Final ID: Mo4059
Genetic Testing Outcomes in Hypertrophic and Dilated Cardiomyopathy: A Five-Year Retrospective Review
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Cardiomyopathies (CM) are rare, inherited heart diseases. Major types include dilated, hypertrophic, restrictive, and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common. Genetic diagnostic testing can identify disease genes associated with inherited cardiomyopathies, which are crucial for diagnosis, risk stratification, and family screening. This study evaluated the outcomes of clinical genetic testing in patients with suspected HCM and CM/DCM over a five-year period.
A retrospective analysis was performed on 949 patient samples with unexplained moderate to severe cardiomyopathy/dilated cardiomyopathy and/or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy referred to clinical genetics laboratory for genetic testing between 2016 and 2024 were included in the study. Among these, 475 were for suspected HCM and 474 for suspected CM/DCM. Genetic screening was performed by next generation sequencing technique. The variants were annotated using disease databases (HGMD, OMIM, ClinVar), Population databases (1000G, ExAC, GnomAD and Indian population specific database). ExomeDepth (v1.1.10), a read-depth comparison method, detected copy number variants (CNVs) from targeted sequence data by comparing test data to a matched aggregate reference dataset. The data was sequentially filtered and variants were prioritized based on clinical symptoms and classified according to ACMG 2015 guidelines. All previously reported variants were re-evaluated using current international databases and classification standards. Diagnostic yield, gene-wise distribution, and reclassification rates were analyzed.
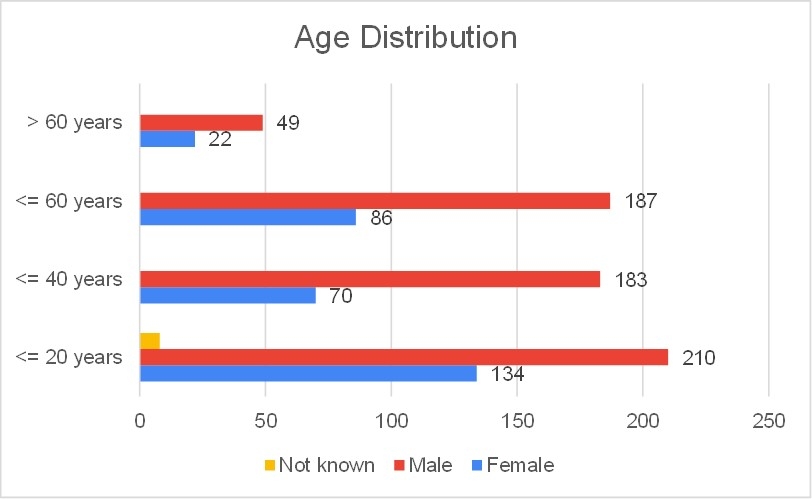
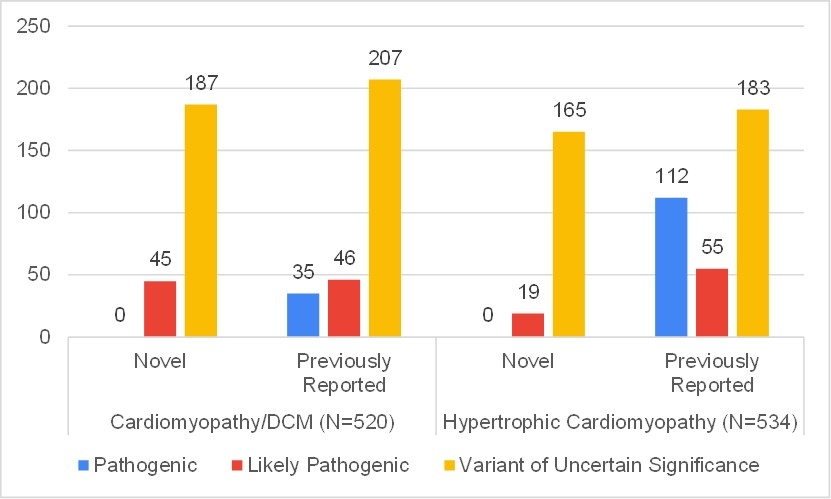
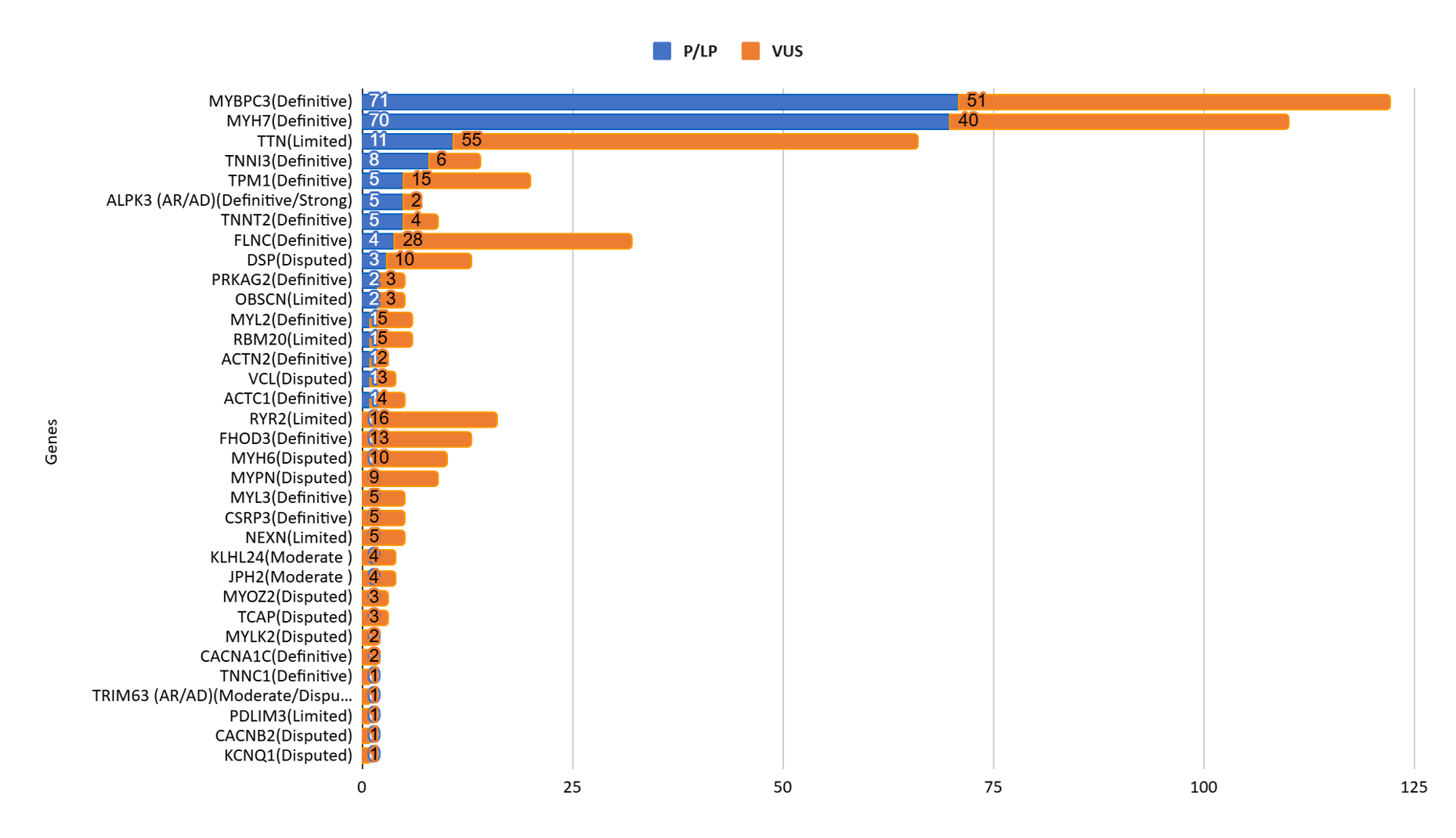
Mean age of the subjects (n = 949) was 32 ± 20 years, 66.3% male [Figure 1]. The overall diagnostic yield was 31.7% (301/949), [Figure 2]. HCM had a higher yield of 38.3% (182/475), with the majority of pathogenic variants found in MYBPC3 (37.9%) and MYH7 (35.2%), [Figure 3]. CM/DCM showed a 25.1% yield (119/474), with key genes being TTN (22.7%) and DSP and MYH7 (6.7%) . We detected copy number variants in 5 of them (2LP; 3VUS). Variant reclassification affected 183 samples (22.05%), with 85 upgraded and 98 downgraded and thus the clinical interpretation.
Genetic testing yields actionable findings in both HCM and DCM, with greater impact in HCM. Reclassification of variants using updated guidelines improves diagnostic clarity and management strategies. These findings support routine re-evaluation of genetic results in inherited cardiomyopathy care.
A retrospective analysis was performed on 949 patient samples with unexplained moderate to severe cardiomyopathy/dilated cardiomyopathy and/or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy referred to clinical genetics laboratory for genetic testing between 2016 and 2024 were included in the study. Among these, 475 were for suspected HCM and 474 for suspected CM/DCM. Genetic screening was performed by next generation sequencing technique. The variants were annotated using disease databases (HGMD, OMIM, ClinVar), Population databases (1000G, ExAC, GnomAD and Indian population specific database). ExomeDepth (v1.1.10), a read-depth comparison method, detected copy number variants (CNVs) from targeted sequence data by comparing test data to a matched aggregate reference dataset. The data was sequentially filtered and variants were prioritized based on clinical symptoms and classified according to ACMG 2015 guidelines. All previously reported variants were re-evaluated using current international databases and classification standards. Diagnostic yield, gene-wise distribution, and reclassification rates were analyzed.
Mean age of the subjects (n = 949) was 32 ± 20 years, 66.3% male [Figure 1]. The overall diagnostic yield was 31.7% (301/949), [Figure 2]. HCM had a higher yield of 38.3% (182/475), with the majority of pathogenic variants found in MYBPC3 (37.9%) and MYH7 (35.2%), [Figure 3]. CM/DCM showed a 25.1% yield (119/474), with key genes being TTN (22.7%) and DSP and MYH7 (6.7%) . We detected copy number variants in 5 of them (2LP; 3VUS). Variant reclassification affected 183 samples (22.05%), with 85 upgraded and 98 downgraded and thus the clinical interpretation.
Genetic testing yields actionable findings in both HCM and DCM, with greater impact in HCM. Reclassification of variants using updated guidelines improves diagnostic clarity and management strategies. These findings support routine re-evaluation of genetic results in inherited cardiomyopathy care.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Clozapine-Induced Myocarditis: An Under-described Side Effect
Ibrahim Rand, Clearo Kellie
3D Chromatin Architectures and Transcription Regulation in Diabetic Endothelial DysfunctionFeng Yuliang, Cai Liuyang, Wang Yigang, Huang Wei, Jiang Lei