Final ID: MP395
Multi-Center Validation of an AI-Enhanced ECG Model for Predicting Echocardiographic Abnormalities: A Large-Scale Study Across 14 Tertiary Care Centers
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
While numerous AI models leverage ECGs to predict specific cardiac abnormalities, few have been validated at scale across diverse populations and echocardiographic pathologies. This study evaluates the external performance of a deep learning ensemble that predicts a composite of major echocardiographic abnormalities —including reduced ejection fraction (≤35%), valvular disease (mild to severe stenosis and/or moderate to severe regurgitation of Mitral, Aortic and/or Tricuspid valves), and elevated pulmonary artery pressure—from standard 12-lead ECG images.
Methods:
We retrospectively analyzed 44,403 ECGs from 43,346 patients (≥15 years) across 14 centers between July and September 2024. The data was split into two cohorts: Co1 included 28,509 ECGs paired with same-day echocardiograms; Co2 included 15,894 ECGs (from 15,401 patients) without same-day echocardiograms. The ensemble model—comprising two InceptionNetV3 and one ResNet50 networks trained on DICOM ECG images—classified ECGs as positive or negative for any one of eight echocardiographic dysfunctions based on the Youden index threshold (0.27) calculated during model development.
Results:
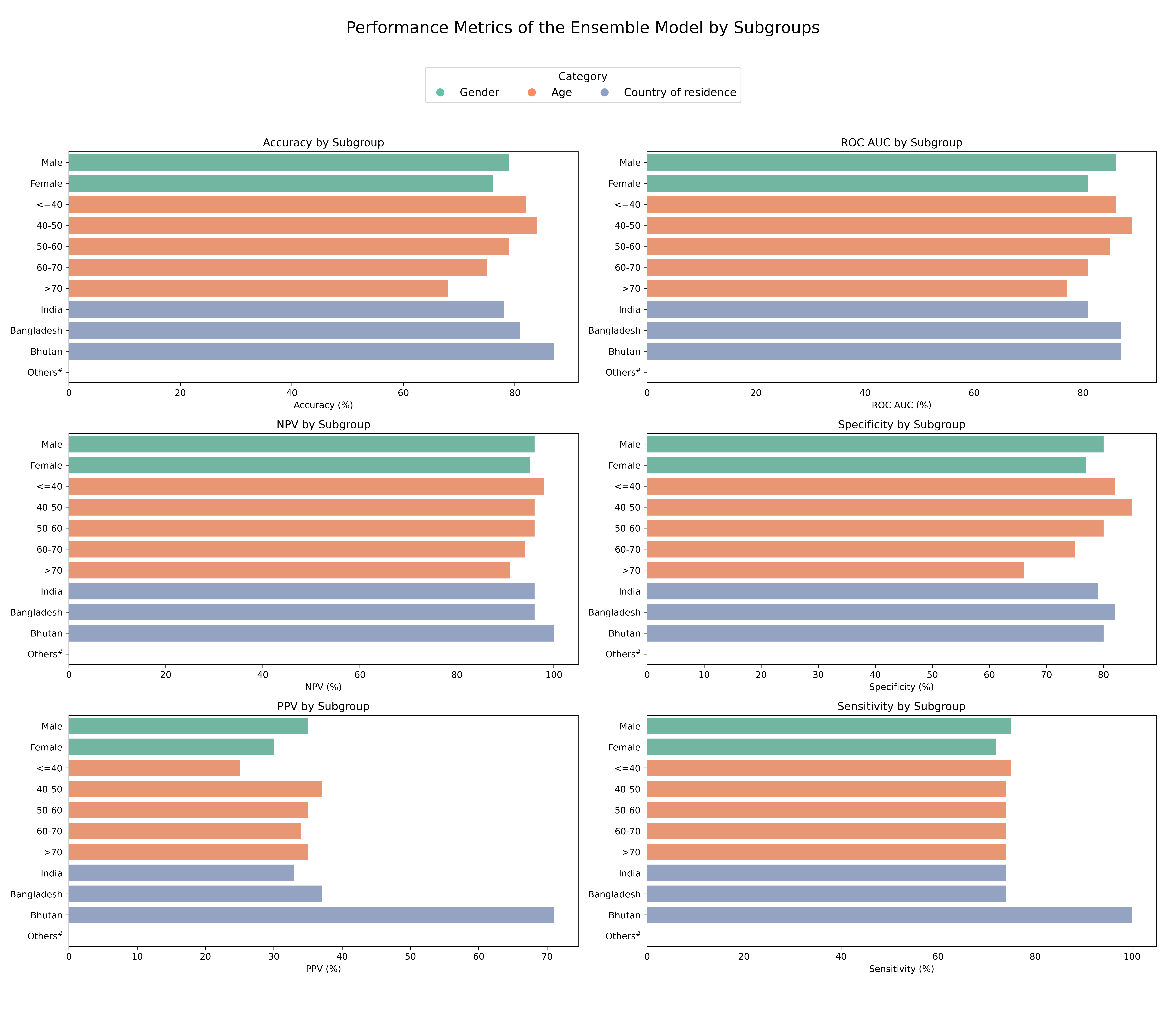
On Co1, the model achieved an ROCAUC of 84%, PR-AUC of 45%, sensitivity 74%, specificity 79%, PPV 34%, NPV 96%, and overall accuracy of 80%. A robust performance was observed in all subsets (Fig. 1). In the subset of false positives (5,127 patients), 932 patients who had follow-up echocardiograms within a median of 54 days revealed that 28% eventually showed echocardiographic dysfunction.
In Co2, out of the 15,401 patients, 2,185 patients underwent at least one echocardiogram within 6 months post-ECG. Among those, of the 830 patients who were previously flagged positive for dysfunction by the model, 49% were found to have dysfunction, with a median interval of 28 days between the initial ECG and echo.
Conclusion:
This AI-enhanced ECG model demonstrates strong generalizability and clinical utility for early identification of echocardiographic abnormalities, offering a scalable solution to triage echocardiography referrals across varied clinical settings, requiring about 2.9 echos to confirm 1 case flagged as dysfunction by the model. Prospective validation is underway to further evaluate its impact on diagnostic workflows and patient outcomes.
While numerous AI models leverage ECGs to predict specific cardiac abnormalities, few have been validated at scale across diverse populations and echocardiographic pathologies. This study evaluates the external performance of a deep learning ensemble that predicts a composite of major echocardiographic abnormalities —including reduced ejection fraction (≤35%), valvular disease (mild to severe stenosis and/or moderate to severe regurgitation of Mitral, Aortic and/or Tricuspid valves), and elevated pulmonary artery pressure—from standard 12-lead ECG images.
Methods:
We retrospectively analyzed 44,403 ECGs from 43,346 patients (≥15 years) across 14 centers between July and September 2024. The data was split into two cohorts: Co1 included 28,509 ECGs paired with same-day echocardiograms; Co2 included 15,894 ECGs (from 15,401 patients) without same-day echocardiograms. The ensemble model—comprising two InceptionNetV3 and one ResNet50 networks trained on DICOM ECG images—classified ECGs as positive or negative for any one of eight echocardiographic dysfunctions based on the Youden index threshold (0.27) calculated during model development.
Results:
On Co1, the model achieved an ROCAUC of 84%, PR-AUC of 45%, sensitivity 74%, specificity 79%, PPV 34%, NPV 96%, and overall accuracy of 80%. A robust performance was observed in all subsets (Fig. 1). In the subset of false positives (5,127 patients), 932 patients who had follow-up echocardiograms within a median of 54 days revealed that 28% eventually showed echocardiographic dysfunction.
In Co2, out of the 15,401 patients, 2,185 patients underwent at least one echocardiogram within 6 months post-ECG. Among those, of the 830 patients who were previously flagged positive for dysfunction by the model, 49% were found to have dysfunction, with a median interval of 28 days between the initial ECG and echo.
Conclusion:
This AI-enhanced ECG model demonstrates strong generalizability and clinical utility for early identification of echocardiographic abnormalities, offering a scalable solution to triage echocardiography referrals across varied clinical settings, requiring about 2.9 echos to confirm 1 case flagged as dysfunction by the model. Prospective validation is underway to further evaluate its impact on diagnostic workflows and patient outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Analysis of Cardiovascular Events in Cancer Survivors: A Comparative Study of Solid Tumors and Hematologic Malignancies at a Tertiary Cardiovascular Center
Amaro Palomo Eder Jonathan, Cortes Flores Claudia Galilea, Diaz Braiana, Araiza Diego, Arias-mendoza Alexandra, Martinez Rios Marco Antonio, Latapi Ruiz Esparza Ximena, Adib Gracia Anna Elisa, Garate Togo Javier, Sierra Lara Martinez Jorge Daniel, Hernandez-pastrana Sarai, Gonzalez Macedo Eder, Santiago Hernández Alberto, Neri Bale Raul Rodrigo
Atrial Fibrillation in Valvular Heart Disease: Assessing the Impact of Genetics in the UK BiobankCristin Luca, Tang Janet, Tastet Lionel, Marcus Gregory, Delling Francesca