Final ID: MP151
Assessment of Left Ventricular Function Measured with Cardiac MRI Feature Tracking Predicts Heart Failure Events in Childhood Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Strain derived from CMR Feature Tracking (CMR-FT) analysis allows more sensitive evaluation of tissue deformation. However, the prognostic value of strain has not been specifically studied in pediatric HCM. We sought to investigate the association between LV strain and heart failure (HF)-related events, and evaluate the incremental prognostic value beyond clinical features.
Methods
This retrospective study consecutively involved 228 primary HCM patients aged ≤18 years with contrast-enhanced CMR. The CMR-FT analysis was performed on the acquired cine images with global longitudinal strain (GLS), global radial strain (GRS) and global circumferential strain (GCS). Clinical and CMR features were analyzed using Cox proportional hazards models with regard to HF-related events, including HF-related mortality, unscheduled hospitalizations for HF management, and heart transplantation.
Results
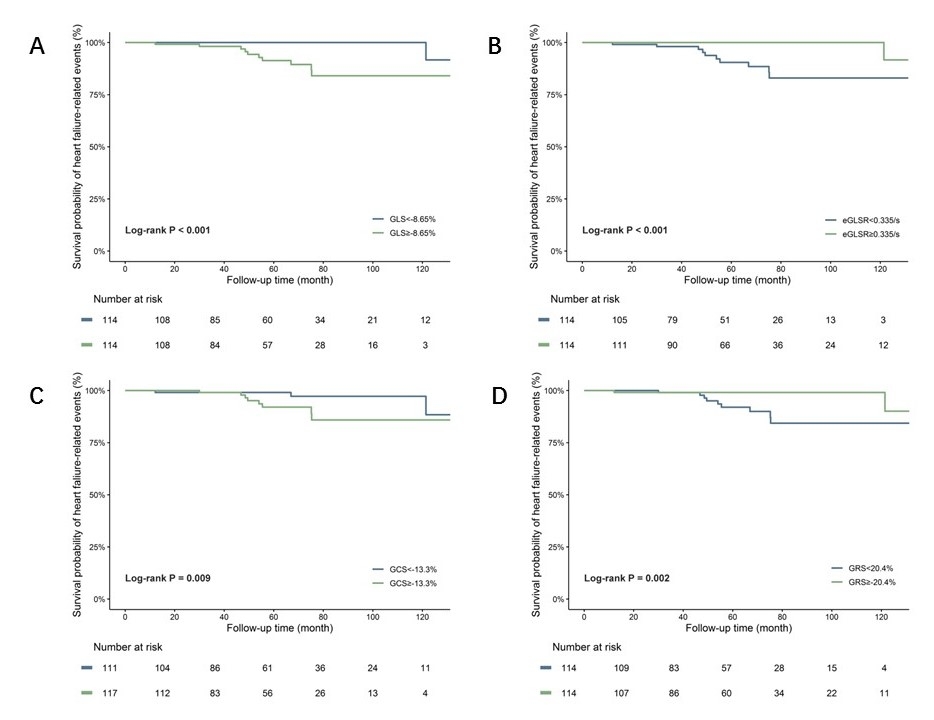
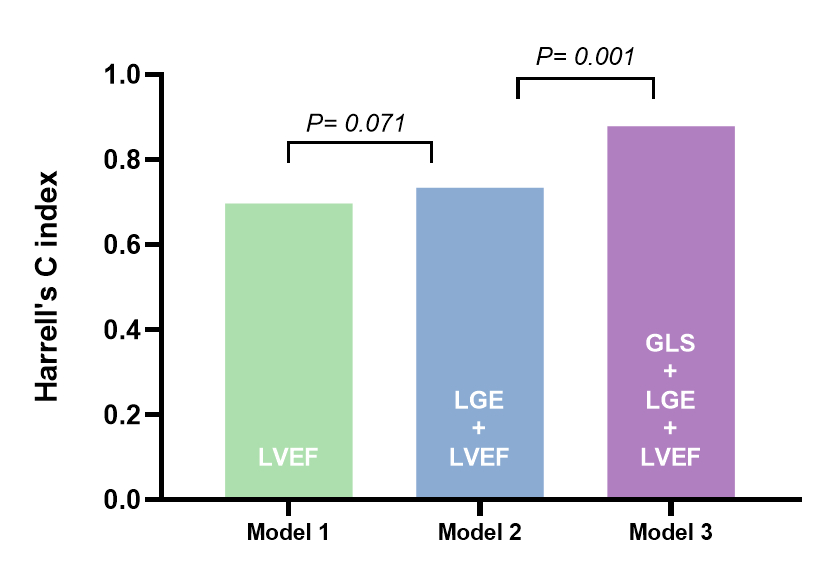
Patients were 15±3 years of age at baseline and 65% were male. During a median follow-up of 61.4 months (IQR: 39.0-84.3), 13(6.5%) patients with HCM reached HF-related events. Patients suffering from HF-related events had larger LV diameter, higher LV mass index and LGE extent, worser GLS, GRS and lower early GLS rate than patients without HF-related events. According to Kaplan-Meier analysis, patients with worse GLS were more likely to experience HF-related events (log-rank P < 0.001). Similar results were observed in worser GRS group (log-rank P = 0.002), worser GCS group (log-rank P = 0.009) and lower early GLS rate (log-rank P < 0.001) group. After univariable analysis and multivariable Cox analysis adjusting clinical and cardiac functional factors respectively, GLS (HR: 1.32, 95%CI: 1.05-1.67, P = 0.020) and LGE extent (HR: 1.13, 95%CI: 1.03-1.23, P = 0.006) were still an independent predictor for HF-related events. Besides, the addition of GLS significantly improved the model’s performance in comparison with the model of traditional markers of LVEF and LGE presence (C index: 0.73 vs 0.88, Delong’s P < 0.001)
Conclusion:
Myocardial strain using CMR-FT provides independent and incremental prognostic value for HF-related events over clinical features in childhood patients with HCM. CMR-FT may serve as a novel marker to improve risk stratification in childhood HCM.
Strain derived from CMR Feature Tracking (CMR-FT) analysis allows more sensitive evaluation of tissue deformation. However, the prognostic value of strain has not been specifically studied in pediatric HCM. We sought to investigate the association between LV strain and heart failure (HF)-related events, and evaluate the incremental prognostic value beyond clinical features.
Methods
This retrospective study consecutively involved 228 primary HCM patients aged ≤18 years with contrast-enhanced CMR. The CMR-FT analysis was performed on the acquired cine images with global longitudinal strain (GLS), global radial strain (GRS) and global circumferential strain (GCS). Clinical and CMR features were analyzed using Cox proportional hazards models with regard to HF-related events, including HF-related mortality, unscheduled hospitalizations for HF management, and heart transplantation.
Results
Patients were 15±3 years of age at baseline and 65% were male. During a median follow-up of 61.4 months (IQR: 39.0-84.3), 13(6.5%) patients with HCM reached HF-related events. Patients suffering from HF-related events had larger LV diameter, higher LV mass index and LGE extent, worser GLS, GRS and lower early GLS rate than patients without HF-related events. According to Kaplan-Meier analysis, patients with worse GLS were more likely to experience HF-related events (log-rank P < 0.001). Similar results were observed in worser GRS group (log-rank P = 0.002), worser GCS group (log-rank P = 0.009) and lower early GLS rate (log-rank P < 0.001) group. After univariable analysis and multivariable Cox analysis adjusting clinical and cardiac functional factors respectively, GLS (HR: 1.32, 95%CI: 1.05-1.67, P = 0.020) and LGE extent (HR: 1.13, 95%CI: 1.03-1.23, P = 0.006) were still an independent predictor for HF-related events. Besides, the addition of GLS significantly improved the model’s performance in comparison with the model of traditional markers of LVEF and LGE presence (C index: 0.73 vs 0.88, Delong’s P < 0.001)
Conclusion:
Myocardial strain using CMR-FT provides independent and incremental prognostic value for HF-related events over clinical features in childhood patients with HCM. CMR-FT may serve as a novel marker to improve risk stratification in childhood HCM.
More abstracts on this topic:
A novel mechanism of pediatric DCM that recapitulates aspects of the human disease via Notch signaling: a pathway to new therapeutics?
Nyarko Obed, Sucharov Carmen
A Heart-pounding Case of Cardiomyopathy in PregnancyTran Linh, Everitt Ian, Vaught Arthur, Barth Andreas, Minhas Anum