Final ID: MP285
Association of Angiotensin Receptor-Neprilysin Inhibitor Initiation With Mortality and Organ Failure Post Non-Acute Myocardial Infarction Cardiogenic Shock: A Multicenter Propensity Matched Retrospective Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Non-acute myocardial infarction (non-AMI) cardiogenic shock (CS) confers high mortality despite advances in therapy. Angiotensin Receptor-Neprilysin Inhibitor (ARNI) is known to improve outcomes in chronic heart failure, but its impact in non-AMI CS remains undefined.
Methods:
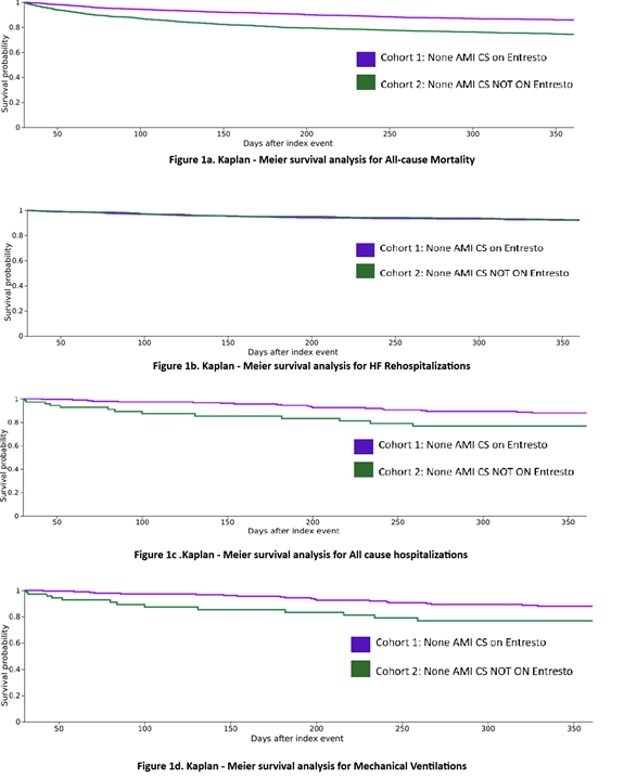
Our retrospective cohort study used the TriNetX US Collaborative Network to identify adult patients (≥18 years) with non-AMI CS receiving ARNI within 7 to 30 days of index admission between July 2015 and May 2024. We performed a 1:1 propensity-matched (PSM) analysis and evaluated the primary outcome: all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes were all-cause and heart failure hospitalization, hemodialysis (HD) initiation, mechanical ventilation (MV), and stroke/transient ischemic attack (TIA). Kaplan-Meier curves were compared by log-rank test, and hazard ratios (HRs) were estimated via Cox proportional hazards models (Figure 1).
Results:
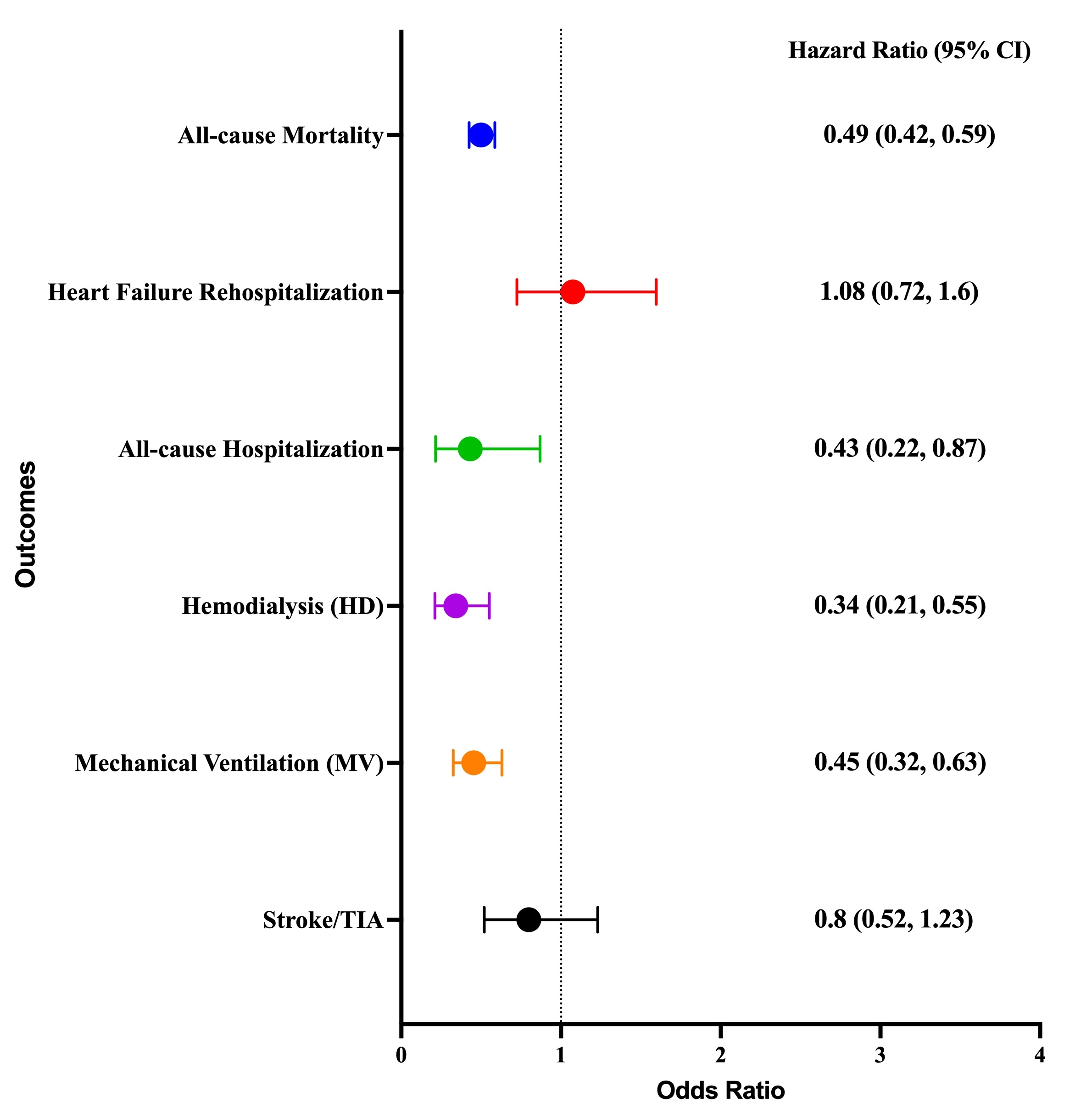
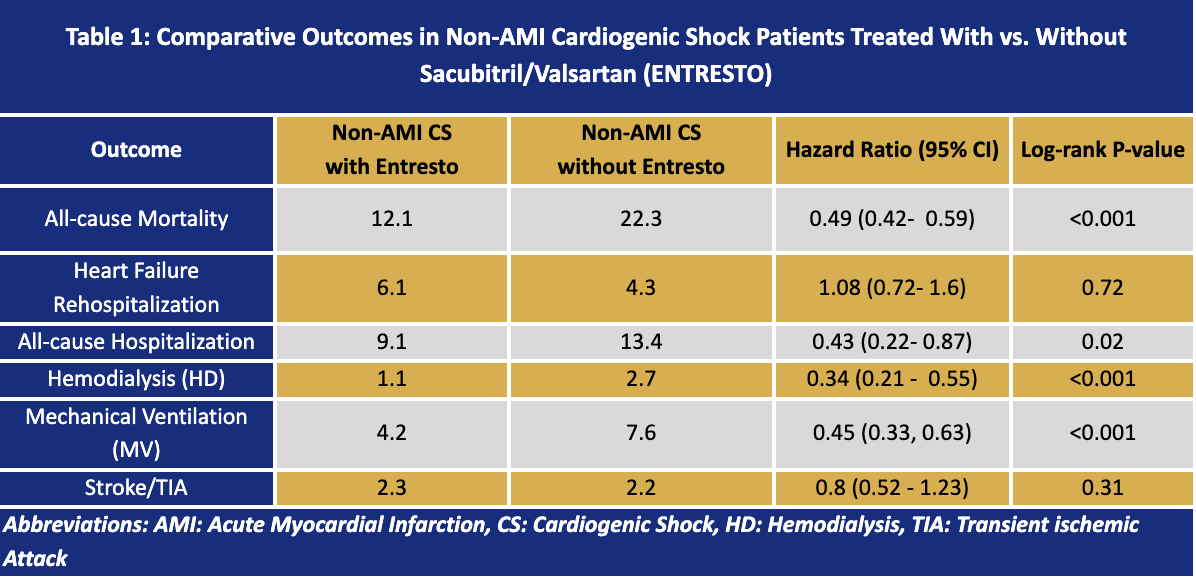
Of 180,498 patients with CS, 65.8% were non-AMI CS (ARNI group, N = 2,640, and No ARNI, N = 79,350). Patients in the ARNI groups were younger (60.2 vs 63 years), male (66.3% vs 57.4%), and of the Black (24.6% vs 18.0%) ethnicity (all p<0.001). In the propensity-matched cohort, ARNI was associated with a lower incidence of 1-year all-cause mortality (12.1% vs. 22.3%, HR 0.49; 95% CI 0.42–0.59; p < 0.001), lower rates of all-cause rehospitalization (9.1% vs. 13.4%; HR 0.43; 95% CI 0.22-0.87; p 0.015), and a significant reduction in HD initiation (3.5% vs. 10.0%; HR 0.34; 95% CI 0.21–0.55; p < 0.001). The risks of heart failure rehospitalization and strokes were similar.
Conclusions:
In our PSM of non-AMI CS patients, ARNI therapy was associated with a marked reduction in 1-year all-cause mortality and a significant reduction in all-cause hospitalizations, mechanical ventilation, and HD initiation with comparable risk of HF rehospitalizations or stroke/TIA. These findings suggest that early initiation of neurohormonal therapy may confer meaningful survival benefits in cardiogenic shock beyond ischemic etiologies.
Non-acute myocardial infarction (non-AMI) cardiogenic shock (CS) confers high mortality despite advances in therapy. Angiotensin Receptor-Neprilysin Inhibitor (ARNI) is known to improve outcomes in chronic heart failure, but its impact in non-AMI CS remains undefined.
Methods:
Our retrospective cohort study used the TriNetX US Collaborative Network to identify adult patients (≥18 years) with non-AMI CS receiving ARNI within 7 to 30 days of index admission between July 2015 and May 2024. We performed a 1:1 propensity-matched (PSM) analysis and evaluated the primary outcome: all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes were all-cause and heart failure hospitalization, hemodialysis (HD) initiation, mechanical ventilation (MV), and stroke/transient ischemic attack (TIA). Kaplan-Meier curves were compared by log-rank test, and hazard ratios (HRs) were estimated via Cox proportional hazards models (Figure 1).
Results:
Of 180,498 patients with CS, 65.8% were non-AMI CS (ARNI group, N = 2,640, and No ARNI, N = 79,350). Patients in the ARNI groups were younger (60.2 vs 63 years), male (66.3% vs 57.4%), and of the Black (24.6% vs 18.0%) ethnicity (all p<0.001). In the propensity-matched cohort, ARNI was associated with a lower incidence of 1-year all-cause mortality (12.1% vs. 22.3%, HR 0.49; 95% CI 0.42–0.59; p < 0.001), lower rates of all-cause rehospitalization (9.1% vs. 13.4%; HR 0.43; 95% CI 0.22-0.87; p 0.015), and a significant reduction in HD initiation (3.5% vs. 10.0%; HR 0.34; 95% CI 0.21–0.55; p < 0.001). The risks of heart failure rehospitalization and strokes were similar.
Conclusions:
In our PSM of non-AMI CS patients, ARNI therapy was associated with a marked reduction in 1-year all-cause mortality and a significant reduction in all-cause hospitalizations, mechanical ventilation, and HD initiation with comparable risk of HF rehospitalizations or stroke/TIA. These findings suggest that early initiation of neurohormonal therapy may confer meaningful survival benefits in cardiogenic shock beyond ischemic etiologies.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Steroid-Refractory Immune-checkpoint-inhibitor Induced Myocarditis Responsive to Mycophenolate and Anti-thymocyte globulin
Dabdoub Jorge, Wilson Michael, Gottbrecht Matthew, Salazar Ryan, Shih Jeffrey
Assessing the Knowledge and Perception of Hypertension Among Patients in a Cardiology ClinicKhurshid Fatima, Owais Muhammad, Tahir Dar Iqra, Siddique Absar, Khurshid Ayesha, Eltawansy Sherif