Final ID: MP1250
Comparable One-Year Efficacy and Safety of Spironolactone Versus Amiloride in Resistant Hypertension: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Spironolactone is frequently used as the fourth-line agent for resistant hypertension, but concerns over hyperkalemia have prompted some clinicians to use amiloride despite limited comparative data. In this study, we compared outcomes between amiloride and spironolactone in patients with resistant hypertension.
Methods
We performed a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX database. We identified adults with hypertension who were previously prescribed an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker, dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker, and a thiazide diuretic within the 12 months prior to the index treatment who initiated either amiloride (n=420) or spironolactone (n=10,434) between January 2012 and April 2024. Eligible patients had systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥ 140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥ 90 mm Hg taken the same day on the index treatment. Patients with stage 4 or 5 kidney disease were excluded. The study evaluated the following outcomes through 52 weeks: acute kidney injury (AKI), all-cause mortality, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE; defined as all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction, and ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke), and attainment of SBP ≤ 130 mm Hg and DBP ≤ 80 mm Hg. Cohorts were matched using propensity matching based on demographics, comorbidities, concomitant medications, and pertinent laboratory values. We matched for a total of 30 variables.
Results
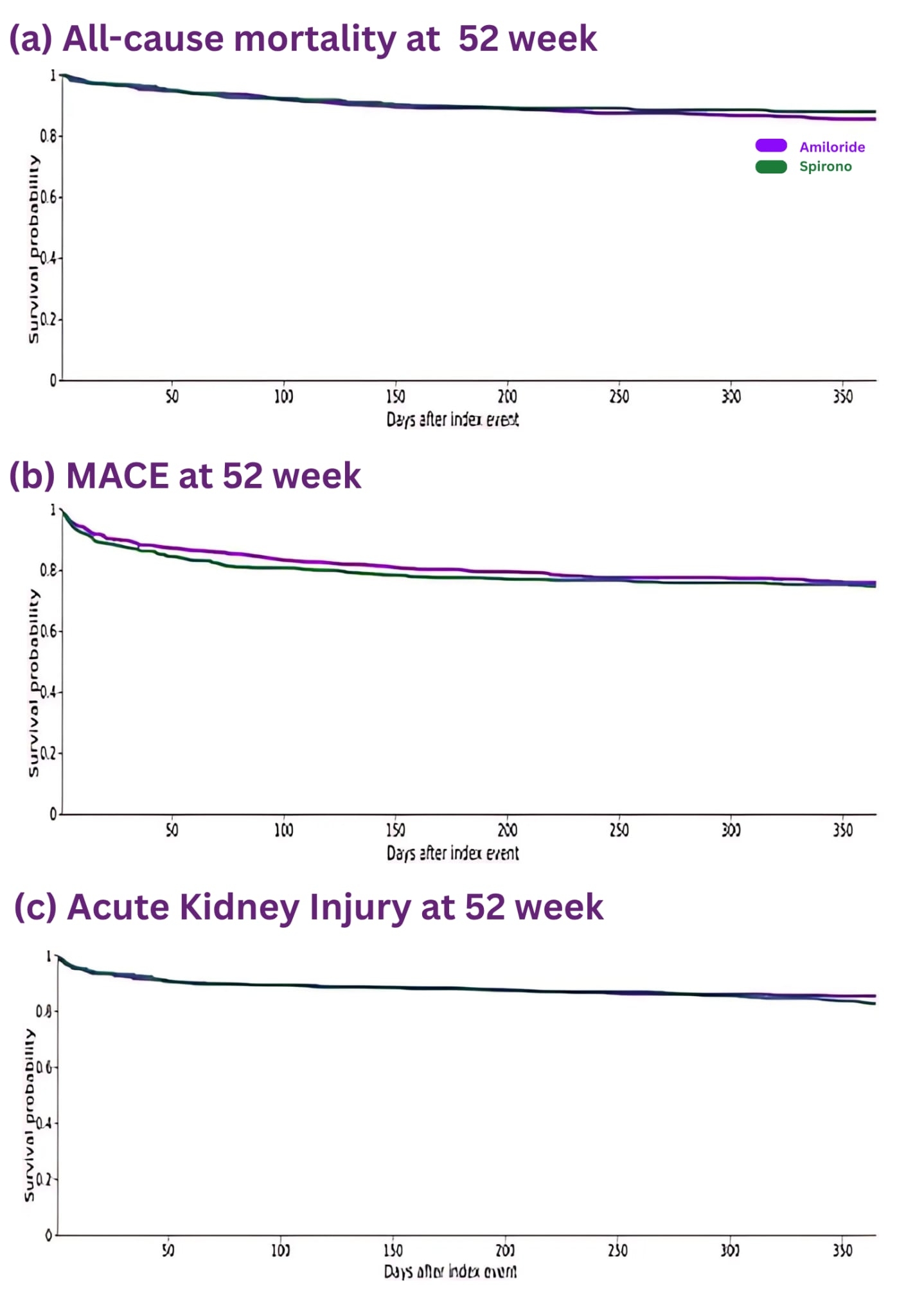
Propensity-score matching generated two well-balanced cohorts (n = 414 each), with comparable age (mean 62.7 vs 63.8 years), sex distribution (54.3 % vs 56.5 % male), and comorbidities (Table 1). At 4 weeks, more amiloride-treated patients achieved SBP ≤ 130 mm Hg (53.6 % vs 44.2 %; RR 1.21, 95 % CI 1.05–1.40) and DBP ≤ 80 mm Hg (62.3 % vs 53.6 %; RR 1.16, 95 % CI 1.03–1.31), whereas by 52 weeks there were no differences in attainment of any blood-pressure target (SBP ≤ 130, SBP ≤ 140, DBP ≤ 80, DBP ≤ 90).
There was no statistically significant difference between groups in all-cause mortality (13.3% vs 11.1%; RR 1.20, 95% CI 0.83–1.73), incidence of acute kidney injury (13.0% vs 15.2%; RR 0.86, 95% CI 0.61–1.20), or major adverse cardiovascular events (22.5% vs 23.7%; RR 0.95, 95% CI 0.74–1.22) at 52 weeks.
Conclusion
Amiloride and spironolactone had similar one-year AKI, MACE, all-cause mortality, and BP control.
Spironolactone is frequently used as the fourth-line agent for resistant hypertension, but concerns over hyperkalemia have prompted some clinicians to use amiloride despite limited comparative data. In this study, we compared outcomes between amiloride and spironolactone in patients with resistant hypertension.
Methods
We performed a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX database. We identified adults with hypertension who were previously prescribed an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker, dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker, and a thiazide diuretic within the 12 months prior to the index treatment who initiated either amiloride (n=420) or spironolactone (n=10,434) between January 2012 and April 2024. Eligible patients had systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥ 140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥ 90 mm Hg taken the same day on the index treatment. Patients with stage 4 or 5 kidney disease were excluded. The study evaluated the following outcomes through 52 weeks: acute kidney injury (AKI), all-cause mortality, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE; defined as all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction, and ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke), and attainment of SBP ≤ 130 mm Hg and DBP ≤ 80 mm Hg. Cohorts were matched using propensity matching based on demographics, comorbidities, concomitant medications, and pertinent laboratory values. We matched for a total of 30 variables.
Results
Propensity-score matching generated two well-balanced cohorts (n = 414 each), with comparable age (mean 62.7 vs 63.8 years), sex distribution (54.3 % vs 56.5 % male), and comorbidities (Table 1). At 4 weeks, more amiloride-treated patients achieved SBP ≤ 130 mm Hg (53.6 % vs 44.2 %; RR 1.21, 95 % CI 1.05–1.40) and DBP ≤ 80 mm Hg (62.3 % vs 53.6 %; RR 1.16, 95 % CI 1.03–1.31), whereas by 52 weeks there were no differences in attainment of any blood-pressure target (SBP ≤ 130, SBP ≤ 140, DBP ≤ 80, DBP ≤ 90).
There was no statistically significant difference between groups in all-cause mortality (13.3% vs 11.1%; RR 1.20, 95% CI 0.83–1.73), incidence of acute kidney injury (13.0% vs 15.2%; RR 0.86, 95% CI 0.61–1.20), or major adverse cardiovascular events (22.5% vs 23.7%; RR 0.95, 95% CI 0.74–1.22) at 52 weeks.
Conclusion
Amiloride and spironolactone had similar one-year AKI, MACE, all-cause mortality, and BP control.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of Antihypertensive Medications with Orthostatic Hypotension among Very Old Adults: Findings from the ARIC Study
Khan Md Marufuzzaman, Coresh Joe, Selvin Elizabeth, Wagenknecht Lynne, Hughes Timothy, Windham B Gwen, Mosley Thomas, Lutsey Pamela, Ring Kimberly, Lipsitz Lewis, Valint Arielle, Col Hannah, Juraschek Stephen, Larbi Fredrick, Patil Dhrumil, Zhang Mingyu, Turkson-ocran Ruth-alma, Ngo Long, Cluett Jennifer, Mukamal Kenneth
Comparative Effectiveness Of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists And Thiazide Diuretics In Essential Hypertension Without Heart Failure: A Retrospective Cohort StudySabri Muhammad, Klair Nimra, Mizrahi Eddy, Watson Robert, Haas Donald