Final ID: MP982
Efficiency of Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Temporal Dispersion Mapping with Pulsed Field Ablation: Integration of Volta AF-Xplorer and Affera Sphere-9 System
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Pulsed Field Ablation (PFA) using the Sphere-9 catheter with the Affera™ Mapping System (S9A) has recently been approved for the treatment of paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation (AF) and atrial flutter. The Volta AF-Xplorer™ mapping software (VX), which detects and maps regions of spatial and temporal dispersion, has shown promise in improving procedural outcomes in AF ablation. However, the combined use of VX with S9A has not been studied. This study aims to evaluate the safety, efficacy, and efficiency of integrating VX with the S9A system during AF ablation.
Methods:
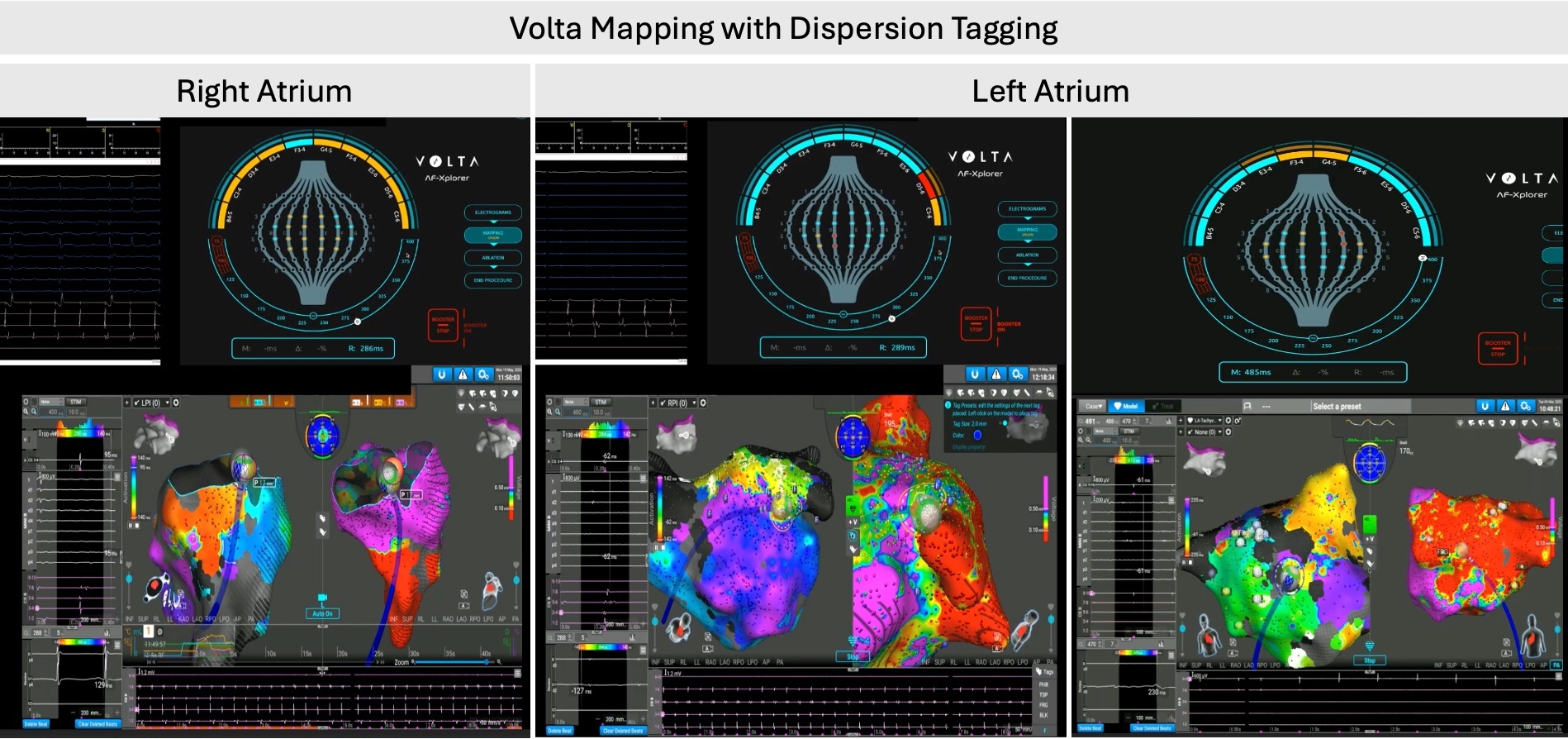
This prospective, single-center study enrolled patients undergoing PFA with S9A and VX between February and May 2025. Real-time 3D mapping of the right and left atria (RA and LA) was performed, with VX used to identify and label regions of spatiotemporal dispersion. Baseline dispersion mapping in AF was conducted, and ablation was carried out at all identified dispersion sites unless contraindicated by clinical judgment.
Results:
Data from 21 patients (52.4% female, mean age 68.8 ± 13.6 years) were analyzed. Pre-procedural ECG showed AF in 76.2% (n=16) and atrial flutter in 23.8% (n=5). Of the cases, 19% were de novo, and 81% were redo ablations. The average procedure duration was 60 ± 10 minutes, with all procedures performed using a zero-fluoroscopy approach. VX identified an average of 12±4 dispersion points in the RA and 18±2 in the LA. AF was terminated with ablation in 85.7% of cases, and only three patients required intraprocedural cardioversion from AF.
Conclusion:
Our findings suggest that combining the Volta AF-Xplorer with the Affera Sphere-9 mapping system during PFA is safe, effective, and efficient. This integrated approach shows promise for improving ablation outcomes. Further studies are warranted to assess long-term results and broader applicability.
Pulsed Field Ablation (PFA) using the Sphere-9 catheter with the Affera™ Mapping System (S9A) has recently been approved for the treatment of paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation (AF) and atrial flutter. The Volta AF-Xplorer™ mapping software (VX), which detects and maps regions of spatial and temporal dispersion, has shown promise in improving procedural outcomes in AF ablation. However, the combined use of VX with S9A has not been studied. This study aims to evaluate the safety, efficacy, and efficiency of integrating VX with the S9A system during AF ablation.
Methods:
This prospective, single-center study enrolled patients undergoing PFA with S9A and VX between February and May 2025. Real-time 3D mapping of the right and left atria (RA and LA) was performed, with VX used to identify and label regions of spatiotemporal dispersion. Baseline dispersion mapping in AF was conducted, and ablation was carried out at all identified dispersion sites unless contraindicated by clinical judgment.
Results:
Data from 21 patients (52.4% female, mean age 68.8 ± 13.6 years) were analyzed. Pre-procedural ECG showed AF in 76.2% (n=16) and atrial flutter in 23.8% (n=5). Of the cases, 19% were de novo, and 81% were redo ablations. The average procedure duration was 60 ± 10 minutes, with all procedures performed using a zero-fluoroscopy approach. VX identified an average of 12±4 dispersion points in the RA and 18±2 in the LA. AF was terminated with ablation in 85.7% of cases, and only three patients required intraprocedural cardioversion from AF.
Conclusion:
Our findings suggest that combining the Volta AF-Xplorer with the Affera Sphere-9 mapping system during PFA is safe, effective, and efficient. This integrated approach shows promise for improving ablation outcomes. Further studies are warranted to assess long-term results and broader applicability.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Curious Complete Heart Block with Carfilzomib
Shah Mohammed, Rahman Naveed, Al-mohamad Talal, Batra Sejal, Vyas Apurva
Adverse Outcomes Following Atrial Fibrillation Ablation in Patients With Connective Tissue Disease: A Propensity-Matched Real-World AnalysisRayyan Abdallah, Obeidat Omar, Alqudah Qusai, Khasawneh Tawfiq, Alomari Ahmad, Mestarihi Aseed, Alnabahneh Nizar, Nasser Hesham, Tong Ann