Final ID: P-304
A Prescription Trend Analysis of Antihypertensive Pharmacotherapy across Different Specialties in India
Abstract Body: Objective: To evaluate the temporal trends in the prescription patterns of antihypertensive medications among healthcare practitioners in India.
Methods: The prescription audit data utilized in this study, sourced from IQVIA, originated from a panel comprising 6000 clinicians practicing within the private sector. These prescriptions encompassed various classes of antihypertensive drugs, namely beta-blockers (BB), calcium channel blockers (CCB), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB), angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and diuretics. The analysis spanned the period from 2014 to 2022. The study also included an examination of combinations involving two or three medications from these drug classes.
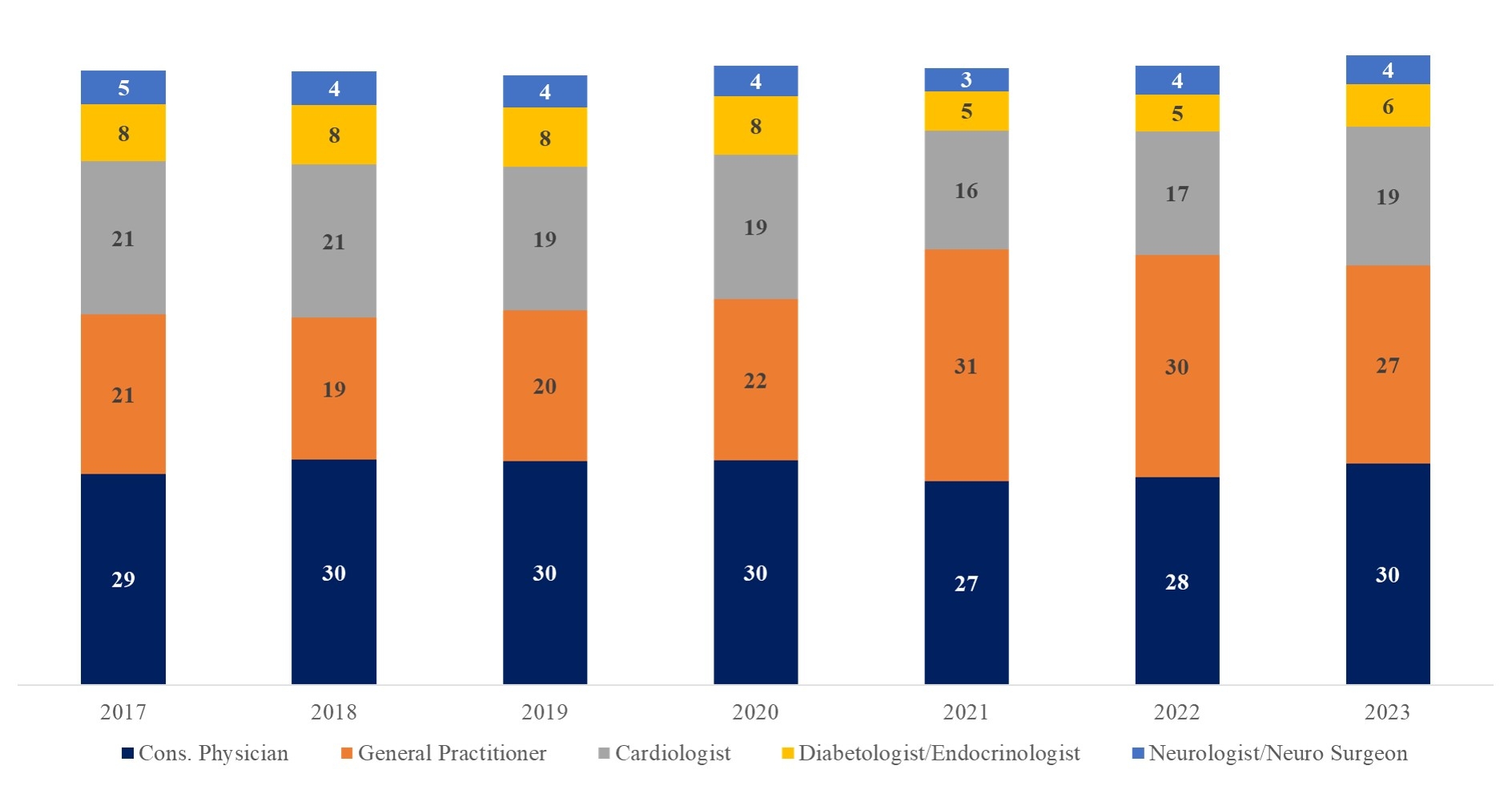
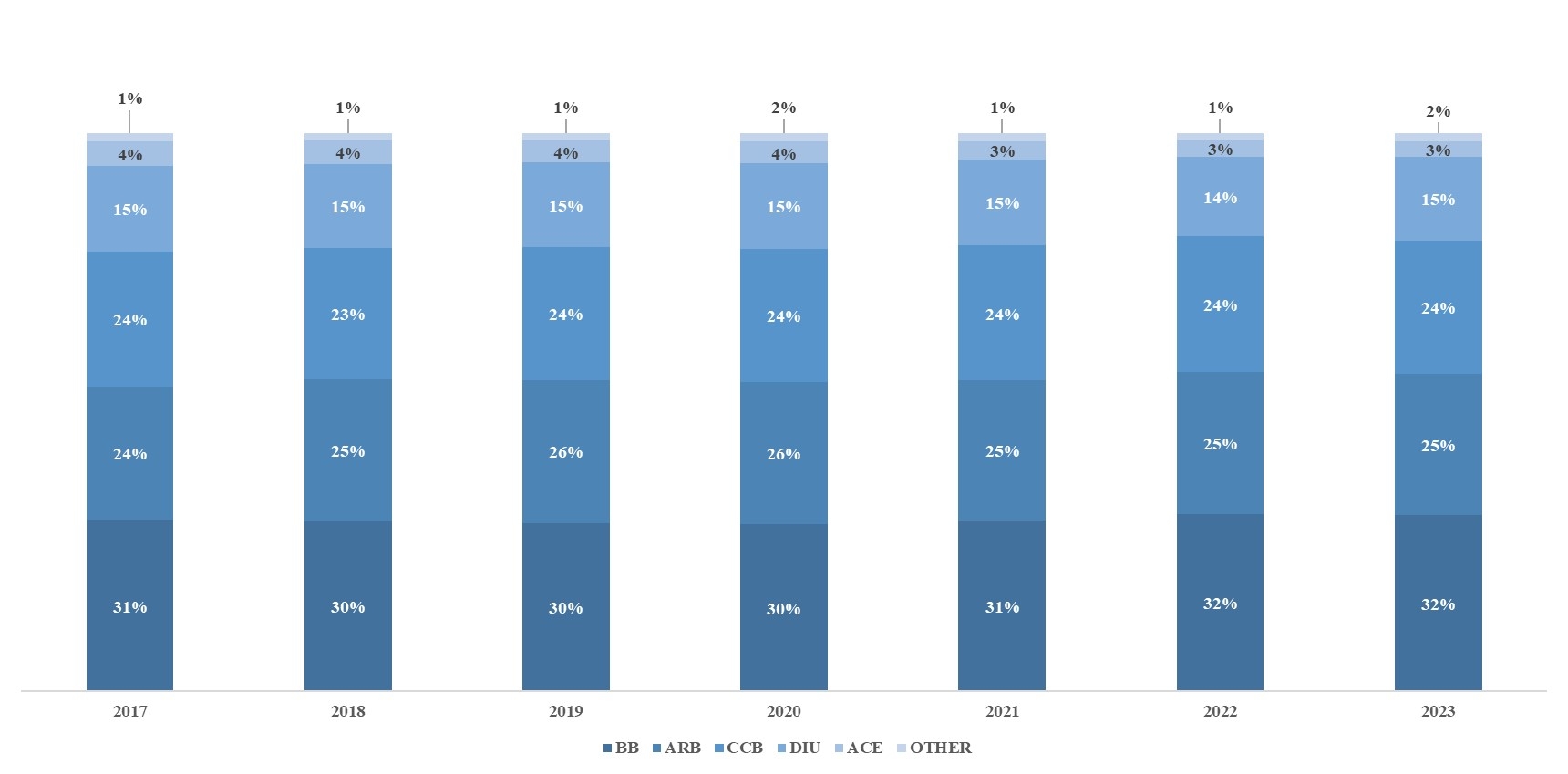
Results: Cardiologists' prescription rates for antihypertensive medications stood at 21% in 2017 and decreased to 19% by 2023. In 2023, the highest rate of prescribing antihypertensive drugs was observed among consultant physicians, with a rate of 30%, followed by general practitioners at 27%. Among anti-hypertensive medications, the prescription rates for BBs were highest (32%), followed by ARBs & CCBs (25% & 24% respectively); which remained almost constant throughout the study period. Single-drug formulation of antihypertensive medications was the most preferred (60%) among Indian clinicians. Prescription shares of fixed-dose combinations (FDC) of two antihypertensive drugs showed a slight decline (36% in 2017 to 34% in 2023) & FDCs of triple-drug exhibited an upward trend (3% in 2017 to 5% in 2023). Among the two drug FDCs, ARB & diuretics were most preferred (25% prescription share) & triple drug FDCs, CCB, ARB & diuretics were most preferred (76% prescription share).
Conclusions: Antihypertensive drugs are the most commonly prescribed medication in the cardiology segment. Consultant physicians and general practitioners manage the majority of hypertension cases. Notably, there has been an observed rise in the preference for triple-drug combinations of antihypertensive medications, indicating a trend toward a more aggressive approach to hypertension management among Indian clinicians. The insights gleaned from this investigation can further assist healthcare professionals in crafting tailored treatment strategies for individuals grappling with hypertension. Such personalized approaches hold promise in enhancing treatment adherence and ultimately improving the quality of life for patients.
Methods: The prescription audit data utilized in this study, sourced from IQVIA, originated from a panel comprising 6000 clinicians practicing within the private sector. These prescriptions encompassed various classes of antihypertensive drugs, namely beta-blockers (BB), calcium channel blockers (CCB), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB), angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and diuretics. The analysis spanned the period from 2014 to 2022. The study also included an examination of combinations involving two or three medications from these drug classes.
Results: Cardiologists' prescription rates for antihypertensive medications stood at 21% in 2017 and decreased to 19% by 2023. In 2023, the highest rate of prescribing antihypertensive drugs was observed among consultant physicians, with a rate of 30%, followed by general practitioners at 27%. Among anti-hypertensive medications, the prescription rates for BBs were highest (32%), followed by ARBs & CCBs (25% & 24% respectively); which remained almost constant throughout the study period. Single-drug formulation of antihypertensive medications was the most preferred (60%) among Indian clinicians. Prescription shares of fixed-dose combinations (FDC) of two antihypertensive drugs showed a slight decline (36% in 2017 to 34% in 2023) & FDCs of triple-drug exhibited an upward trend (3% in 2017 to 5% in 2023). Among the two drug FDCs, ARB & diuretics were most preferred (25% prescription share) & triple drug FDCs, CCB, ARB & diuretics were most preferred (76% prescription share).
Conclusions: Antihypertensive drugs are the most commonly prescribed medication in the cardiology segment. Consultant physicians and general practitioners manage the majority of hypertension cases. Notably, there has been an observed rise in the preference for triple-drug combinations of antihypertensive medications, indicating a trend toward a more aggressive approach to hypertension management among Indian clinicians. The insights gleaned from this investigation can further assist healthcare professionals in crafting tailored treatment strategies for individuals grappling with hypertension. Such personalized approaches hold promise in enhancing treatment adherence and ultimately improving the quality of life for patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Blood(y) Pressure Crisis: Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage as a Rare Manifestation of Severely Uncontrolled Hypertension
Nandyal Shreyas, Amdetsion Gedion Yilma, Varma Revati, Kohli Saksham, Hammo Hasan
Coordinated Calcium Oscillations Within Juxtaglomerular Cell Clusters: A Central Mediator Of Renin-Angiotensin SystemYamaguchi Hiroki, Nieh Edward, Gomez Ariel, Sequeira Maria Luisa, Guagliardo Nick, Bell Laura, Yamaguchi Manako, Matsuoka Daisuke, Xu Fang, Smith Jason, Almeida Lucas, Medrano Silvia