Final ID: Su2088
Derivation and Validation of a Machine Learning Approach for Preeclampsia Phenotyping
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Preeclampsia is a heterogeneous disorder, with emerging evidence indicating the presence of multiple phenotypes. Identifying distinct clinical phenotypes may facilitate precise therapies and improve the clinical outcomes. This study aims to identify and validate preeclampsia phenotypes using machine learning and evaluate their associations with adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Hypothesis: Machine learning-based clustering methods applied to routinely-collected clinical variables can identify distinct preeclampsia phenotypes, each associated with unique clinical profiles and differential risks of adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Methods: In the derivation cohort (n=2,386), phenotypes were derived using k-means clustering applied to 26 routinely-collected clinical variables. A machine learning classifier incorporating key biomarkers was developed and externally validated to assign phenotypes within the validation cohort (n=1,570). Biological markers, clinical outcomes (primary outcome: composite of small for gestational age [SGA], preterm delivery, stillbirth, and neonatal death), and heterogenous impacts of delivery timing in term preeclampsia were analyzed across phenotypes.
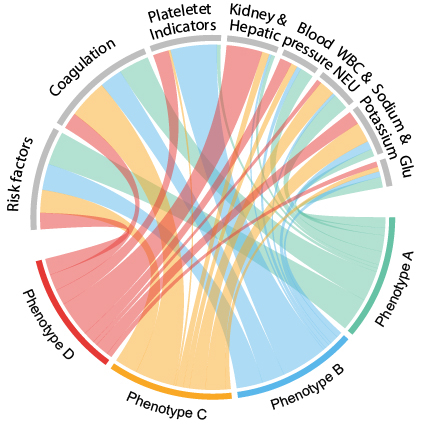
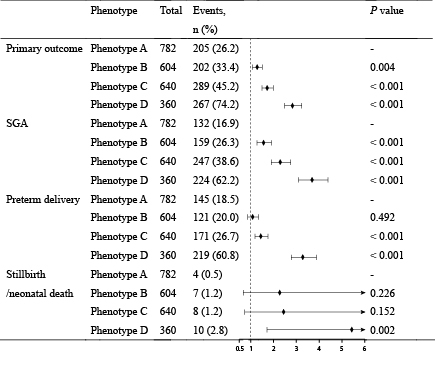
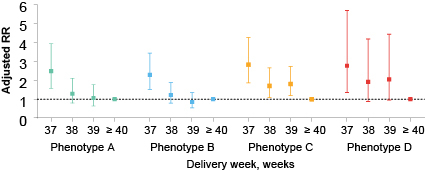
Results: Four distinct phenotypes were identified in the derivation cohort. Phenotype A exhibited hypocoagulation, while Phenotype B displayed relative thrombocytopenia. Phenotype C demonstrated hypercoagulation, and Phenotype D presented with hepatic and renal dysfunction, elevated potassium, and coagulation abnormalities. These findings were replicated in the validation cohort. Compared with Phenotype A, Phenotype D had the highest risk for the primary outcome (relative risk [RR] 2.83, 95% CI 2.48–3.23, P < 0.001), followed by Phenotypes C (RR 1.72, 95% CI 1.49–1.99) and B (RR 1.28, 95% CI 1.08–1.50). In term preeclampsia, delivery at 37 weeks increased adverse outcome risks relative to after 40 weeks in Phenotypes A, B, and D; Phenotype C exhibited elevated risks from 37–39 weeks.
Conclusion: Four clinical phenotypes of preeclampsia were identified by using routinely-collected health data, each characterized by unique maternal feature profiles and associated with varying fetal outcomes. These phenotypes reflect diverse underlying pathophysiological processes, and may inform individualized decisions regarding delivery timing. Machine learning-based phenotyping represents a promising strategy to advance precision obstetrics and improve the understanding and management of preeclampsia.
Hypothesis: Machine learning-based clustering methods applied to routinely-collected clinical variables can identify distinct preeclampsia phenotypes, each associated with unique clinical profiles and differential risks of adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Methods: In the derivation cohort (n=2,386), phenotypes were derived using k-means clustering applied to 26 routinely-collected clinical variables. A machine learning classifier incorporating key biomarkers was developed and externally validated to assign phenotypes within the validation cohort (n=1,570). Biological markers, clinical outcomes (primary outcome: composite of small for gestational age [SGA], preterm delivery, stillbirth, and neonatal death), and heterogenous impacts of delivery timing in term preeclampsia were analyzed across phenotypes.
Results: Four distinct phenotypes were identified in the derivation cohort. Phenotype A exhibited hypocoagulation, while Phenotype B displayed relative thrombocytopenia. Phenotype C demonstrated hypercoagulation, and Phenotype D presented with hepatic and renal dysfunction, elevated potassium, and coagulation abnormalities. These findings were replicated in the validation cohort. Compared with Phenotype A, Phenotype D had the highest risk for the primary outcome (relative risk [RR] 2.83, 95% CI 2.48–3.23, P < 0.001), followed by Phenotypes C (RR 1.72, 95% CI 1.49–1.99) and B (RR 1.28, 95% CI 1.08–1.50). In term preeclampsia, delivery at 37 weeks increased adverse outcome risks relative to after 40 weeks in Phenotypes A, B, and D; Phenotype C exhibited elevated risks from 37–39 weeks.
Conclusion: Four clinical phenotypes of preeclampsia were identified by using routinely-collected health data, each characterized by unique maternal feature profiles and associated with varying fetal outcomes. These phenotypes reflect diverse underlying pathophysiological processes, and may inform individualized decisions regarding delivery timing. Machine learning-based phenotyping represents a promising strategy to advance precision obstetrics and improve the understanding and management of preeclampsia.
More abstracts on this topic:
3D Statistical Shape Analysis Predicts Type A Aortic Dissection Better Than Aortic Diameters
Marway Prabhvir, Campello Jorge Carlos Alberto, Wagner Catherine, Baker Timothy, Burris Nicholas
Adrenal Zona Glomerulosa Long Form Leptin Receptor (LepRb) Protects from Leptin-Mediated Vascular Disorders in Female MiceOno Yoichi, Kennard Simone, Breault David, Belin De Chantemele Eric