Final ID: Mo4075
Deep Learning-based OCT-FLIm Imaging for Quantitative Assessment of Plaque Compositions
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLIm) integrated with optical coherence tomography (OCT) enables compositional assessment of atherosclerotic plaques. However, the lack of histopathological validation for complex multi-channel FLIm signals limits their clinical applicability. We hypothesized that a deep learning based OCT-FLIm imaging of fresh human coronary specimens could accurately and quantitatively derive composition-specific fluorescence lifetime profiles.
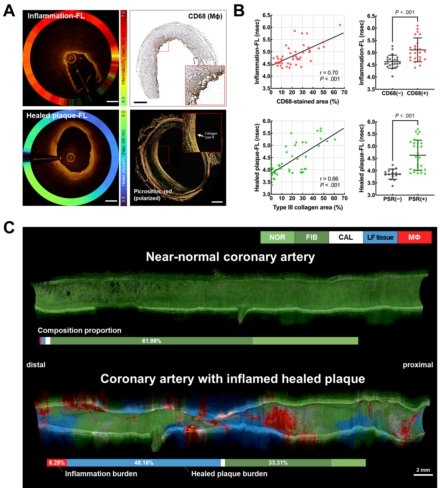
Method and results: In 24 vessels from eight explanted human transplanted hearts from donors with coronary artery disease, OCT-FLIm imaging was performed. Regions of interest (ROIs) were ink-marked and prepared as 5 µm-thick paraffin sections. Ground-truth labels were established through immunohistochemical (IHC) staining using composition-specific markers. OCT images were used to guide pixel-level co-registration between FLIm signals and histological sections. Within each ROI, averaged fluorescence lifetime values were compared with corresponding IHC results, revealing significant associations between lifetime profiles and key plaque compositions (macrophages, loose fibrous tissue, lipid, and calcifications, p < 0.01). Quantitative analysis using IHC staining intensity demonstrated a strong linear relationship with the corresponding fluorescence lifetime values (r > 0.8). The validated associations were used to train a deep learning model for quantitative compositional analysis of OCT-FLIm images. The model was validated on independent coronary samples, demonstrating over 90% classification accuracy across all plaque compositions. Quantitative predictions closely matched IHC-based compositional measurements, with correlation coefficients of >0.8 for each tissue type.
Conclusion: OCT-FLIm imaging with fresh coronary tissues validation enables precise mapping of fluorescence lifetime signatures across atherosclerotic plaque key compositions. The strong correlation between FLIm signals and quantitative IHC measurements, together with the high accuracy achieved by the trained deep learning model, establishes a robust foundation for AI-driven plaque characterization and supports the clinical translation of OCT-FLIm multi-modal imaging for accurate, component-resolved assessment and personalized management of coronary artery disease.
Method and results: In 24 vessels from eight explanted human transplanted hearts from donors with coronary artery disease, OCT-FLIm imaging was performed. Regions of interest (ROIs) were ink-marked and prepared as 5 µm-thick paraffin sections. Ground-truth labels were established through immunohistochemical (IHC) staining using composition-specific markers. OCT images were used to guide pixel-level co-registration between FLIm signals and histological sections. Within each ROI, averaged fluorescence lifetime values were compared with corresponding IHC results, revealing significant associations between lifetime profiles and key plaque compositions (macrophages, loose fibrous tissue, lipid, and calcifications, p < 0.01). Quantitative analysis using IHC staining intensity demonstrated a strong linear relationship with the corresponding fluorescence lifetime values (r > 0.8). The validated associations were used to train a deep learning model for quantitative compositional analysis of OCT-FLIm images. The model was validated on independent coronary samples, demonstrating over 90% classification accuracy across all plaque compositions. Quantitative predictions closely matched IHC-based compositional measurements, with correlation coefficients of >0.8 for each tissue type.
Conclusion: OCT-FLIm imaging with fresh coronary tissues validation enables precise mapping of fluorescence lifetime signatures across atherosclerotic plaque key compositions. The strong correlation between FLIm signals and quantitative IHC measurements, together with the high accuracy achieved by the trained deep learning model, establishes a robust foundation for AI-driven plaque characterization and supports the clinical translation of OCT-FLIm multi-modal imaging for accurate, component-resolved assessment and personalized management of coronary artery disease.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Measure of Residential Segregation and Thrombo-inflammation in Black and White Americans
Manogaran Erin, Cushman Mary, Kamin Mukaz Debora, Sparks Andrew, Packer Ryan, Brochu Paige, Judd Suzanne, Howard Virginia, Plante Timothy, Long Leann, Cheung Katherine
Blood Pressure Magnitude as a Modulator of Perivascular Adipose Tissue Fibrotic ResponseRendon C. Javier, Lefkowitz Rebecca, Garver Hannah, Lauver Adam, Fink Gregory, Krieger-burke Teresa, Watts Stephanie, Contreras Andres