Final ID: MP512
Remote Time-Restricted Eating and Mindfulness Pilot Intervention Improves Cardiovascular Disease Risk Markers in Young Adults with Obesity
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Hypothesis: The concurrent implementation of time restricted eating (TRE) and a Mindfulness intervention yields superior outcomes in cardiovascular disease risk markers and stress response when compared with each intervention individually and control.
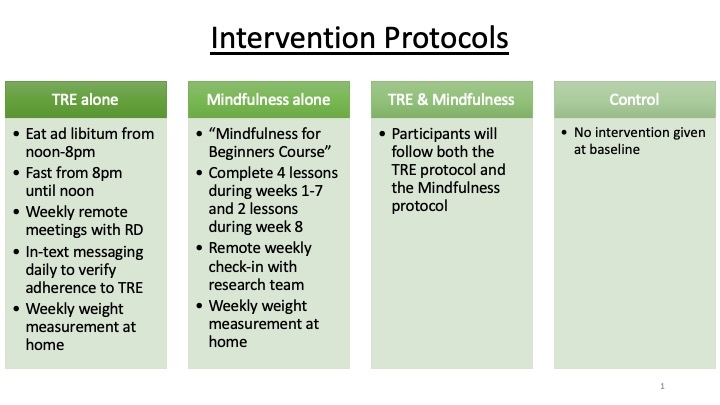
Methods: We conducted an 8-week randomized controlled parallel arm pilot study evaluating TRE (ad libitum eating between 12-8pm) and Mindfulness (“Mindfulness for Beginners” from Calm.com®) among young adults (18-39 years old) with obesity (BMI ≥ 30 and ≤ 49.9 kg/m2) and a Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) ≥14 indicating moderate to severe perceived stress. Individuals were randomized to the following: TRE; Mindfulness; TRE & Mindfulness; or Control. We explored changes in body weight, body composition, cardiovascular disease risk markers and stress.
Results: Forty-three participants were randomized. Participants in the TRE group lost a mean -0.38 (95% CI -2.49, 1.73) kg; Mindfulness group lost a mean -2.10 (95% CI -5.21,1.02) kg; TRE & Mindfulness group lost mean -1.89 (95% CI -4.32, 0.55) kg; and Control group lost a mean of -0.0.9 (95% CI -1.15,0.98) kg from baseline to post-intervention. The Mindfulness group showed the largest decrease in body fat mass (-2.20; 95% CI -4.64, 0.23 kg) while the TRE & Mindfulness group demonstrated the largest decrease in visceral fat mass (-315.4; 95% CI -965.13, 334.33 g). For cardiovascular disease risk markers, the TRE & Mindfulness group presented the largest decrease in diastolic blood pressure (-3.20; 95% CI -8.77, 2.37 mmHg) and a statistically significant decrease in heart rate (-1.93; 95% CI -3.70, -0.16 beats/min). For estimated heart rate variability (Root Mean Square of Successive Differences - RMSSD), all intervention arms demonstrated an increase in RMSSD, which is indicative of increased cardiac vagal tone, with the Mindfulness arm presenting the highest mean change from baseline (mean 7.61; 95% CI -1.5, 16.71 milliseconds). PSS scores decreased significantly within all arms except for Control. There was a statistically significant decrease in high sensitivity C-reactive protein from baseline to post-intervention in the TRE arm only (-1.58; 95% CI: -3.08, -0.09 mg/L).
Conclusion: Results from this pilot study indicated a potential positive combined effect of TRE & Mindfulness for improving anthropometric and cardiovascular disease risk markers measures among young adults with obesity and moderate to severe perceived stress compared to either intervention alone.
Methods: We conducted an 8-week randomized controlled parallel arm pilot study evaluating TRE (ad libitum eating between 12-8pm) and Mindfulness (“Mindfulness for Beginners” from Calm.com®) among young adults (18-39 years old) with obesity (BMI ≥ 30 and ≤ 49.9 kg/m2) and a Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) ≥14 indicating moderate to severe perceived stress. Individuals were randomized to the following: TRE; Mindfulness; TRE & Mindfulness; or Control. We explored changes in body weight, body composition, cardiovascular disease risk markers and stress.
Results: Forty-three participants were randomized. Participants in the TRE group lost a mean -0.38 (95% CI -2.49, 1.73) kg; Mindfulness group lost a mean -2.10 (95% CI -5.21,1.02) kg; TRE & Mindfulness group lost mean -1.89 (95% CI -4.32, 0.55) kg; and Control group lost a mean of -0.0.9 (95% CI -1.15,0.98) kg from baseline to post-intervention. The Mindfulness group showed the largest decrease in body fat mass (-2.20; 95% CI -4.64, 0.23 kg) while the TRE & Mindfulness group demonstrated the largest decrease in visceral fat mass (-315.4; 95% CI -965.13, 334.33 g). For cardiovascular disease risk markers, the TRE & Mindfulness group presented the largest decrease in diastolic blood pressure (-3.20; 95% CI -8.77, 2.37 mmHg) and a statistically significant decrease in heart rate (-1.93; 95% CI -3.70, -0.16 beats/min). For estimated heart rate variability (Root Mean Square of Successive Differences - RMSSD), all intervention arms demonstrated an increase in RMSSD, which is indicative of increased cardiac vagal tone, with the Mindfulness arm presenting the highest mean change from baseline (mean 7.61; 95% CI -1.5, 16.71 milliseconds). PSS scores decreased significantly within all arms except for Control. There was a statistically significant decrease in high sensitivity C-reactive protein from baseline to post-intervention in the TRE arm only (-1.58; 95% CI: -3.08, -0.09 mg/L).
Conclusion: Results from this pilot study indicated a potential positive combined effect of TRE & Mindfulness for improving anthropometric and cardiovascular disease risk markers measures among young adults with obesity and moderate to severe perceived stress compared to either intervention alone.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Mechanistic Insight Into The Connection Between Metabolism And Differentiation In ACTA2 P. R179 Smooth Muscle Cells
Esparza Pinelo Jose, Krenz Hannah, Chen Jessica, Kaw Anita, Milewicz Dianna, Kwartler Callie
Circulating Metabolomic Biomarkers of 5-Year Unintentional Weight Loss in a Biracial Community-Dwelling Older CohortYao Shanshan, Marron Megan, Miljkovic Iva, Farsijani Samaneh, Tseng George, Shah Ravi, Murthy Venkatesh, Newman Anne