Final ID: MP1495
Triglyceride in different ApoB-containing lipoproteins and risk of coronary artery disease: particle type matters
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Plasma triglyceride (TG), mostly embedded in apoB-containing particle (apoB-P), has been proposed as a potential residual risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). However, the atherogenicity of TG in different types of ApoB-P, especially the causality, remains unclear given that the per-particle atherogenicity varies among different types of apoB-P.
Research questions
To investigate the association TG content in various types of ApoB-P with the risk of coronary artery disease (CAD) in both observational and genetic study.
Methods
Observational study was conducted in 169 301 UK Biobank participants with complete nuclear magnetic resonance lipoprotein profiling data and without a history of ASCVD, diabetes, or lipid-lowering therapy. Multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression was used to determine the association between TG levels in different apoB-P and risk of incident CAD. Genetic study was performed using individual-level data from 472 495 UK Biobank participants of European ancestry. One-sample mendelian randomization (MR) was performed with weighted polygenic scores as instrumental variables, which were calculated with genetic variants strongly associated with TG in various subfractions of ApoB-P.
Results
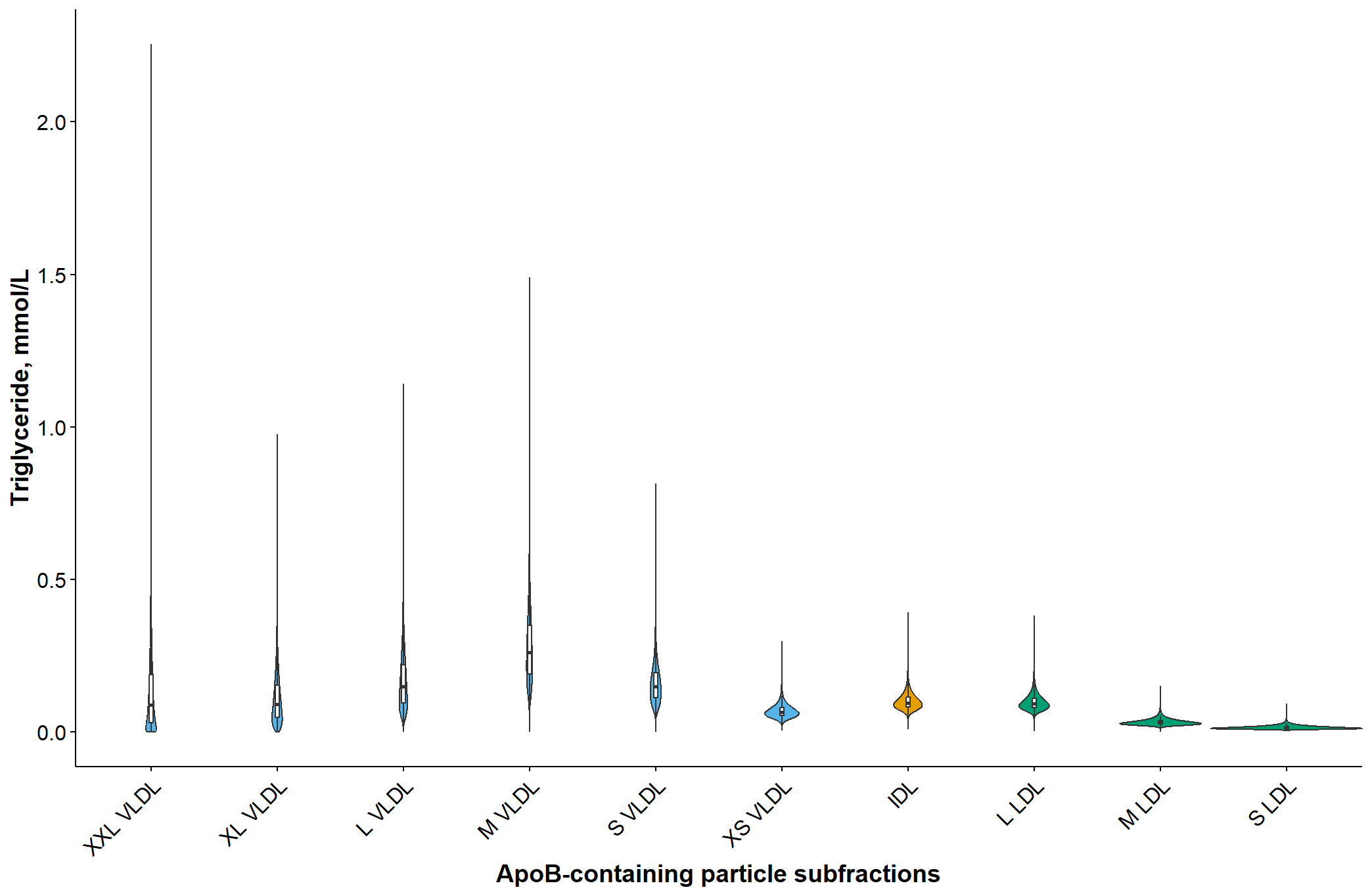
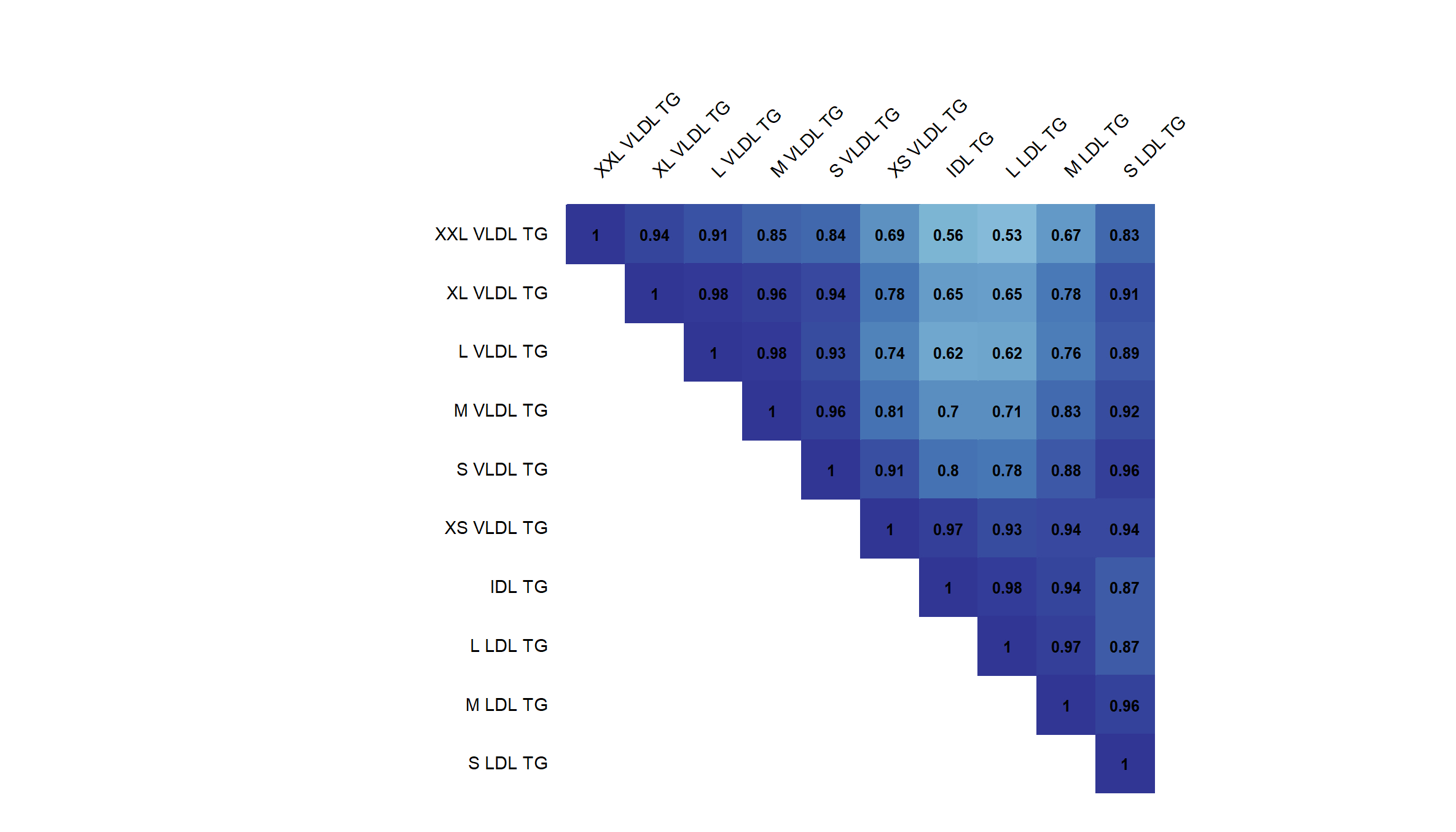
In the observational study, very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) TG (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] per one standard deviation [SD], 1.04; 95% CI, 1.02 - 1.06), intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL) TG (aHR per one SD, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.08-1.12) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) TG (aHR per one SD, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.07-1.11) were each individually associated with incident CAD. When subfractions of apoB-P were taken into account, the aHR were higher with TG in smaller size VLDL, ranging from 1.03 (95% CI, 1.01 - 1.05) for extra extra large VLDL TG to 1.08 (95% CI, 1.06 - 1.10) for extra small VLDL TG, whereas lower with TG in smaller size LDL, ranging from 1.06 (95% CI, 1.04 - 1.08) for small LDL TG to 1.10 (95% CI, 1.08 - 1.12) for large LDL TG. In one-sample MR, odds ratios (95% CI) per one SD higher genetically predicted VLDL TG, IDL TG, and LDL TG were 1.16 (1.12 - 1.21), 1.34 (1.29 - 1.39), and 1.37 (1.32 - 1.42) for CAD, respectively.
Conclusions
The atherogenicity of both observed and genetically determined TG in apoB-P differs with regard to different particle size. The present observation reinforced the atherogenic mechanism of different apoB-P and shed light on critical target of TG-lowering strategy.
Plasma triglyceride (TG), mostly embedded in apoB-containing particle (apoB-P), has been proposed as a potential residual risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). However, the atherogenicity of TG in different types of ApoB-P, especially the causality, remains unclear given that the per-particle atherogenicity varies among different types of apoB-P.
Research questions
To investigate the association TG content in various types of ApoB-P with the risk of coronary artery disease (CAD) in both observational and genetic study.
Methods
Observational study was conducted in 169 301 UK Biobank participants with complete nuclear magnetic resonance lipoprotein profiling data and without a history of ASCVD, diabetes, or lipid-lowering therapy. Multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression was used to determine the association between TG levels in different apoB-P and risk of incident CAD. Genetic study was performed using individual-level data from 472 495 UK Biobank participants of European ancestry. One-sample mendelian randomization (MR) was performed with weighted polygenic scores as instrumental variables, which were calculated with genetic variants strongly associated with TG in various subfractions of ApoB-P.
Results
In the observational study, very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) TG (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] per one standard deviation [SD], 1.04; 95% CI, 1.02 - 1.06), intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL) TG (aHR per one SD, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.08-1.12) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) TG (aHR per one SD, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.07-1.11) were each individually associated with incident CAD. When subfractions of apoB-P were taken into account, the aHR were higher with TG in smaller size VLDL, ranging from 1.03 (95% CI, 1.01 - 1.05) for extra extra large VLDL TG to 1.08 (95% CI, 1.06 - 1.10) for extra small VLDL TG, whereas lower with TG in smaller size LDL, ranging from 1.06 (95% CI, 1.04 - 1.08) for small LDL TG to 1.10 (95% CI, 1.08 - 1.12) for large LDL TG. In one-sample MR, odds ratios (95% CI) per one SD higher genetically predicted VLDL TG, IDL TG, and LDL TG were 1.16 (1.12 - 1.21), 1.34 (1.29 - 1.39), and 1.37 (1.32 - 1.42) for CAD, respectively.
Conclusions
The atherogenicity of both observed and genetically determined TG in apoB-P differs with regard to different particle size. The present observation reinforced the atherogenic mechanism of different apoB-P and shed light on critical target of TG-lowering strategy.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Role for Lipoprotein(a) in Potentiating Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation
Mouawad Sahar, Boffa Michael, Koschinsky Marlys
A Multi-Population-First Approach Leveraging UK Biobank (UKBB) and All of Us (AoU) Datasets Reveals Higher Cardiomyopathy Variant Burden in Individuals with MyocarditisGurumoorthi Manasa, Khanji Mohammed, Munroe Patricia, Petersen Steffen, Landstrom Andrew, Chahal Anwar, Hesse Kerrick, Asatryan Babken, Shah Ravi, Sharaf Dabbagh Ghaith, Wolfe Rachel, Shyam Sundar Vijay, Mohiddin Saidi, Aung Nay