Final ID: MP345
Effectiveness of Nifedipine Versus Labetalol for Postpartum Hypertension Control: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Postpartum hypertensive disorders are a major cause of maternal mortality and hospital readmission. If untreated, elevated blood pressure can lead to complications such as eclampsia, stroke, and pulmonary edema. Labetalol, a combined α- and β-blocker, and nifedipine, a calcium channel blocker, are widely used oral agents for managing postpartum hypertension.
Hypothesis
To compare the efficacy and safety of nifedipine versus labetalol in managing postpartum hypertension.
Methods
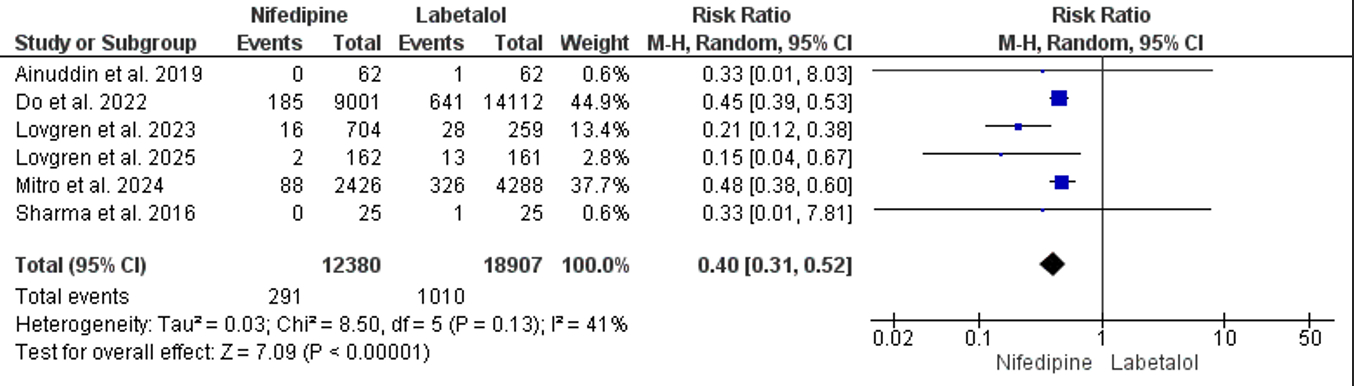
A systematic review of PubMed, Google Scholar, and the Cochrane Library identified eight studies involving 31,436 patients (12,479 treated with nifedipine; 18,957 treated with labetalol). All randomized controlled trials and observational studies comparing nifedipine and labetalol in postpartum women were included. The primary outcome was hospital readmission. Secondary outcomes included time to blood pressure control, discharge on initial dose, and adverse effects, which included constipation, flushing, and headache. Dichotomous data were analyzed using risk ratios (RRs), and continuous data were assessed using mean differences (MDs) with their respective 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs). Statistical analysis was performed using Review Manager (RevMan) version 5.4.1. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Nifedipine significantly reduced the risk of readmission compared to labetalol (RR = 0.40, 95% CI [0.31, 0.52]; P < 0.00001). No significant differences were found in time to blood pressure control (MD = –0.68, 95% CI [–2.20, 0.84]; P = 0.38), discharge on initial medication (RR = 0.78, 95% CI [0.45, 1.34]; P = 0.37), or incidence of adverse effects.
Conclusion
Nifedipine was associated with lower readmission risk than labetalol, with comparable efficacy and safety in postpartum hypertension management.
Keywords:
Nifedipine, Labetalol, Postpartum hypertension, Oral antihypertensive
Postpartum hypertensive disorders are a major cause of maternal mortality and hospital readmission. If untreated, elevated blood pressure can lead to complications such as eclampsia, stroke, and pulmonary edema. Labetalol, a combined α- and β-blocker, and nifedipine, a calcium channel blocker, are widely used oral agents for managing postpartum hypertension.
Hypothesis
To compare the efficacy and safety of nifedipine versus labetalol in managing postpartum hypertension.
Methods
A systematic review of PubMed, Google Scholar, and the Cochrane Library identified eight studies involving 31,436 patients (12,479 treated with nifedipine; 18,957 treated with labetalol). All randomized controlled trials and observational studies comparing nifedipine and labetalol in postpartum women were included. The primary outcome was hospital readmission. Secondary outcomes included time to blood pressure control, discharge on initial dose, and adverse effects, which included constipation, flushing, and headache. Dichotomous data were analyzed using risk ratios (RRs), and continuous data were assessed using mean differences (MDs) with their respective 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs). Statistical analysis was performed using Review Manager (RevMan) version 5.4.1. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Nifedipine significantly reduced the risk of readmission compared to labetalol (RR = 0.40, 95% CI [0.31, 0.52]; P < 0.00001). No significant differences were found in time to blood pressure control (MD = –0.68, 95% CI [–2.20, 0.84]; P = 0.38), discharge on initial medication (RR = 0.78, 95% CI [0.45, 1.34]; P = 0.37), or incidence of adverse effects.
Conclusion
Nifedipine was associated with lower readmission risk than labetalol, with comparable efficacy and safety in postpartum hypertension management.
Keywords:
Nifedipine, Labetalol, Postpartum hypertension, Oral antihypertensive
More abstracts on this topic:
Beta blockers and calcium channel blockers in pre-symptomatic patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: prevalence, discontinuation, and effectiveness
Bradlow William, Sehnert Amy, Bastien Arnaud, Blizard Perry, Ripoll-vera Tomas, Pericas Pau, Fudim Marat, Balu Suresh, Hintze Bradley, Salah Husam, Patel Manesh, Elgui Kevin, Foucher Aurelie, Charron Philippe, Klopfenstein Quentin, Balazard Felix, Trichelair Paul, Touzot Maxime, Micsinai Balan Mariann, Van Haelst Paul, Sandler Belinda
Acute Bilateral Breast Swelling as a Rare Manifestation of Heart Failure Exacerbation: A Case ReportMohyeldin Moiud, Anto Anandu, Hossain Muhammad