Final ID: MP2378
Impact of a Familial Hypercholesterolemia Education Initiative on Use of Lipid Lowering Treatment: the CARE-FH Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): BACKROUND: Undertreatment of elevated LDL-Cholesterol (LDL-C) is a national public health issue. The Collaborative Approach to Reach Everyone with Familial Hypercholesterolemia (CARE-FH) is a clinical trial within an integrated health system to foster the application of FH screening guidance in primary care, to identify and to improve early initiation of treatment of individuals with FH and/or elevated LDL-C. We hypothesized that primary care providers would be more likely to initiate lipid lowering therapy in those with LDL-C > 190 mg/dl after an educational intervention regarding FH, and might also be more likely to treat those not at goal as defined by the 2018 multi-society lipid guidelines.
METHODS: Stepped-wedge cluster randomized design was employed to implement the intervention across participating clinics. From the electronic health record we identified all adult patients at Geisinger with a lipid profile obtained during the study time window. Data collected included LDL-C levels, new lipid prescriptions, referrals to cardiology/lipid specialist/pharmacy treatment program, and achievement of treatment goal. Providers who received the intervention were compared to those who had not to assess impact of the intervention on lipid treatment outcomes.
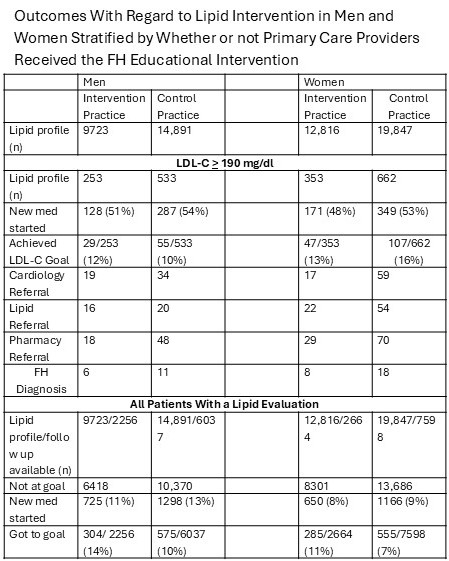
RESULTS: Overall, there were 57,277 patients with an LDL-C value (22,539 (39%) in intervention practices; 24,614 male (43%)). The Table shows key results stratified by sex. Overall, slightly more than half of those with an LDL-C > 190 mg/dl had a lipid lowering medication started, with about 20% being referred for further evaluation. The educational intervention did not appear to impact these rates (Chi-square test, p = 0.13 for new meds; p = 0.60 for achieved goal). For the cohort at large, about 10% overall had a new medication started and about 10% got to goal at follow up, with women less likely than men to have a medication started (OR = 0.66 [0.61, 0.70], p < 0.001) or get to goal (OR = 0.72 [0.65, 0.79], p < 0.001).
CONCLUSION: These results are disappointing. Overall, lipid lowering medication initiation rates for extreme elevations in LDL-C were low and an educational intervention to improve FH diagnosis had no impact on outcomes. For all those with actionable lipid profiles, women were less likely to receive treatment than men.
METHODS: Stepped-wedge cluster randomized design was employed to implement the intervention across participating clinics. From the electronic health record we identified all adult patients at Geisinger with a lipid profile obtained during the study time window. Data collected included LDL-C levels, new lipid prescriptions, referrals to cardiology/lipid specialist/pharmacy treatment program, and achievement of treatment goal. Providers who received the intervention were compared to those who had not to assess impact of the intervention on lipid treatment outcomes.
RESULTS: Overall, there were 57,277 patients with an LDL-C value (22,539 (39%) in intervention practices; 24,614 male (43%)). The Table shows key results stratified by sex. Overall, slightly more than half of those with an LDL-C > 190 mg/dl had a lipid lowering medication started, with about 20% being referred for further evaluation. The educational intervention did not appear to impact these rates (Chi-square test, p = 0.13 for new meds; p = 0.60 for achieved goal). For the cohort at large, about 10% overall had a new medication started and about 10% got to goal at follow up, with women less likely than men to have a medication started (OR = 0.66 [0.61, 0.70], p < 0.001) or get to goal (OR = 0.72 [0.65, 0.79], p < 0.001).
CONCLUSION: These results are disappointing. Overall, lipid lowering medication initiation rates for extreme elevations in LDL-C were low and an educational intervention to improve FH diagnosis had no impact on outcomes. For all those with actionable lipid profiles, women were less likely to receive treatment than men.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Framework for Developing Prehospital Intracerebral Hemorrhage Recognition Scales and Technologies
Taleb Shayandokht, Hsu Jamie, Saver Jeffrey
Apolipoprotein A1 infusion in patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of randomized trialsPrata Alonzo, Gioli-pereira Luciana, Fukunaga Christian, Katsuyama Eric, Coan Ana Carolina, Scardini Pedro Gabriel, Petri Santos Pinheiro Rafael, Falco Neto Wilson, Fernandes Julia, Andrade Naieli