Final ID: MP2014
Association of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance-Derived Myocardial Strain with Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy and Preserved Systolic Function
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): BACKGROUND: Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) feature tracking enables non-invasive quantification of myocardial strain. In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) with preserved ejection fraction, the prognostic value of different left ventricular (LV) strain components remains unclear.
OBJECTIVES: This study aimed to assess the independent prognostic value of LV global longitudinal (GLS), circumferential (GCS), and radial strain (GRS) metrics in predicting cardiovascular morbidity and mortality using a large HCM cohort with preserved LV ejection fraction (LVEF).
METHODS: Participants with LVEF≥50% from a HCM cohort study were included. CMR cine images were utilized to calculate LV strains by feature tracking technique. Univariable and multivariable Cox models were used to evaluate the association of each strain marker (GLS, GCS, GRS) with 1) cardiovascular morbidity (e.g., heart failure, new-onset atrial fibrillation, and stroke); 2) mortality (e.g., sudden cardiac death [SCD], cardiovascular death [CVD], and all-cause death), separately. The multivariable models were tested with adjustment for prognostically important clinical features and conventional global LV imaging markers relevant for each outcome.
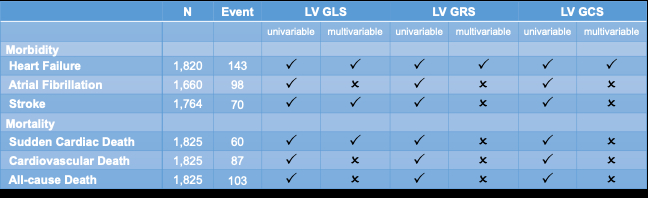
RESULTS: Overall, 1,825 participants were included in the study (average age 49.5 years), with a median follow-up period of 7.5 years. All univariable and multivariable models demonstrated that GLS was independent predictors for incidence of heart failure (HR: 1.09; 95% CI: 1.02-1.15, P=.005), stroke (HR: 1.09; 95% CI: 1.02-1.18, P=.014), and SCD (HR: 1.09; 95% CI: 1.01-1.18, P=.03). GCS and GRS were associated with increased incidence of cardiovascular adverse outcomes in univariable analysis, but only remain significantly associated with heart failure after adjusting other clinical and imaging parameters (GCS: HR: 1.09; 95% CI: 1.04-1.14, P<.001; GRS: HR: 0.97; 95% CI: 0.95-0.99, P=.006). None of the strains showed an independent relation with atrial fibrillation, CVD, or all-cause death in multivariable analysis.
CONCLUSIONS: In the HCM patients with preserved systolic function, LV strain metrics derived using CMR-FT in radial, circumferential, and longitudinal directions are independently predictive of heart failure, but only GLS is independently predictive of stroke and SCD in this population.
OBJECTIVES: This study aimed to assess the independent prognostic value of LV global longitudinal (GLS), circumferential (GCS), and radial strain (GRS) metrics in predicting cardiovascular morbidity and mortality using a large HCM cohort with preserved LV ejection fraction (LVEF).
METHODS: Participants with LVEF≥50% from a HCM cohort study were included. CMR cine images were utilized to calculate LV strains by feature tracking technique. Univariable and multivariable Cox models were used to evaluate the association of each strain marker (GLS, GCS, GRS) with 1) cardiovascular morbidity (e.g., heart failure, new-onset atrial fibrillation, and stroke); 2) mortality (e.g., sudden cardiac death [SCD], cardiovascular death [CVD], and all-cause death), separately. The multivariable models were tested with adjustment for prognostically important clinical features and conventional global LV imaging markers relevant for each outcome.
RESULTS: Overall, 1,825 participants were included in the study (average age 49.5 years), with a median follow-up period of 7.5 years. All univariable and multivariable models demonstrated that GLS was independent predictors for incidence of heart failure (HR: 1.09; 95% CI: 1.02-1.15, P=.005), stroke (HR: 1.09; 95% CI: 1.02-1.18, P=.014), and SCD (HR: 1.09; 95% CI: 1.01-1.18, P=.03). GCS and GRS were associated with increased incidence of cardiovascular adverse outcomes in univariable analysis, but only remain significantly associated with heart failure after adjusting other clinical and imaging parameters (GCS: HR: 1.09; 95% CI: 1.04-1.14, P<.001; GRS: HR: 0.97; 95% CI: 0.95-0.99, P=.006). None of the strains showed an independent relation with atrial fibrillation, CVD, or all-cause death in multivariable analysis.
CONCLUSIONS: In the HCM patients with preserved systolic function, LV strain metrics derived using CMR-FT in radial, circumferential, and longitudinal directions are independently predictive of heart failure, but only GLS is independently predictive of stroke and SCD in this population.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acute Severe Mitral Regurgitation Due to Flail Posterior Leaflet without Chordal Rupture Following Myosin Inhibitor Treatment of Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy
Patel Shreyan, Taha Israa, Elmi Daniel, Shirani Jamshid
A Case of Successful Resuscitation After Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest Caused by Undiagnosed Pheochromocytoma-induced CardiomyopathyHatakeyama Toshihiro, Suetsugu Yusuke, Watanabe Kaoru, Matsushima Hisao