Final ID: Sa3049
Efficacy and Safety of Oral Anticoagulant Monotherapy vs. Dual Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation with Stable Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
In patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and stable ischemic heart disease, guidelines currently recommend oral anticoagulant (OAC) monotherapy over combination therapy with OAC and a single antiplatelet agent (SAPT). However, the comparative safety and efficacy of these strategies remain under-investigated.
Methods:
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies comparing OAC monotherapy to OAC + SAPT in patients with nonvalvular AF and stable CAD. Databases searched included PubMed, Google Scholar, Cochrane Library, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, and ClinicalTrials.gov. Outcomes assessed were all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, major adverse cardiac events (MACE), myocardial infarction (MI), stroke (ischemic and hemorrhagic), and various bleeding events.
Results:
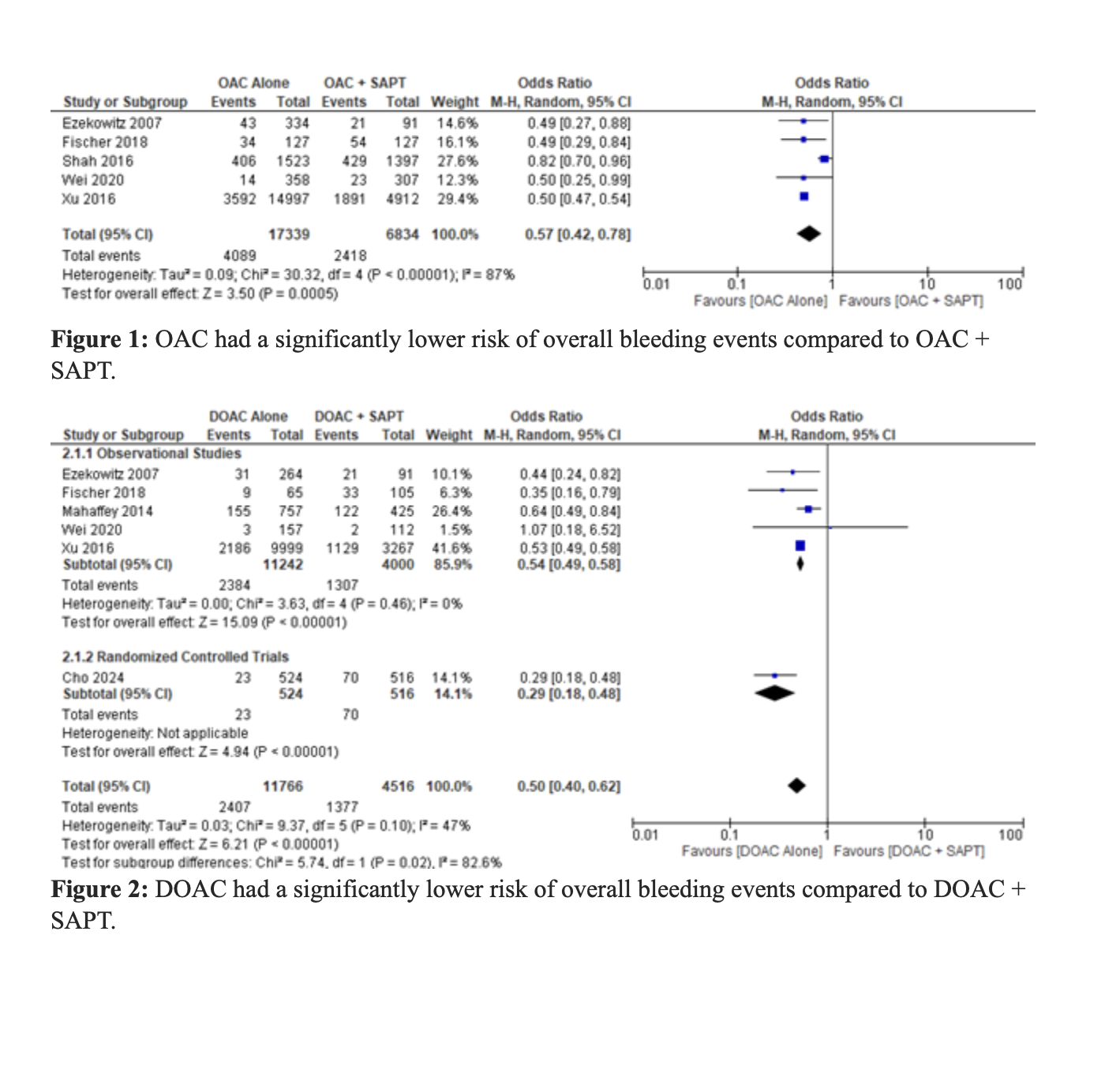
Twenty-three studies (3 RCTs, 20 observational), encompassing 51,396 patients (mean age 72.5 years, mean follow-up 4.8 years), were included. OAC monotherapy was associated with a significantly lower risk of overall bleeding compared to OAC + SAPT (OR 0.57, 95% CI 0.42–0.78; P=0.0005). DOAC monotherapy also significantly reduced the risk of overall bleeding compared to DOAC + SAPT [OR 0.50, 95% CI 0.40–0.62; P < 0.00001]. Among DOACs, apixaban provided the greatest reduction in overall bleeding events [OR 0.35, 95% CI 0.16–0.79; P=0.01]. OAC monotherapy was similarly effective in reducing the risk of major bleeding events compared to OAC + SAPT [OR 0.64, 95% CI 0.59–0.69; P < 0.00001], with DOACs showing a comparable benefit [OR 0.61, 95% CI 0.48–0.78; P < 0.0001]. Edoxaban showed the greatest reduction in major bleeding risk [OR 0.45, 95% CI 0.21–0.96; P=0.04]. OAC monotherapy also significantly reduced gastrointestinal bleeding (OR 0.61, P=0.003) and MI (OR 0.86, P=0.004), with edoxaban again demonstrating the greatest MI reduction (OR 0.67, P=0.004).While reductions in MACE were borderline significant (OR 0.82, P=0.02), DOAC monotherapy showed a similar trend (OR 0.71, P=0.03). There were no significant differences in all-cause or cardiovascular mortality, or stroke outcomes, between OAC monotherapy and combination therapy.
Conclusion:
OAC monotherapy offers superior bleeding and MI risk reduction compared to OAC + SAPT in patients with AF and stable CAD, with no increased risk of mortality or stroke. These findings support current guideline recommendations favoring OAC monotherapy in this population.
In patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and stable ischemic heart disease, guidelines currently recommend oral anticoagulant (OAC) monotherapy over combination therapy with OAC and a single antiplatelet agent (SAPT). However, the comparative safety and efficacy of these strategies remain under-investigated.
Methods:
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies comparing OAC monotherapy to OAC + SAPT in patients with nonvalvular AF and stable CAD. Databases searched included PubMed, Google Scholar, Cochrane Library, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, and ClinicalTrials.gov. Outcomes assessed were all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, major adverse cardiac events (MACE), myocardial infarction (MI), stroke (ischemic and hemorrhagic), and various bleeding events.
Results:
Twenty-three studies (3 RCTs, 20 observational), encompassing 51,396 patients (mean age 72.5 years, mean follow-up 4.8 years), were included. OAC monotherapy was associated with a significantly lower risk of overall bleeding compared to OAC + SAPT (OR 0.57, 95% CI 0.42–0.78; P=0.0005). DOAC monotherapy also significantly reduced the risk of overall bleeding compared to DOAC + SAPT [OR 0.50, 95% CI 0.40–0.62; P < 0.00001]. Among DOACs, apixaban provided the greatest reduction in overall bleeding events [OR 0.35, 95% CI 0.16–0.79; P=0.01]. OAC monotherapy was similarly effective in reducing the risk of major bleeding events compared to OAC + SAPT [OR 0.64, 95% CI 0.59–0.69; P < 0.00001], with DOACs showing a comparable benefit [OR 0.61, 95% CI 0.48–0.78; P < 0.0001]. Edoxaban showed the greatest reduction in major bleeding risk [OR 0.45, 95% CI 0.21–0.96; P=0.04]. OAC monotherapy also significantly reduced gastrointestinal bleeding (OR 0.61, P=0.003) and MI (OR 0.86, P=0.004), with edoxaban again demonstrating the greatest MI reduction (OR 0.67, P=0.004).While reductions in MACE were borderline significant (OR 0.82, P=0.02), DOAC monotherapy showed a similar trend (OR 0.71, P=0.03). There were no significant differences in all-cause or cardiovascular mortality, or stroke outcomes, between OAC monotherapy and combination therapy.
Conclusion:
OAC monotherapy offers superior bleeding and MI risk reduction compared to OAC + SAPT in patients with AF and stable CAD, with no increased risk of mortality or stroke. These findings support current guideline recommendations favoring OAC monotherapy in this population.
More abstracts on this topic:
Anticoagulation versus Antiplatelets Across Subgroups of Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source: A Meta-Analysis of Seven Randomized Controlled Trials
Ghannam Malik, Elkind Mitchell, Tirschwell David, Poli Sven, Kamel Hooman, Yaghi Shadi, Al-qudah Abdullah, Alshaer Qasem, Kronmal Richard, Ntaios George, Longstreth W, Furie Karen, Saver Jeffrey, Kasner Scott
Bivalirudin Reduces Major Bleeding And Cardiovascular Mortality in MI patients Undergoing PCI Compared to Unfractionated Heparin.Sharma Anubhuti, Panjiyar Binay, Sharma Arundhati, Daid Simranpreet Singh, Sanghvi Urja, Dantuluri Sahitya, Syed Saif, Senthil Velmurugan Isha, Seelam Laxmi Priya, Aryal Saurav