Final ID: MDP1218
Efficacy and Safety of Impella, Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation, and Intra-aortic Balloon Pump in Acute Myocardial Infarction- related Cardiogenic Shock: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Abstract:
Introduction:
Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) is being increasingly utilized for cardiogenic shock (CS). We compare the outcomes of using isolated mechanical circulatory support (MCS) versus Impella or intra-aortic baloon pump (IABP) for left ventricular unloading (LVU) in the context of VA-ECMO.
Methods:
We searched for Impella, VA-ECMO, and IABP utilization in acute myocardial infarction (MI) related cardiogenic shock. Primary outcomes included 30-day and 12-month mortality rates, major bleeding, and limb ischemia. Secondary outcomes were occurrence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and stroke. Data analysis utilized frequentist network meta-analysis with random-effects models, calculating odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results:
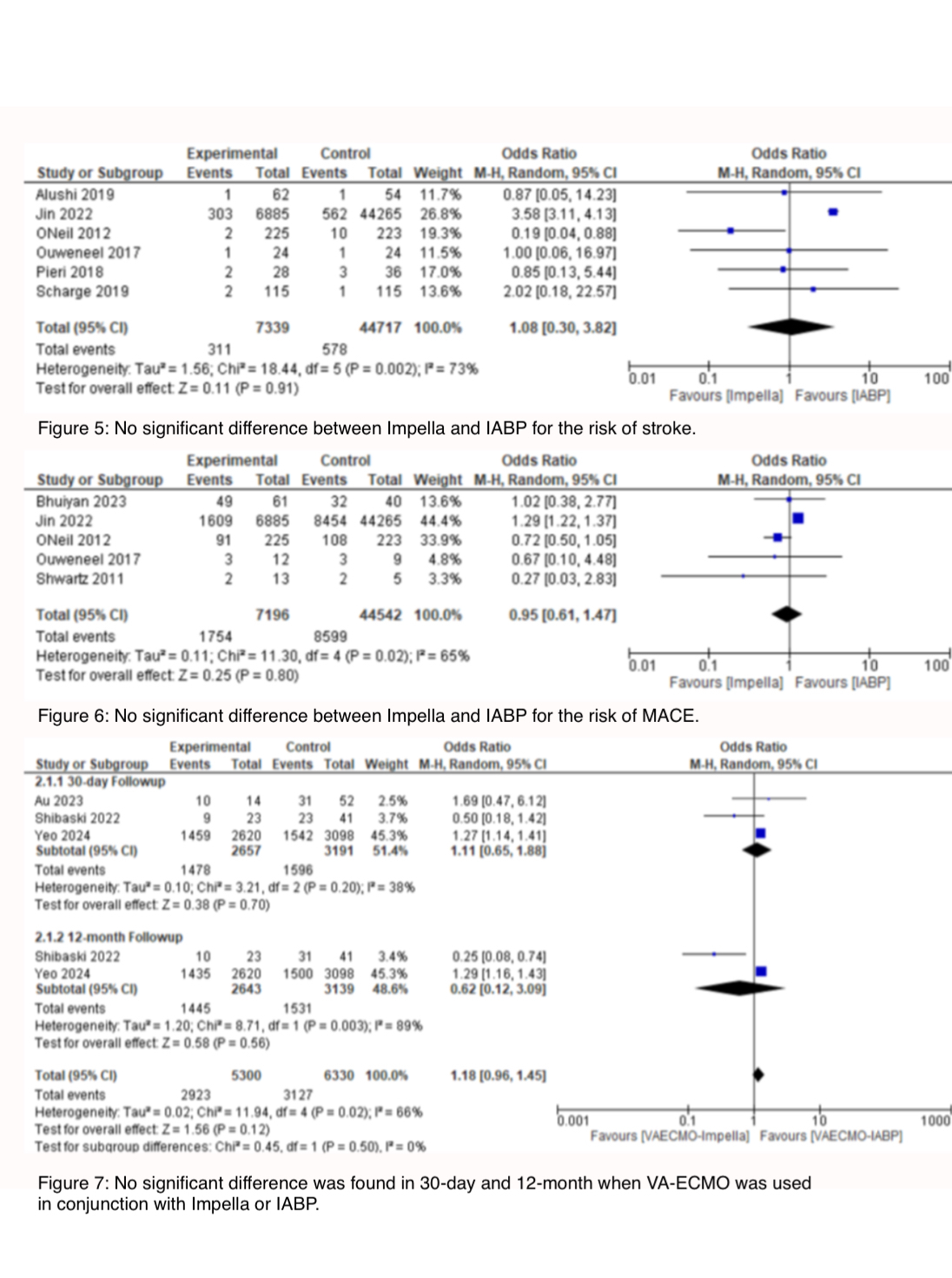
We identified 22 studies, including 4 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and 18 observational studies, involving a total of 79,149 participants. The average follow-up duration for these studies was 11 months, and the mean age of the included patients was 63 years. Regarding the 30-day mortality rate, IABP alone demonstrated a significant reduction compared to Impella and VA-ECMO [OR 0.54, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.72]. On the other hand, Impella alone exhibited the lowest 12-month mortality rate [OR 0.66, 95% CI 0.51 to 0.85]. Regarding complications, IABP showed a significantly lower risk of major bleeding [OR 0.29, 95% CI 0.14 to 0.61] and limb ischemia [OR 0.14, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.47] when compared to VA-ECMO and Impella. However, no significant difference was observed in the occurrence of stroke and MACE between Impella and IABP. Furthermore, there was no significant difference in the 30-day or 12-month mortality rate when VA-ECMO was combined with IABP or Impella.
Conclusion:
Impella offers significant long-term survival benefits, while IABP excels in short-term survival outcomes and reduces bleeding and thrombotic events with no significant difference in stroke and MACE risk.
Introduction:
Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) is being increasingly utilized for cardiogenic shock (CS). We compare the outcomes of using isolated mechanical circulatory support (MCS) versus Impella or intra-aortic baloon pump (IABP) for left ventricular unloading (LVU) in the context of VA-ECMO.
Methods:
We searched for Impella, VA-ECMO, and IABP utilization in acute myocardial infarction (MI) related cardiogenic shock. Primary outcomes included 30-day and 12-month mortality rates, major bleeding, and limb ischemia. Secondary outcomes were occurrence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and stroke. Data analysis utilized frequentist network meta-analysis with random-effects models, calculating odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results:
We identified 22 studies, including 4 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and 18 observational studies, involving a total of 79,149 participants. The average follow-up duration for these studies was 11 months, and the mean age of the included patients was 63 years. Regarding the 30-day mortality rate, IABP alone demonstrated a significant reduction compared to Impella and VA-ECMO [OR 0.54, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.72]. On the other hand, Impella alone exhibited the lowest 12-month mortality rate [OR 0.66, 95% CI 0.51 to 0.85]. Regarding complications, IABP showed a significantly lower risk of major bleeding [OR 0.29, 95% CI 0.14 to 0.61] and limb ischemia [OR 0.14, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.47] when compared to VA-ECMO and Impella. However, no significant difference was observed in the occurrence of stroke and MACE between Impella and IABP. Furthermore, there was no significant difference in the 30-day or 12-month mortality rate when VA-ECMO was combined with IABP or Impella.
Conclusion:
Impella offers significant long-term survival benefits, while IABP excels in short-term survival outcomes and reduces bleeding and thrombotic events with no significant difference in stroke and MACE risk.
More abstracts on this topic:
Admission Acid-Base Status and Mortality in Cardiac Intensive Care Unit Patients
Canova Tyler, Lipps Kirsten, Hillerson Dustin, Kashani Kianoush, Dahiya Garima, Jentzer Jacob
A Contactless and Automated Approach to the Acute Stroke AssessmentSaadat Moh, Titus Ryan, Verkuilen Haley, Fleming Phil, Sur Sanjib, Sen Souvik