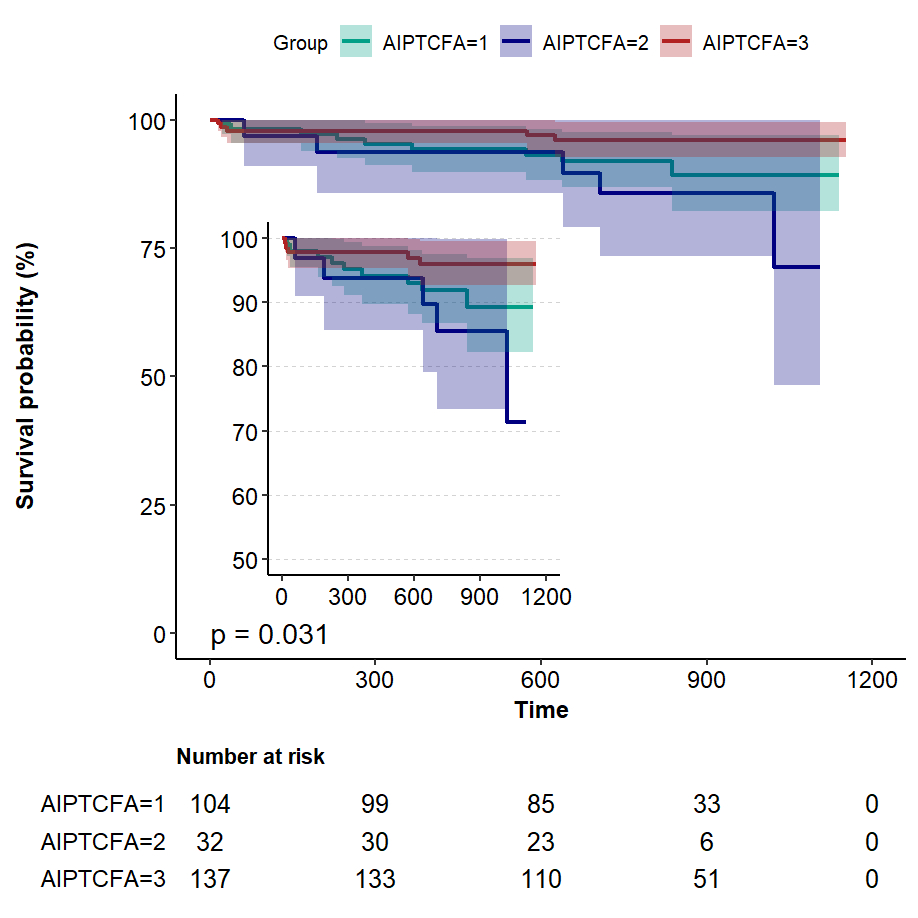
Outcomes Patients in Group IV exhibited a higher prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus (p = 0.006), elevated triglyceride-glucose index (TyG index) levels (p < 0.001), increased LDL-C levels (p = 0.006), higher triglycerides levels (p < 0.001), and elevated LP(a) rates (p < 0.001), indicating accelerated atherosclerosis. Furthermore, individuals within higher tertiles of AIP demonstrated a greater frequency of healing plaques (p = 0.021). Multivariable Cox regression analysis revealed that the incidence of MACEs among patients in Group IV (AIP > median & with TCFA) increased by 72% compared to those in Group I. Kaplan-Meier analyses confirmed risk stratification for MACEs based on interactions between AIP-TCFA interaction (log-rank p =0.031) and AIP-fibrous plaque interaction(log-rank p =0.032).
Conclusion Microstructural features observed via OCT for culprit lesions, combined with the AIP index—an important marker for cardiovascular disease—may be utilized clinically to support risk stratification and predict adverse events among STEMI patients.
Methods A total of 274 patients with STEMI aged ≥ 18 years who underwent pre-intervention OCT imaging of culprit lesions between March 2017 and March 2019 were enrolled. AIP index was calculated using the formula: log 10 (triglycerides [TG]/ high-density lipoprotein cholesterol [HDL-C]). We stratified the cohort into four groups according to the presence of Thin-Cap Fibroatheroma (TCFA), as assessed by OCT, and the median value of AIP: Group I consisted of patients with AIP < median & without TCFA; Group II had AIP < median & with TCFA; Group III included those with AIP > median & without TCFA; and Group IV comprised patients with AIP > median & with TCFA.
Outcomes Patients in Group IV exhibited a higher prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus (p = 0.006), elevated triglyceride-glucose index (TyG index) levels (p < 0.001), increased LDL-C levels (p = 0.006), higher triglycerides levels (p < 0.001), and elevated LP(a) rates (p < 0.001), indicating accelerated atherosclerosis. Furthermore, individuals within higher tertiles of AIP demonstrated a greater frequency of healing plaques (p = 0.021). Multivariable Cox regression analysis revealed that the incidence of MACEs among patients in Group IV (AIP > median & with TCFA) increased by 72% compared to those in Group I. Kaplan-Meier analyses confirmed risk stratification for MACEs based on interactions between AIP-TCFA interaction (log-rank p =0.031) and AIP-fibrous plaque interaction(log-rank p =0.032).
Conclusion Microstructural features observed via OCT for culprit lesions, combined with the AIP index—an important marker for cardiovascular disease—may be utilized clinically to support risk stratification and predict adverse events among STEMI patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
Admission Cell-free DNA Predicts Cardiogenic Shock Progression and In-Hospital Mortality
Park Ashley, Kong Hyesik, Andargie Temesgen, Jang Moon, Solomon Michael, Brusca Samuel, Barnett Christopher, Obrien Connor, Agbor-enoh Sean
ADC-based Infarct Density – Validating a Novel Imaging Biomarker of Functional Outcome after Endovascular ThrombectomyFavilla Christopher, Bonkhoff Anna, Rost Natalia, Messe Steven, Regenhardt Robert, Denny Braden, Simonsen Claus, Shakibajahromi Banafsheh, Patel Aman, Leslie-mazwi Thabele, Dmytriw Adam, Schirmer Markus