Final ID: MP2632
End Stage Renal Disease, Atrial Runs, and Age are the Strongest Associates of Atrial Fibrillation Detection in Patients with Cryptogenic Stroke
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Introduction: Patients who suffer from cryptogenic stroke (CS) are routinely screened for asymptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) with implantable loop recorders (ILRs). The clinical risk factors associated with AF after CS are not fully defined, and it is a common perception that ILRs are not helpful in younger patients with CS.
Research Questions/Objectives: To identify which clinical characteristics are associated with AF detection via ILR in patients who have suffered CS. To identify if there is an age cut-off, below which ILR implantation is likely to be futile in patients with CS.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted on patients with CS who underwent ILR implantation at Thomas Jefferson University Hospital from 04/2019 to 04/2021. Patients were excluded from the analysis if there was <6 months of ILR follow-up, delayed ILR placement (>1 year after CS), or pre-existing (known) AF. Baseline demographics and clinical characteristics were collected (Table 1). Patients with and without AF detection within 1 year of CS were compared and multivariable logistic regression was applied to the univariate predictors that were significant (Table 2). Analyses were run in R Studio 4.4.2.
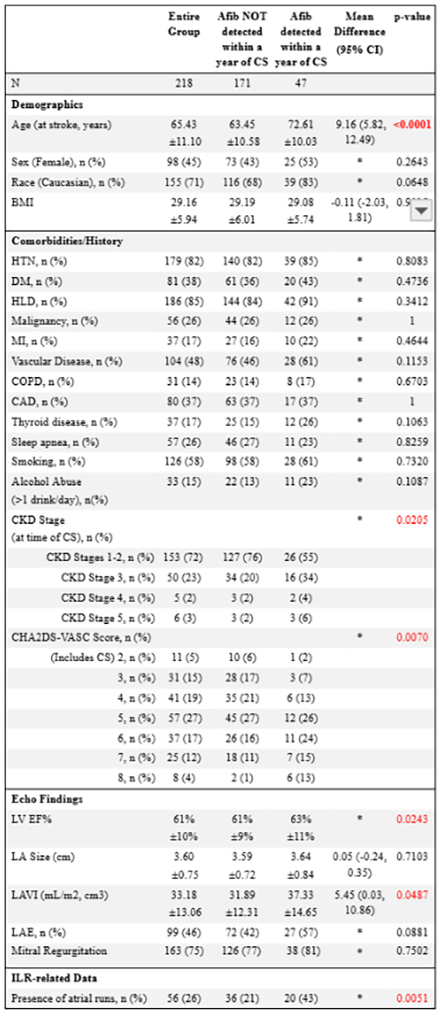
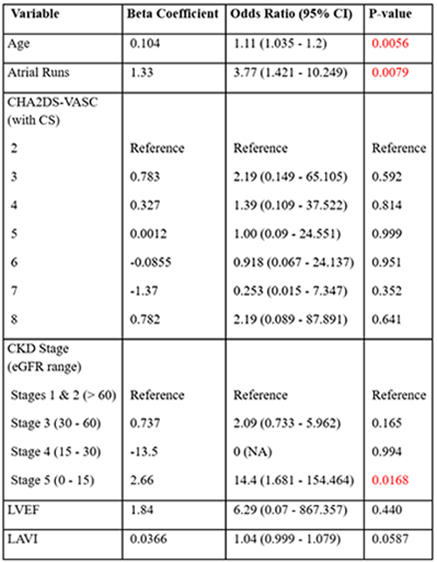
Results: We identified a total of 282 patients with CS who received ILRs. Of these 282 patients, 218 formed the study group after applying exclusion criteria (age 63.45±10.58 years, 45% female). AF was detected within 1 year of CS in 47 patients (21.6%) with a mean time from CS to AF detection of 125.30± 94.64 days. In univariate analyses, AF was statistically significantly associated with older age, LAVI, CHA2DS2-VASc score, LVEF%, CKD stage, and presence of atrial runs (Table 1). After multivariable adjustment (Table 2), CKD stage 5 (OR 14.4, p=0.0168), atrial runs (OR 3.77, p=0.0079), and age (OR 1.11, p=0.0056) remained significantly associated with AF detection. However, there were 5 patients below the age of 60 who had AF detected. No significant differences were observed in sex, race, BMI, or other comorbidities.
Conclusions: Stage 5 CKD, atrial runs, and age showed significant association with AF detection after cryptogenic stroke. Although age was statistically significant, the OR was low (1.11), and 5 patients below the age of 60 had AF detected. Renal failure and atrial runs were the strongest associates of AF detection after CS. We conclude that there should be no minimum age cut-off for ILR implantation in CS patients.
Introduction: Patients who suffer from cryptogenic stroke (CS) are routinely screened for asymptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) with implantable loop recorders (ILRs). The clinical risk factors associated with AF after CS are not fully defined, and it is a common perception that ILRs are not helpful in younger patients with CS.
Research Questions/Objectives: To identify which clinical characteristics are associated with AF detection via ILR in patients who have suffered CS. To identify if there is an age cut-off, below which ILR implantation is likely to be futile in patients with CS.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted on patients with CS who underwent ILR implantation at Thomas Jefferson University Hospital from 04/2019 to 04/2021. Patients were excluded from the analysis if there was <6 months of ILR follow-up, delayed ILR placement (>1 year after CS), or pre-existing (known) AF. Baseline demographics and clinical characteristics were collected (Table 1). Patients with and without AF detection within 1 year of CS were compared and multivariable logistic regression was applied to the univariate predictors that were significant (Table 2). Analyses were run in R Studio 4.4.2.
Results: We identified a total of 282 patients with CS who received ILRs. Of these 282 patients, 218 formed the study group after applying exclusion criteria (age 63.45±10.58 years, 45% female). AF was detected within 1 year of CS in 47 patients (21.6%) with a mean time from CS to AF detection of 125.30± 94.64 days. In univariate analyses, AF was statistically significantly associated with older age, LAVI, CHA2DS2-VASc score, LVEF%, CKD stage, and presence of atrial runs (Table 1). After multivariable adjustment (Table 2), CKD stage 5 (OR 14.4, p=0.0168), atrial runs (OR 3.77, p=0.0079), and age (OR 1.11, p=0.0056) remained significantly associated with AF detection. However, there were 5 patients below the age of 60 who had AF detected. No significant differences were observed in sex, race, BMI, or other comorbidities.
Conclusions: Stage 5 CKD, atrial runs, and age showed significant association with AF detection after cryptogenic stroke. Although age was statistically significant, the OR was low (1.11), and 5 patients below the age of 60 had AF detected. Renal failure and atrial runs were the strongest associates of AF detection after CS. We conclude that there should be no minimum age cut-off for ILR implantation in CS patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
4D Cardiac Optogenetics Enable Complex Arrhythmia Modelling and Precise Interventional Simulation
Wexler Yehuda, Grinstein Harel, Landesberg Michal, Glatstein Shany, Huber Irit, Arbel Gil, Gepstein Lior
A Fat Chance: Paradoxical Embolic Stroke from Lipomatous Hypertrophy of the Interatrial SeptumKalathoor Abraham